Design and Testing of Electric Whipstock with Gear Transmission for Coiled Tubing Drilling
-
摘要:
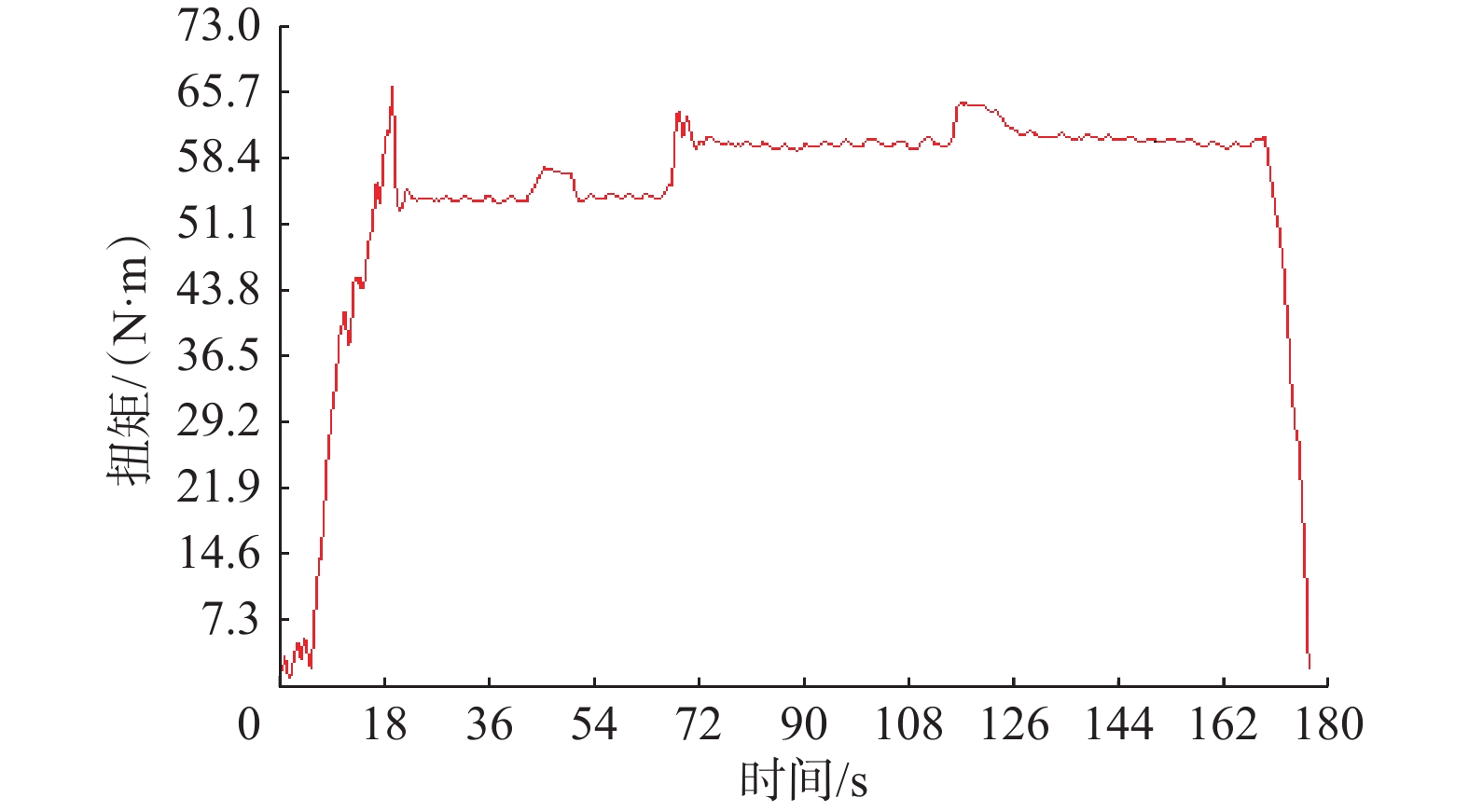
定向器是连续管钻井中实现定向作业的必备工具,其中电动定向器能够连续准确地调整工具面角,具有很大的技术优势,但受限于井下狭小径向空间和定向作业大扭矩要求,其中关键部件齿轮减速器是设计的难点。设计了一种基于大扭矩电机和多级行星齿轮减速器相配合的电动定向器,对其行星减速齿轮进行了优化,以弯曲疲劳强度安全系数、接触疲劳强度安全系数和输出扭矩3个关键参数的乘积为优化依据,得到了在要求空间下的最优齿数比,并对其进行了有限元强度校核和实际承载能力室内试验。研究结果表明,电动定向器两级行星齿轮减速器的实际承载能力超过800 N·m的设计目标,瞬时可达1 260 N·m,满足现场连续管钻井定向作业要求。研究结果为今后电动定向器设计和加工组装提供了参考。
Abstract:Whipstock is essential for directional drilling with coiled tubing, and the electric whipstock offers great technical advantages with its ability to make continuous and accurate tool face angle adjustments. However, due to narrow downhole radial space and high torque requirements for directional drilling, the design of the key structure in the electric whipstock, namely the gear reducer, becomes a difficult point of development. Therefore, a kind of electric whipstock based on a high-torque motor and multi-stage planetary gear reducer was designed, and the planetary gear reducer was optimized. The product of three key parameters, i.e, bending fatigue strength safety factor, contact fatigue strength safety factor, and output torque, was used as the basis for optimization so that the optimal gear ratio was obtained under the required space, and the finite-element strength calibration and the actual load carrying capacity of the gear reducer tests were carried out. The results show that the actual load bearing capacity of the designed two-stage planetary gear reducer of the electric whipstock exceeds the design target of 800 N·m, and the instantaneous capacity can reach 1 260 N·m, which meets the requirements of directional drilling operation of the coiled tubing drilling in the field. The research results can provide a reference for the design and processing assembly of future electric whipstock.
-
Keywords:
- coiled tubing drilling /
- electric whipstock /
- planetary gear reducer /
- gear ratio
-
-
-
[1] 贺会群. 连续油管技术与装备发展综述[J]. 石油机械,2006,34(1):1–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4578.2006.01.001 HE Huiqun. Development of coiled tubing technique and equipment[J]. China Petroleum Machinery, 2006, 34(1): 1–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4578.2006.01.001
[2] 胡亮,高德利. 连续管钻定向井工具面角调整方法研究[J]. 石油钻探技术,2015,43(2):50–53. HU Liang, GAO Deli. Study on a method for tool face re-orientation with coiled tubing drilling[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2015, 43(2): 50–53.
[3] 贾涛,张燕萍,吴千里. 连续管侧钻技术的研究及现场试验[J]. 石油机械,2017,45(7):30–33. JIA Tao, ZHANG Yanping, WU Qianli. Research and field test of coiled tubing sidetracking technology[J]. China Petroleum Machinery, 2017, 45(7): 30–33.
[4] CHOUDHARY A, MENEZES R, OGRA R, et al. Hybrid drilling rig with rotating coiled tubing[R]. SPE 112888, 2008.
[5] 李寅,尹方雷,白冬青. 连续管钻井技术研究进展及应用[J]. 焊管,2023,46(7):71–75. LI Yin, YIN Fanglei, BAI Dongqing. Research progress and application of coiled tubing drilling technology[J]. Welded Pipe and Tube, 2023, 46(7): 71–75.
[6] 苗芷芃,万教育,徐华冬,等. 连续管钻井液压定向器的设计与室内试验评价[J]. 石油管材与仪器,2021,7(4):5–8. MIAO Zhipeng, WAN Jiaoyu, XU Huadong, et al. Development and laboratory test of continuous pipe drilling orientation tool[J]. Petroleum Tubular Goods & Instruments, 2021, 7(4): 5–8.
[7] ROSS M, ANYANWU O N, KLOTZ C, et al. Rib-steered motor technology: The revolutionary approach extends the coiled tubing drilling application scope[R]. SPE 153573, 2012.
[8] 邢志晟,孔璐琳,祝传增,等. 连续管钻井肋式定向器执行机构偏置位移优化[J]. 石油机械,2023,51(2):26–32. XING Zhisheng, KONG Lulin, ZHU Chuanzeng, et al. Research on optimization of actuator offset displacement of rib-type orientation tool for coiled tubing drilling[J]. China Petroleum Machinery, 2023, 51(2): 26–32.
[9] MEEK D E, LEISING L J, ROWATT J D. Apparatus and method for orienting a downhole tool: US 6419014 B1[P]. 2002-07-16.
[10] ZEGARRA E, MEEK D, UDO C, et al. Intelligent wireless orienter for coiled tubing drilling: development to field test[R]. SPE 74836, 2002.
[11] 苗芷芃,夏宏南,南丽华,等. 连续管钻井液压定向器的研制[J]. 石油机械,2019,47(6):22–27. MIAO Zhipeng, XIA Hongnan, NAN Lihua, et al. Hydraulic orientation tool for coiled tubing drilling[J]. China Petroleum Machinery, 2019, 47(6): 22–27.
[12] 胡亮,阮臣良,崔晓杰,等. 新型连续管钻井用电液定向装置的研制[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2019,41(6):728–733. HU Liang, RUAN Chenliang, CUI Xiaojie, et al. The development of a novel electric-hydraulic orienter used for coiled tubing drilling[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2019, 41(6): 728–733.
[13] 马卫国,王力,王程飞. 连续管钻井电液双螺旋传动定向器的设计[J]. 石油机械,2020,48(4):37–42. MA Weiguo, WANG Li, WANG Chengfei. Design of electro-hydraulic double helix drive orienter for coiled tubing drilling[J]. China Petroleum Machinery, 2020, 48(4): 37–42.
[14] 李猛,贺会群,张云飞,等. 连续管钻井定向器技术现状与发展建议[J]. 石油机械,2015,43(1):32–37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4578.2015.01.007 LI Meng, HE Huiqun, ZHANG Yunfei, et al. The status quo and development suggestion on the coiled tubing drilling orienter[J]. China Petroleum Machinery, 2015, 43(1): 32–37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4578.2015.01.007
[15] 李猛,贺会群,都亚男,等. 连续管钻井电液定向器结构设计[J]. 石油机械,2015,43(11):1–6. LI Meng, HE Huiqun, DU Yanan, et al. Structure design of CTD electric-over-hydraulic orienter[J]. China Petroleum Machinery, 2015, 43(11): 1–6.
[16] THATCHER D A A, SZUTIAK G A, LEMAY M M. Integration of coiled tubing underbalanced drilling services to improve efficiency and value[R]. SPE 60708, 2000.
[17] TURNER D R, HARRIS T W R, SLATER M, et al. Electric coiled tubing drilling: A smarter CT drilling system[R]. SPE 52791, 1999.
[18] ANDERSON D R, DOREL A, MARTIN R. A new, integrated, wireline-steerable, bottom hole assembly brings rotary drilling-like capabilities to coiled tubing drilling[R]. SPE 37654, 2008.
[19] 张展,武文辉. 2K−H型行星齿轮装置设计[J]. 矿山机械,2020,48(11):45–49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3954.2020.11.010 ZHANG Zhan, WU Wenhui. Design of 2K-H planetary gear device[J]. Mining & Processing Equipment, 2020, 48(11): 45–49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3954.2020.11.010
[20] OHLINGER J J, GANTT L L, MCCARTY T M. A comparison of mud pulse and E-line telemetry in Alaska CTD operations[R]. SPE 74842, 2002.
[21] 张展. 实用齿轮设计计算手册[M]. 北京:机械工业出版社,2010:695-698. ZHANG Zhan. Practical gear design and calculation[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2010: 695-698.




 下载:
下载: