Permeability Evaluation from Logs based on Classification and Optimization of Flow Unit in Tight Sandstone
-
摘要:
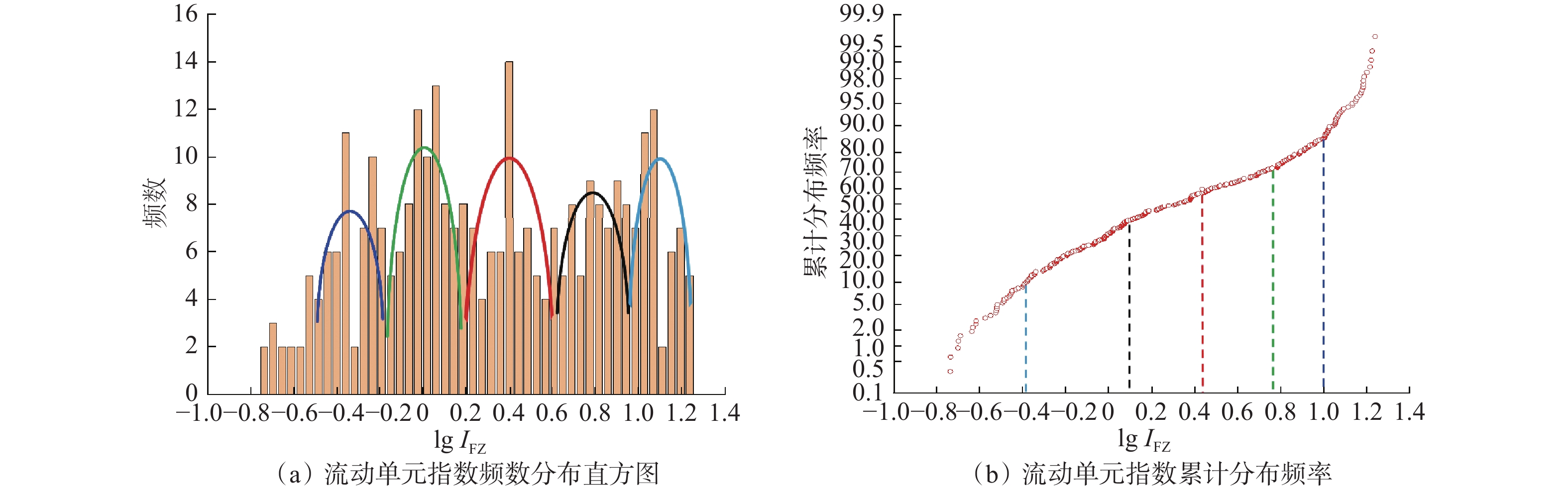
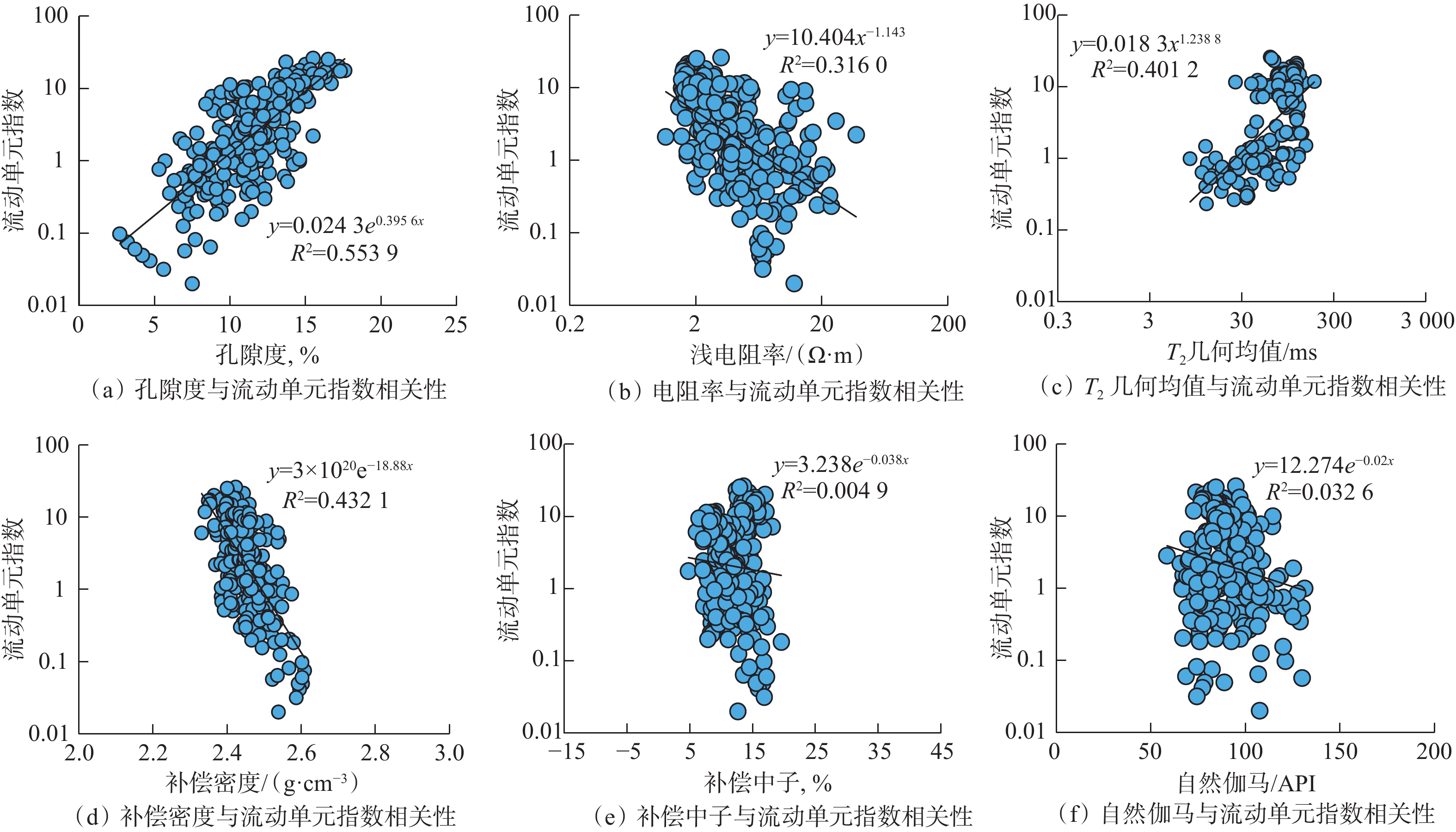
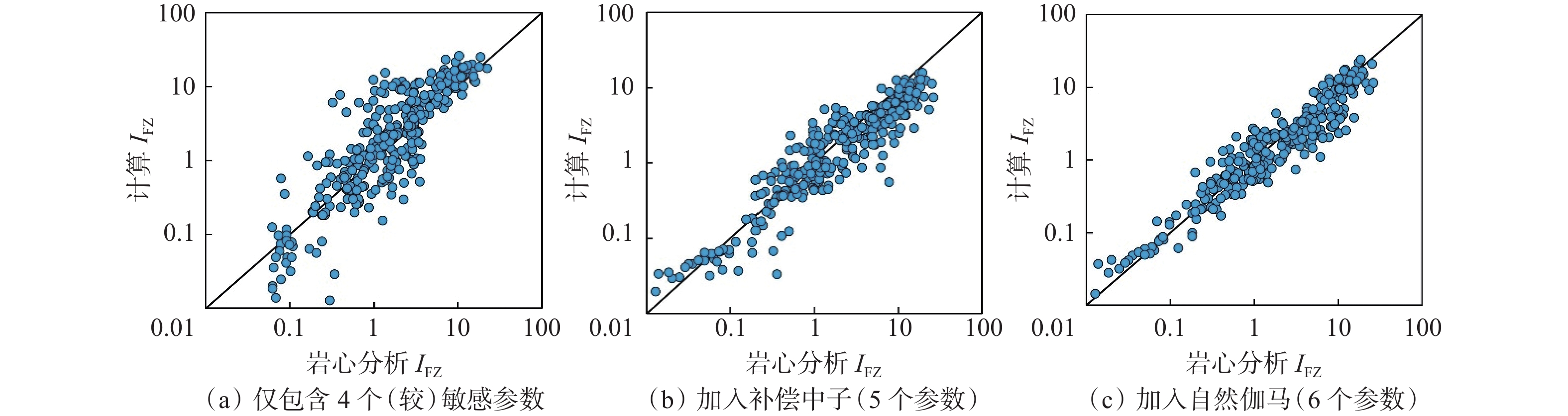
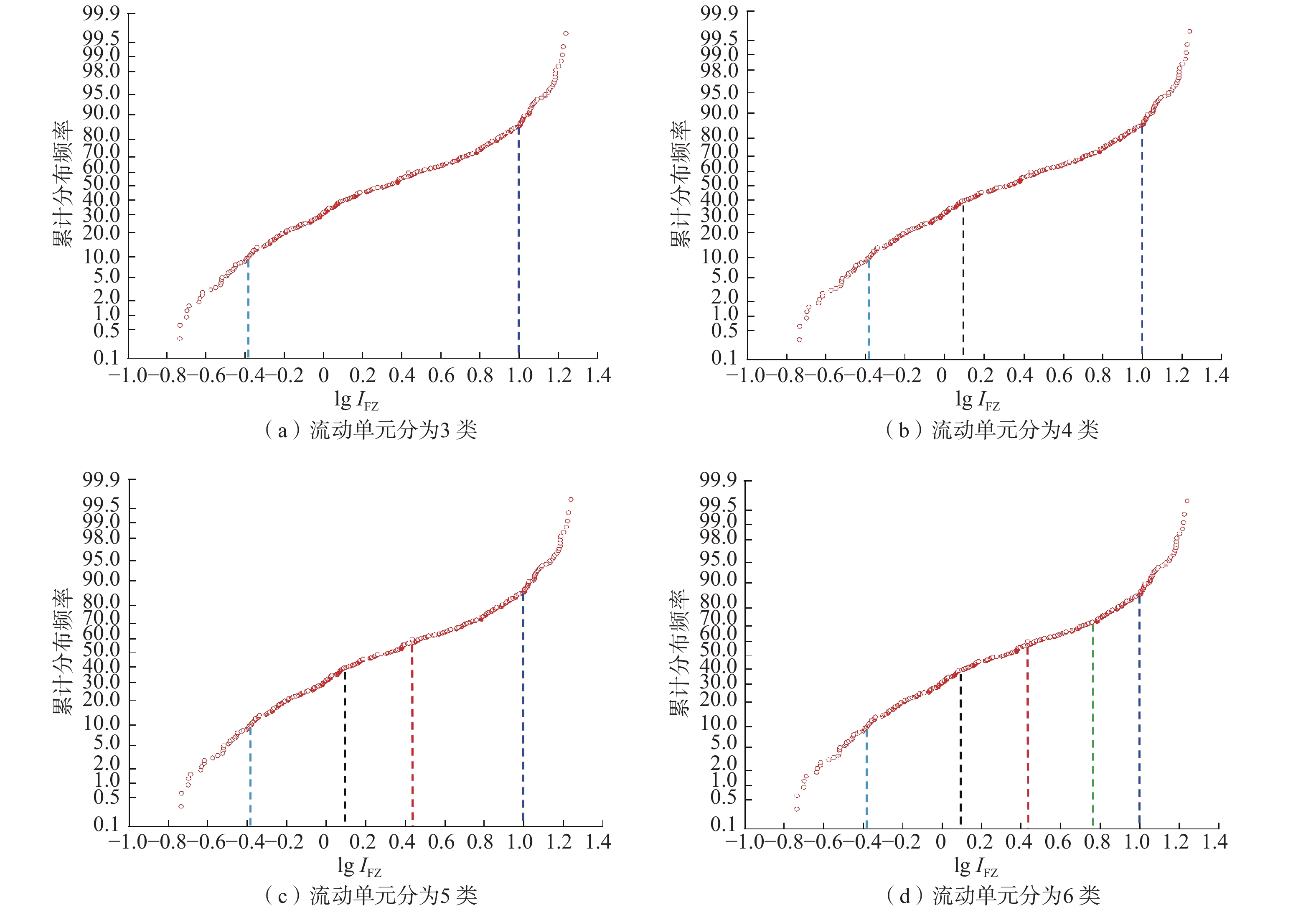
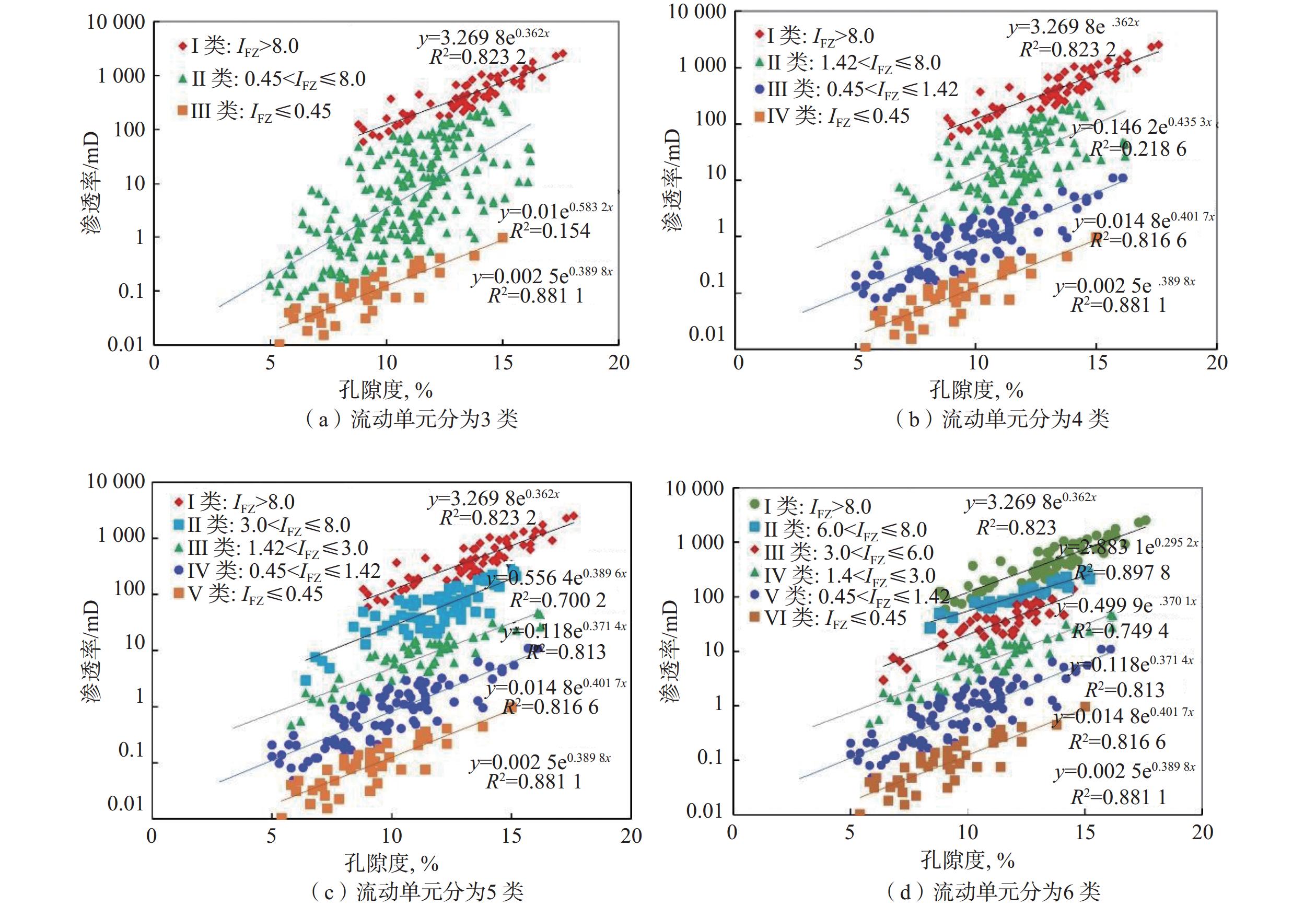
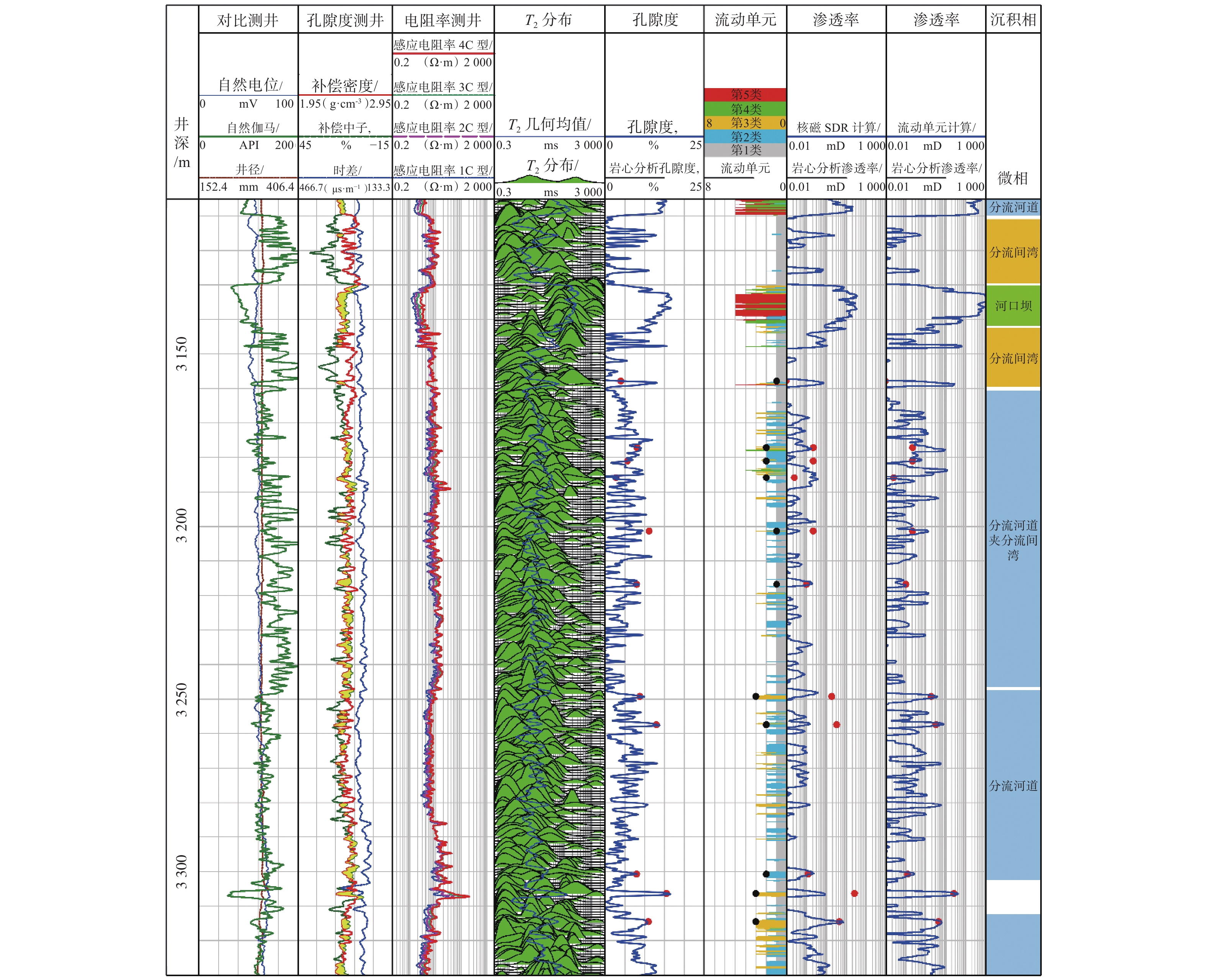
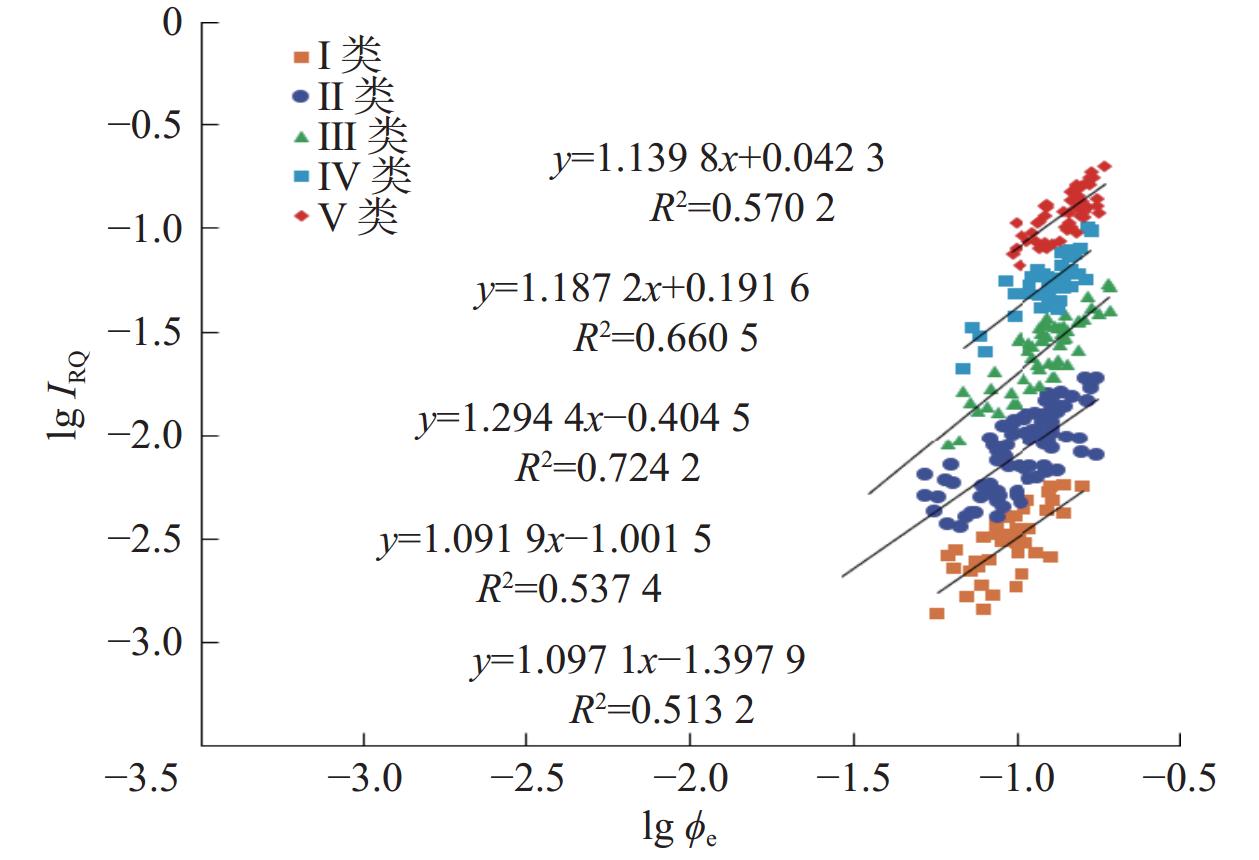
致密砂岩储层非均质性强,常规测井解释模型没有考虑储层纵向上渗流特征的差异性,导致渗透率解释精度低。为此,采用储层流动单元描述致密砂岩储层非均质特征,建立了具有不同渗流单元的渗透率解释模型,以提高渗透率预测精度。首先,结合岩心实验流动单元指数频数分布与累计分布频率,建立流动单元分类标准,并优选流动单元分类数目,分类构建渗透率模型;然后,引入深度神经网络,结合常规测井和核磁测井数据,预测流动单元指数;最后,基于分类渗透率解释模型,计算储层渗透率。珠江口盆地惠州凹陷古近系恩平组应用该渗透率计算方法进行计算,流动单元分为5类最佳,测井尺度的流动单元识别分类与沉积相具有较好的一致性,渗透率计算准确度相比核磁模型明显提高。研究结果为深层致密砂岩储层渗透率评价提供了新的计算方法。
Abstract:Conventional log interpretation models usually overlook the longitudinal flow properties due to the heterogeneity of tight sandstone reservoirs, leading to low accuracy in permeability interpretation. Therefore, the flow units (FU) are utilized to describe the heterogeneity characteristics of tight sandstone reservoirs. Constructing permeability models of different FU are expected to improve the evaluation accuracy of permeability. In this study, the flow unit classification standard is established by combining the frequency distribution histogram and cumulative probability plot of experimental Flow Zone Indicator (IFZ), and the optimal number of flow unit is selected to establish multiple permeability models. Additionally, the deep neural network (DNN) is introduced to predict IFZ by combining conventional logging and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) logging data. Finally, well permeability is calculated based on multiple permeability interpretation models. This permeability calculation method is applied to Paleogene Enping Formation in HuiZhou depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin, and five FU types are selected to optimal classification. The application result shows that the predicted FU types are well aligned with sedimentary facies and the accuracy of permeability calculations has significantly improved compared to NMR model. Overall, the permeability calculation method based on classification and optimization of FU provides a new insight for accurate evaluation of logging permeability in deep tight sandstone reservoirs.
-
Keywords:
- tight sandstone /
- permeability evaluation /
- flow unit /
- deep learning
-
-
表 1 5类流动单元类型的储层特征
Table 1 Reservoir properties of flow units with five types
流动单元分类 沉积微相 流动单元指数/μm 岩性 孔隙度,% 渗透率/mD Ⅰ类 分流间湾 IFZ≤0.45 泥质粉砂岩、中–细砂岩为主 5.4~15.0(9.4) 0.01~0.96(0.08) Ⅱ类 河口坝 0.45 < IFZ≤1.42 中–细砂,少量粗砂和含砾中砂 5.0~16.1(9.8) 0.07~11.00 (0.75) Ⅲ类 河口坝, 分流河道 1.42< IFZ≤3.00 中–细砂为主,含砾粗砂次之 6.2~16.2(10.7) 0.56~48.00 (6.76) Ⅳ类 分流河道 3.00< IFZ≤8.00 中–粗砂为主,含砾粗砂次之 7.0~15.2(12.1) 2.9~379.0(70.0) Ⅴ类 分流河道 IFZ >8.00 粗砂和含砾粗砂 9.0~17.6(14.2) 101~ 3611 (758)注:孔隙度及渗透率数值后()内数值为平均值。 -
[1] 贾爱林,位云生,郭智,等. 中国致密砂岩气开发现状与前景展望[J]. 天然气工业,2022,42(1):83–92. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2022.01.008 JIA Ailin, WEI Yunsheng, GUO Zhi, et al. Development status and prospect of tight sandstone gas in China[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(1): 83–92. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2022.01.008
[2] 季汉生,张立宽,张立强,等. 基于自发渗吸接触角分布的致密砂岩油储层混合润湿性测量和表征[J]. 东北石油大学学报,2023,47(2):117–124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4107.2023.02.010 JI Hansheng, ZHANG Likuan, ZHANG Liqiang, et al. Measurement and characterization of mixed wettability for tight sandstone based on spontaneous imbibition contact angle distribution[J]. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 2023, 47(2): 117–124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4107.2023.02.010
[3] 李登华,刘卓亚,张国生,等. 中美致密油成藏条件、分布特征和开发现状对比与启示[J]. 天然气地球科学,2017,28(7):1126–1138. LI Denghua, LIU Zhuoya, ZHANG Guosheng, et al. Comparison and revelation of tight oil accumulation conditions, distribution characteristics and development status between China and U. S.[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2017, 28(7): 1126–1138.
[4] 路萍,王浩辰,高春云,等. 致密砂岩储层渗透率预测技术研究进展[J]. 地球物理学进展,2022,37(6):2428–2438. doi: 10.6038/pg2022FF0236 LU Ping, WANG Haochen, GAO Chunyun, et al. Research progress of permeability prediction technology for tight sandstone reservoirs[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2022, 37(6): 2428–2438. doi: 10.6038/pg2022FF0236
[5] 王谦,谭茂金,石玉江,等. 径向基函数神经网络法致密砂岩储层相对渗透率预测与含水率计算[J]. 石油地球物理勘探,2020,55(4):864–872. WANG Qian, TAN Maojin, SHI Yujiang, et al. Prediction of relative permeability and calculation of water cut of tight sandstone reservoir based on radial basis function neural network[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2020, 55(4): 864–872.
[6] 时磊,王璞,刘俊州,等. 致密砂岩储层物性参数预测方法研究[J]. 石油物探,2020,59(1):98–107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2020.01.011 SHI Lei, WANG Pu, LIU Junzhou, et al. Physical properties prediction for tight sandstone reservoirs[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2020, 59(1): 98–107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2020.01.011
[7] 张冲,张占松,张超谟. 基于等效岩石组分理论的渗透率解释模型[J]. 测井技术,2014,38(6):690–694. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1338.2014.06.010 ZHANG Chong, ZHANG Zhansong, ZHANG Chaomo. A permeability interpretation model based on equivalent rock elements theory[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2014, 38(6): 690–694. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1338.2014.06.010
[8] KOZENY J. Ueber kapillare leitung des Wassers in Boden[J]. Royal Academy of Sciencc Vienna Proc, 1927, 136(2a): 271–306.
[9] CARMAN P C. Permeability of saturated sands, soils and clays[J]. The Journal of Agricultural Science, 1939, 29(2): 262–273. doi: 10.1017/S0021859600051789
[10] TIMUR A. An investigation of permeability, porosity, & residual water saturation relationships for sandstone reservoirs[J]. The Log Analyst, 1968, 9(4): 8–17.
[11] KENYON W E, DAY P I, STRALEY C, et al. A three-part study of NMR longitudinal relaxation properties of water-saturated sandstones[J]. SPE Formation Evaluation, 1988, 3(3): 622–636. doi: 10.2118/15643-PA
[12] 李荣强,高莹,杨永飞,等. 基于CT扫描的岩心压敏效应实验研究[J]. 石油钻探技术,2015,43(5):37–43. LI Rongqiang, GAO Ying, YANG Yongfei, et al. Experimental study on the pressure sensitive effects of cores based on CT scanning[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2015, 43(5): 37–43.
[13] 王清辉,朱明,冯进,等. 基于渗透率合成技术的砂岩油藏产能预测方法[J]. 石油钻探技术,2021,49(6):105–112. WANG Qinghui, ZHU Ming, FENG Jin, et al. A method for predicting productivity of sandstone reservoirs based on permeability synthesis technology[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2021, 49(6): 105–112.
[14] 邓浩阳. 高孔低渗碳酸盐岩储层孔隙结构及物性表征方法研究[D]. 成都:西南石油大学,2018. DENG Haoyang. The evaluation method of pore structure and physical property in carbonate rock reservoir with high porosity and low permeability[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2018.
[15] 周雪晴,张占松,张超谟,等. 基于粗糙集:随机森林算法的复杂岩性识别[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发,2017,36(6):127–133. ZHOU Xueqing, ZHANG Zhansong, ZHANG Chaomo, et al. Complex lithologic identification based on rough set-random forest algorism[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2017, 36(6): 127–133.
[16] 郭建宏,张占松,张超谟,等. 用地球物理测井资料预测煤层气含量:基于斜率关联度—随机森林方法的工作案例[J]. 物探与化探,2021,45(1):18–28. GUO Jianhong, ZHANG Zhansong, ZHANG Chaomo, et al. The exploration of predicting CBM content by geophysical logging data: a case study based on slope correlation random forest method[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(1): 18–28.
[17] 闫星宇,顾汉明,肖逸飞,等. XGBoost算法在致密砂岩气储层测井解释中的应用[J]. 石油地球物理勘探,2019,54(2):447–455. YAN Xingyu, GU Hanming, XIAO Yifei, et al. XGBoost algorithm applied in the interpretation of tight-sand gas reservoir on well logging data[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2019, 54(2): 447–455.
[18] 王远雄. 基于测井的改进TCN-Attention网络在储层孔隙度、渗透率预测中的应用[D]. 大庆:东北石油大学,2022. WANG Yuanxiong. Application of improved TCN-attention network based on logging in reservoir porosity and permeability prediction[D]. Daqing: Northeast Petroleum University, 2022.
[19] 杨旺旺,张冲,杨梦琼,等. 基于长短期记忆循环神经网络的伊拉克H油田碳酸盐岩储层渗透率测井评价[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发,2022,41(1):126–133. YANG Wangwang, ZHANG Chong, YANG Mengqiong, et al. Permeability logging evaluation of carbonate reservoirs in Oilfield H of Iraq based on long short-term memory recurrent neural network[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2022, 41(1): 126–133.
[20] AMRAEI H, FALAHAT R. Improved ST-FZI method for permeability estimation to include the impact of porosity type and lithology[J]. Journal of Petroleum Exploration and Production Technology, 2021, 11(1): 109–115. doi: 10.1007/s13202-020-01061-6
[21] 高颖,高楚桥,赵彬,等. 基于储层分类计算东海低渗致密储层渗透率[J]. 断块油气田,2019,26(3):309–313. GAO Ying, GAO Chuqiao, ZHAO Bin, et al. Permeability calculation based on reservoir classification for low permeability tight reservoirs in East China Sea[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2019, 26(3): 309–313.
[22] HAMD-ALLAH S M, NOOR B M, WATTEN A R. Permeability prediction for Nahr-Umr reservoir/Subba field by using FZI method[J]. Journal of Engineering, 2016, 22(9): 160–171. doi: 10.31026/j.eng.2016.09.10
[23] KORONCZ P, VIZHÁNYÓ Z, FARKAS M P, et al. Experimental rock characterisation of Upper Pannonian sandstones from Szentes Geothermal Field, Hungary[J]. Energies, 2022, 15(23): 9136. doi: 10.3390/en15239136
[24] 赵辉,齐怀彦,王凯,等. 致密砂岩油藏测井响应特征及有利区评价[J]. 特种油气藏,2023,30(5):35–41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2023.05.005 ZHAO Hui, QI Huaiyan, WANG Kai, et al. Characteristics of well logging response and evaluation of favorable zones in tight sandstone reservoirs[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2023, 30(5): 35–41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2023.05.005
[25] 董春梅,林承焰,赵海朋,等. 基于流动单元的测井储层参数解释模型[J]. 测井技术,2006,30(5):425–428. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1338.2006.05.011 DONG Chunmei, LIN Chengyan, ZHAO Haipeng, et al. Model of well logging reservoir parameters interpretation based on flow units[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2006, 30(5): 425–428. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1338.2006.05.011
[26] 葛祥,温丹妮,叶泰然,等. 川西气田雷四段白云岩储层流动单元测井评价方法[J]. 石油钻探技术,2023,51(6):120–127. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2023049 GE Xiang, WEN Danni, YE Tairan, et al. Logging evaluation method of flow units in a dolomite reservoir in the 4th member of the Leikoupo Formation in western Sichuan Gas Field[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2023, 51(6): 120–127. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2023049
[27] 李熙盛. 强非均质性储层构型表征与流动单元智能分类评价[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2024,40(9):28–37. LI Xisheng. Characterization of strongly heterogeneous reservoir architecture and intelligent classification evaluation of flow units[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2024, 40(9): 28–37.
[28] 王猛,刘志杰,杨玉卿,等. 基于区域测井大数据和实验资料的储层流动单元渗透率建模方法[J]. 地球物理学进展,2021,36(1):274–280. doi: 10.6038/pg2021EE0199 WANG Meng, LIU Zhijie, YANG Yuqing, et al. Permeability calculation in reservoir flow unit based on regional logging big data and experimental data[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2021, 36(1): 274–280. doi: 10.6038/pg2021EE0199
[29] ALIZADEH N, RAHMATI N, NAJAFI A, et al. A novel approach by integrating the core derived FZI and well logging data into artificial neural network model for improved permeability prediction in a heterogeneous gas reservoir[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2022, 214: 110573. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2022.110573
[30] 阿斯顿•张,李沐,扎卡里•C. 立顿,等. 动手学深度学习[M]. 北京:人民邮电出版社,2019:136-150. ZHANG A, LI Mu, LIPTON Z C, et al. Dive into deep learning[M]. Beijing: Posts & Telecom Press, 2019: 136-150.
-
期刊类型引用(14)
1. 于富安,刘维平,孙健越. 双聚防塌冲洗液在覆盖层钻探中的应用. 钻探工程. 2025(02): 59-64 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张统得,樊腊生,刘伟,蒋炳,邓伟,陆俊泽. 页岩气调查井复杂地层有机硅聚合物钻井液体系的研制与应用. 科学技术与工程. 2024(02): 520-527 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 宋瀚轩,叶艳,郑连杰,孙振玮,周童,张謦文. 钻井液微纳米封堵性能评价方法研究进展. 应用化工. 2024(02): 383-385 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 廖龙,刘坤翔,鲁毅,杨纯,陈香琴. 强力网堵漏技术及施工工艺分析. 石化技术. 2024(05): 144-146 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王中华. 国内钻井液技术现状与发展建议. 石油钻探技术. 2023(04): 114-123 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 宋瀚轩,叶艳,周童,郑蔚茹,张謦文. 纳米颗粒材料在水基钻井液中封堵性能研究与评价. 应用化工. 2023(09): 2501-2505+2510 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 王苏南,狄明利,马积贺,苗海龙,郭磊,邱正松,单锴. 南海东部某油田古近系复杂煤层防塌钻井液技术研究. 能源化工. 2023(04): 53-57 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 陈香琴,刘坤翔,肖梦林,徐聪. 加固保护井壁创新技术在某油田的应用. 化工管理. 2023(32): 76-79+83 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 张冬明. 松辽盆地中上部水敏性地层高密度油基钻井液研究. 西部探矿工程. 2022(07): 83-87 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 胡清富,刘春来,牟少敏,李增乐,司小东. 伊拉克东巴油田Tanuma组泥页岩高效防塌钻井液技术. 石油钻探技术. 2022(04): 76-82 .  本站查看
本站查看
11. 肖夏,陈彬. 南海东部M区块古近系地层井壁稳定钻井液技术. 海洋石油. 2022(03): 81-84 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 薛亮,肖夏,艾飞. 硅酸盐钻井液在XJ区块古近系地层的应用. 中国石油和化工标准与质量. 2021(07): 142-143 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 金勇,张强,覃建宇,张永涛,狄明利,单锴. 陆丰古近系复杂地层防塌钻井液技术研究. 当代化工. 2021(06): 1464-1467+1478 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 赵素丽. 强抑制高润滑丙三醇基钻井液体系研究与性能评价. 石油钻探技术. 2020(04): 56-62 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(2)



 下载:
下载: