Practices and Understandings of Acid Fracturing of Ultra/Extra-Deep Exploratory Wells in Sichuan Basin and Its Periphery
-
摘要:
同普通深探井相比,四川盆地及盆地周缘超深/特深探井酸压改造面临井深更深、温度和压力更高、流体和岩性更复杂的工作环境,施工摩阻偏大、排量偏小、规模偏小、酸液有效作用距离偏短,改造效果较差,工具可靠性差、改造施工一次成功率低、安全保障难度高,投入大、产量不理想,勘探进展较为缓慢。为此,应用国内外油气行业、制造业的最新研究成果,结合自身实际和经验教训开展技术攻关,用新型大通径高强度气密封入井管柱替代传统管柱,降阻提排量;用可同时激发的双向双金属密封替代双向单金属密封,实现密封能力可检验和长期保持稳定,以提高井口控制能力;用双向锚定胀封封隔器取代底端锚定旋转加压坐封封隔器,以降低酸压期间管柱伸缩引起胶筒移动和密封失效的概率,多套减振器串联可以降低爆轰力的不利影响;用“四阀一封”取代“两阀一封”备份阀件并串联使用,以提升可靠性;研发适应温度≥220 ℃、压力≥180 MPa的缓蚀、缓速工作液;将只相信两联作的理念改为两联作和三联作并重,形成了酸压工艺优选方法。现场应用进展顺利,安全保障能力、改造规模及压裂效果、施工一次成功率均显著提升,可为同类井酸压改造提供技术借鉴。
Abstract:Compared with that of ordinary deep exploratory wells, the acid fracturing of ultra/extra-deep wells in the Sichuan Basin and its periphery faces the working environments featuring deeper wells, higher temperature and pressure, and more complicated fluid and lithology, and it has the problems of large operating friction, low flow rate, small scale, short effective distance of acid solution, poor fracturing result, unreliable tools, low success rate of the first operation execution, difficult security guarantee, expensive investment, and unsatisfactory yield. Therefore, the exploration progress of such wells is slow. By applying the latest achievements of the oil and gas industry and manufacturing industry in China and abroad, the technical research was conducted based on actual experiences and lessons, and the new large-diameter and high-strength air-tight seal pipe string was used to replace the traditional pipe string to reduce the friction and increase the flow rate. The bi-directional bimetal seal which could be motivated simultaneously was used to replace the bi-directional single-metal seal to test the sealability and maintain the long-term stability, so as to increase the wellhead control capacity; and the bi-directional anchored expansion packer was used to replace the bottom-anchored rotary pressure setting packer, so as to reduce the probability of cylinder movement and seal failure caused by pipe string expansion during acid fracturing. Multiple sets of shock absorbers were connected in series to reduce the adverse effects of detonation force, and the “four-valve-one-packer” method was adopted to replace the “two-valve-one-packer” method. In addition, the backup valves were connected in series to improve reliability, and the corrosion-inhibiting and velocity-retarding working fluid suitable for temperature of ≥220 °C and pressure of ≥180 MPa was developed. Equal emphasis was placed on simultaneous two-step operation and simultaneous three-step operation instead of the traditional emphasis on simultaneous two-step operation, and thus the optimum selection method of the acid fracturing process was established. The field application was progressing smoothly, and the safety guarantee ability, fracturing scale, fracturing effect, and success rate of the first operation execution were significantly improved, providing a reference for acid fracturing of similar wells.
-
井漏是影响钻井作业安全的井下复杂情况之一,钻井过程中发生井漏不仅延误钻井周期,同时造成巨大经济损失[1-5]。近年来,随着油气勘探开发的深入,井漏情况日益突出,如川渝的威远–长宁区块、鄂尔多斯盆地北部杭锦旗区块等井漏问题严重,影响了钻井效率与速度。据统计,这些区块绝大部分井的漏失类型为裂缝性漏失。目前,针对裂缝性漏失的堵漏剂主要有桥接型堵漏剂、高失水堵漏剂、暂堵型堵漏剂、膨胀类堵漏剂、水泥速凝类堵漏剂、可固化型堵漏剂和复合材料堵漏剂等类型 [6-9]。其中,桥接型堵漏剂相对其他堵漏剂使用简便,成本较低。但常规桥堵材料多采用核桃壳等架桥颗粒及纤维等填充物,其在高温下易发生碳化,长时间碳化后容易发生堵漏失效,特别是在深层环境中极易发生复漏。同时,常规堵漏材料与裂缝匹配性差,难以有效进入漏层形成封堵,堵漏成功率低[10-13]。针对这一问题,笔者优选了一种高弹性、可压缩的聚氨酯泡沫弹性孔网材料,评价了其堵漏效果,并在威远、彭州和神木等油气田应用了15井次,一次堵漏成功率达86.7%。
1. 弹性孔网材料优选
裂缝性漏失地层具有承压能力低和在压力作用下诱导开启闭合的特征。针对裂缝性地层特征及封堵的技术难点,确定选择具有可压缩、高回弹、耐高温的弹性孔网材料作为架桥堵漏材料。弹性孔网材料是一种聚氨酯泡沫,具有开孔的泡孔结构,弹性高,堆积密度小于0.02 g/cm3。考虑钻井液应用情况,筛选了2种材质、9种泡孔规格的聚氨酯泡沫弹性孔网材料(见表1),对其压缩回弹性、抗拉强度和抗温性等性能进行了评价。
表 1 不同类型弹性孔网材料的泡孔规格Table 1. Specifications of different elastic mesh materials编号 弹性孔网类型 泡孔规格/目 1# 阻燃型 12 2# 阻燃型 6 3# 阻燃型 4 4# 阻燃型 2 5# 过滤型 8 6# 过滤型 6 7# 过滤型 2 8# 过滤型 10 9# 过滤型 4 1.1 压缩回弹性
弹性孔网材料的压缩回弹性能越好,越有利于在井底压差作用下发挥自转向性,进入不同开度的裂缝进行自适应堵漏。参照标准《软质泡沫聚合材料:压缩永久变形的测定》(GB/T 6669—2008)给出的试验方法[14],室内测试了弹性孔网材料的50%压缩永久变形率,结果如图1所示。
由图1可知,1#和2#弹性孔网材料的50%压缩永久变形率均小于10%,其余7种弹性孔网材料的50%压缩永久变形率均大于10%。
1.2 抗拉强度
弹性孔网材料要求具有较高的抗拉强度,能承受井下不同应力作用,形成较高强度的致密承压封堵层,增强封堵层的剪切强度。参照标准《软质泡沫聚合材料:拉伸强度和断裂伸长率的测定》(GB/T 6344—2008)给出的试验方法[15],测试了弹性孔网材料的抗拉强度,结果如图2所示。
由图2可知,1#和2#弹性孔网材料的抗拉强度分别为150 kPa和137 kPa,其余7种弹性孔网材料的抗拉强度均小于130 kPa,表明1#和2#弹性孔网材料的抗拉强度优于其余7种材料。
1.3 抗温性
测试弹性孔网材料在钻井液中老化后的质量保留率和抗拉强度保持率,评价其抗温能力。钻井液配方为4.0%膨润土浆+0.3%HV-PAC,取一定质量的弹性孔网材料加入400 mL钻井液中,老化后过10目筛、洗涤并烘干,测量弹性孔网材料老化后的质量和抗拉强度,结果分别见图3和图4。
由图3和图4可知,150 ℃老化16 h后,1#弹性孔网材料的质量保留率和抗拉强度保持率分别为92.5%和88.4%,其余8种弹性孔网材料的质量保留率和抗拉强度保持率均低于85.0%。实验结果表明,1# 弹性孔网材料的抗温能力可达150 ℃。综合考虑以上试验结果,选择1#弹性孔网材料作为堵漏材料,并开展堵漏性能评价试验。
2. 弹性孔网材料堵漏性能评价
2.1 堵漏性能评价方法
利用中国石油大学(华东)自行研制的长裂缝封堵模拟试验装置,评价弹性孔网材料对裂缝的封堵性能。长裂缝封堵模拟试验装置由高温高压钻井液釜体、楔形长裂缝模具夹持器、温度压力测量控制系统及数据采集处理系统组成,工作压力范围0~25 MPa,工作温度范围室温至180 ℃。为了更好地模拟地层裂缝状态和进行堵漏效果评价,裂缝模具设计为两端缝宽不等的楔形,裂缝长度为1 000 mm,楔形长裂缝试验模具包括1.0 mm×0.5 mm,2.0 mm×1.0 mm,3.0 mm×2.0 mm,4.0 mm×3.0 mm和5.0 mm×4.0 mm(表示前端缝宽×后端缝宽)等5种规格,用来模拟不同缝宽的漏层。
长裂缝封堵模拟实验方法为:1)打开高温高压钻井液釜体,配制2 000 mL堵漏浆倒入釜体内;2)将楔形长裂缝模块装入模具夹持器中,连接围压管线、滤液出口管线和活塞压力管线;3)围压加至15 MPa,加热至实验温度100 ℃;4)打开滤液出口阀,计量漏出的堵漏浆体积,对釜体内堵漏浆加压,快速将压力加至3.5 MPa,计时并记录累计漏失量,计算漏失速率,根据漏失速率优选堵漏材料。
2.2 堵漏效果影响因素分析
2.2.1 弹性孔网材料形状
将优选的1#弹性孔网材料分别加工成正方体、长方体和三棱柱等3种形状(见图5),其尺寸分别为5.0 mm×5.0 mm×5.0 mm(正方体形)、2.0 mm×2.0 mm×5.0 mm(长方体形)和5.0 mm×5.0 mm×5.0 mm(三棱柱形),利用楔形长裂缝试验装置(楔形缝宽为5.0×4.0 mm),考察不同形状的弹性孔网材料对堵漏基浆堵漏性能的影响,结果见表2。其中,实验用堵漏基浆配方为6.0%膨润土浆+0.3%HV-PAC。
表 2 不同形状弹性孔网材料楔形长裂缝封堵试验结果Table 2. Long wedge-shaped fractures plugged with elastic mesh materials in different shapes堵漏浆配方 漏失速率/(L·s–1) 封堵情况 堵漏基浆 0.50 堵漏基浆+0.08%正方体形弹性孔网材料 0.06 滞留在裂缝中 堵漏基浆+0.08%长方体形弹性孔网材料 0.40 随堵漏浆漏失 堵漏基浆+0.08%三棱柱形弹性孔网材料 0.20 少量滞留在裂缝中 由表2可知,加入正方体形弹性孔网材料后,漏失速率为0.06 L/s,弹性孔网材料可有效滞留在裂缝内;加入长方体形弹性孔网材料后,漏失速率为0.40 L/s,弹性孔网材料随堵漏浆漏失,无法有效滞留在裂缝中;加入三棱柱形弹性孔网材料后,漏失速率为0.20 L/s,弹性孔网材料随堵漏浆漏失,少量弹性孔网材料滞留在裂缝中。试验结果表明,正方体形弹性孔网材料可有效滞留在裂缝内,堵漏效果较好。
2.2.2 弹性孔网材料尺寸
将弹性孔网材料加工成不同尺寸的正方体形,利用缝宽为5.0 mm×4.0 mm的楔形长裂缝试验装置,考察了不同形状的弹性孔网材料对堵漏性能的影响,结果见表3。
表 3 不同尺寸弹性孔网材料封堵楔形长裂缝试验结果Table 3. Long wedge-shaped fractures plugged with elastic mesh materials in different sizes堵漏浆配方 漏失速率/(L·s–1) 封堵情况 堵漏基浆 0.50 堵漏基浆+0.08% 弹性孔网
材料(15.0 mm×15.0 mm×15.0 mm)0.40 封堵缝口 堵漏基浆+0.08% 弹性孔网
材料(10.0 mm×10.0 mm×10.0 mm)0.10 进入裂缝浅 堵漏基浆+0.08%弹性孔网
材料(5.0 mm×5.0 mm×5.0 mm)0.06 进入裂缝深 由表3可知,堵漏基浆的漏失速率为0.50 L/s;加入0.08%尺寸为15.0 mm×15.0 mm×15.0 mm的弹性孔网材料后,漏失速率降至0.40 L/s,但由于弹性孔网材料尺寸过大,导致其无法进入裂缝中,堆积在缝口处;加入0.08%尺寸为10.0 mm×10.0 mm×10.0 mm的弹性孔网材料后,漏失速率降至0.10 L/s,弹性孔网材料进入裂缝较浅;加入0.08%尺寸为5.0 mm×5.0 mm×5.0 mm的弹性孔网材料,漏失速率降至0.06 L/s,表明其可进入裂缝较深部位。因此,可根据漏失速率(或裂缝大小)选择合适尺寸的弹性孔网材料,以达到最优的堵漏效果。
2.2.3 弹性孔网材料加量
利用缝宽为5.0 mm×4.0 mm的楔形长裂缝试验装置,选用尺寸为5.0 mm×5.0 mm×5.0 mm的正方体形弹性孔网材料,考察了弹性孔网材料加量对堵漏效果的影响,试验结果见表4。
表 4 不同加量弹性孔网材料的长裂缝封堵试验结果Table 4. Long fractures plugged with elastic mesh materials in different concentrations堵漏浆配方 漏失速率/(L·s–1) 封堵情况 堵漏基浆 0.50 堵漏基浆+0.04% 弹性孔网材料 0.30 进入裂缝中 堵漏基浆+0.08% 弹性孔网材料 0.06 进入裂缝中 堵漏基浆+0.12% 弹性孔网材料 0.20 封堵缝口 由表4可知,加入0.04%弹性孔网材料后,其可进入裂缝中,漏失速率降至0.30 L/s;随着弹性孔网材料加量增大,裂缝中弹性孔网材料的数量显著增多,漏失速率大幅降低;但加入0.12%弹性孔网材料后,由于其加量过大,无法进入裂缝,堆积在缝口处封堵缝口。
3. 弹性孔网材料裂缝封堵作用机理
基于弹性孔网材料裂缝封堵试验结果,其裂缝封堵作用机理可概括为以下几个方面(见图6):
1)弹性变形,挤入裂缝。弹性孔网材料在井底压差作用下可发生压缩变形,挤入裂缝,对于不同开度的地层裂缝均具有较强的自适应性。
2)捕集作用。挤入裂缝的弹性孔网材料在裂缝中可形成一个过滤网,变缝为孔,通过“网兜效应”易于捕获其他类型堵漏材料,形成三维立体封堵隔墙(层),提高堵漏材料在裂缝中的滞留能力,提高堵漏成功率。
3)提高封堵层承压能力。填充材料在过滤网中不断堆积,封堵域较长,大量弹性孔网材料封堵隔墙协同作用,承担外部载荷,提高了封堵层的致密承压能力[16-18]。
4. 现场应用
四川盆地彭州区块须家河组、雷口坡组及马鞍塘组地层发生漏速15~38 m3/h的裂缝性漏失,威远区块龙马溪组地层发生漏速52.2 m3/h的裂缝性漏失,陕北神木区块刘家沟组地层发生漏速20 m3/h的裂缝性漏失,应用弹性孔网材料进行堵漏施工后,均一次堵漏成功。截至目前,弹性孔网材料已累计应用15井次,一次堵漏成功13井次,一次堵漏成功率达86.7%。下面以元坝701井为例介绍弹性孔网材料的应用情况。
元坝701井是位于四川盆地川北坳陷九龙山背斜南的一口评价井,目的层为下二叠统茅口组三段,设计井深6 845.00 m。该区块陆相地层自流井组—须家河组地层中有高压低渗裂缝性气藏,岩性分布比较复杂,砂砾岩储层发育,岩石以灰色钙屑砂岩、碳酸盐为主,且多为钙质胶结,灰质含量较高;高角度裂缝发育,裂缝的发育程度和分布规模不均一;钻井液安全密度窗口窄,常出现井漏、井涌同存的问题。
元坝701井采用密度为1.96 kg/L的钻井液钻至自流井组东岳庙段3 834.76 m发生漏失,漏速24 m3/h,累计漏失钻井液38.0 m3;短起5柱,配制堵漏浆进行桥浆堵漏,堵漏浆配方为:井浆+4%核桃壳(1.0~3.0 mm)+3%核桃壳(0.5~1.0 mm)+4%酸溶暂堵剂+4%承压封堵剂+2%刚性堵漏剂(2.0~3.0 mm)+2%橡胶颗粒(0.5~1.0 mm)+2%木质纤维素+3%超细碳酸钙。注入堵漏浆后静止堵漏,静止6 h后下钻到底小排量循环不漏,排量提高至正常钻进排量45 L/s时发生漏失,漏速13 m3/h。鉴于即将钻进须家河组高压地层,钻井液密度需提至2.10 kg/L以上,配制40 m3堵漏浆进行承压堵漏,承压堵漏浆配方为:井浆+0.08%弹性孔网材料+5.00%核桃壳(1.0~3.0 mm)+4.00%核桃壳(0.5~1.0 mm)+4.00%酸溶暂堵剂+4.00%承压封堵剂+2.00%刚性堵漏剂(2.0~3.0 mm)+3.00%弹性颗粒+3.00%木质纤维素+5.00%超细碳酸钙。具体施工程序为:光钻杆下至3 700 m,泵入33.0 m3堵漏浆,泵入期间环空返浆,泵注完堵漏浆后替入35.0 m3井浆;然后起钻至3 300 m,关井正挤憋压,累计泵入10次共8.2 m3钻井液,立压保持在6.23 MPa,开井循环不漏失,换算井底压力当量密度最高为2.13 kg/L。
堵漏成功后更换钻具组合,下钻到底正常钻进排量循环不漏失,钻进至须家河组地层前逐渐将钻井液密度提高至2.12 kg/L,三开顺利钻穿须家河组地层,未发生漏失等井下复杂情况。
5. 结论与建议
1)弹性孔网材料具有较好的压缩回弹性能,在压差作用下能够挤入裂缝,变缝为孔,增强堵漏材料在裂缝中的滞留能力,提高了裂缝封堵效果。
2)现场多口井的应用结果表明,弹性孔网材料配合其他填充堵漏材料进行堵漏,对裂缝性漏失的堵漏效果更显著。
3)弹性孔网材料密度小,现场使用时添加到钻井液中后需长时间搅拌才能混合均匀,建议开展现场施工工艺研究,以提高堵漏时效。
-
表 1 超深/特深井储层改造油管改进情况
Table 1 Improvement of pipe string for reservoir stimulation of ultra/extra-deep wells
外径/mm 钢级 壁厚/mm 抗拉强度/kN 抗挤强度/MPa 抗内压强度/MPa 备注 114.3 110SS 8.56 2 157 98.9 99.4 改进前 114.3 110SS 14.22 3 392 165.2 165.2 改进后 88.9 110SS 9.52 1 802 145.1 142.2 改进前 88.9 110SS 12.09 2 213 178.3 180.5 改进后 73.0 110SS 7.01 1 052 125.6 121.6 改进前 73.0 110SS 7.82 1 215 145.2 142.2 改进后 表 2 4.00 m3/min排量下RT-1井储层改造管柱三轴应力安全系数校核
Table 2 Triaxial stress safety factor check of pipe string for reservoir stimulation of Well RT-1 at a flow rate of 4.00 m3/min
井深/m 温度/℃ 油压/MPa 套压/MPa 轴向力/kN 三轴应力校核安全系数 0 16.00 110.0 26.3 2 070.80 1.60 2 400 20.35 115.4 56.8 1 078.20 1.80 6 700 46.45 125.0 111.6 136.92 2.79 8 122 58.69 128.1 129.0 −60.76 3.62 表 3 超高温缓蚀剂酸腐蚀试验情况
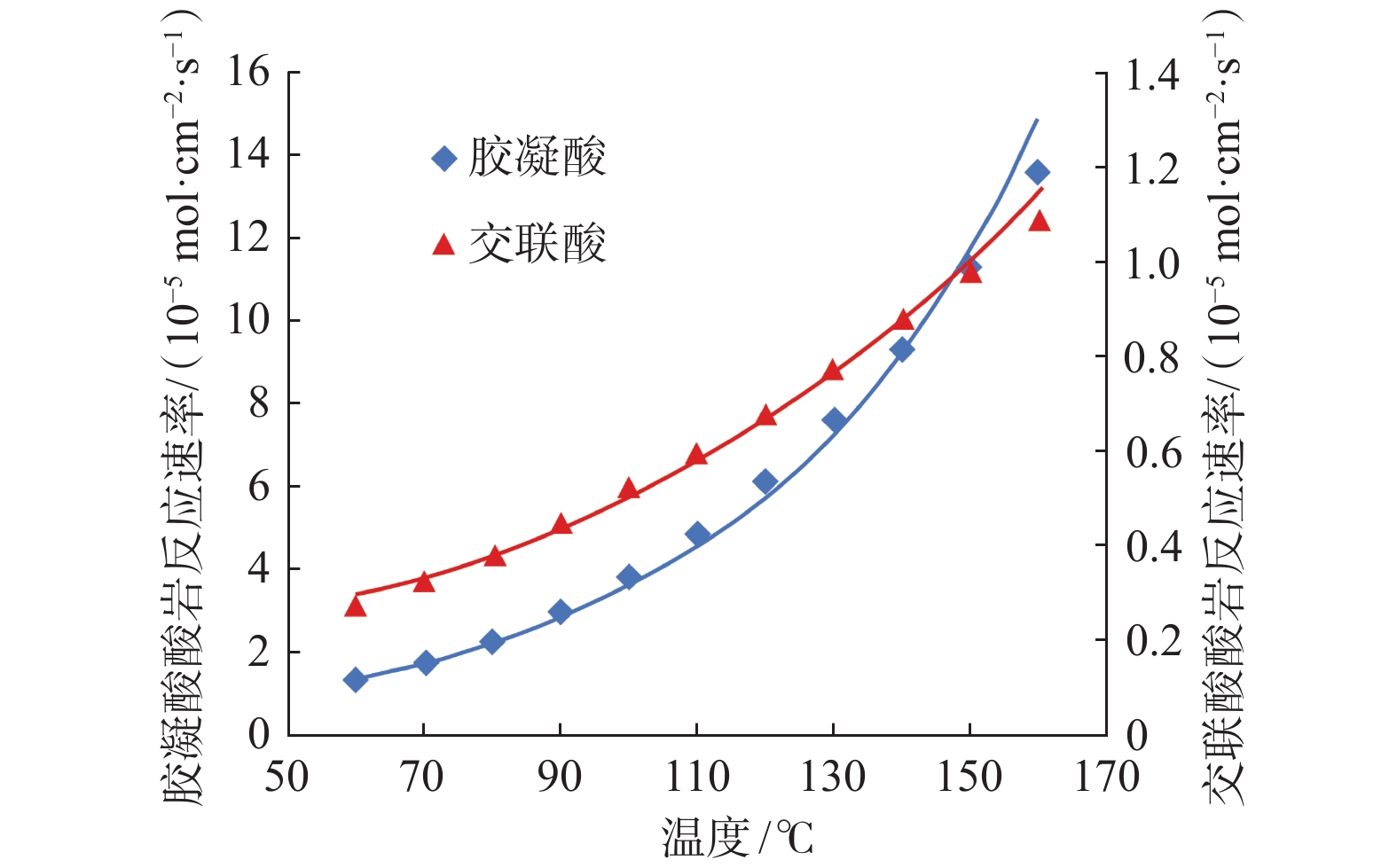
Table 3 Acid corrosion experiments of ultra-high temperature corrosion inhibitor
酸液/温度 酸浓度 腐蚀速率标准/
(g·m−2·h−1)钢片编号 实际腐蚀速率/
(g·m−2·h−1)降破酸
(200 ℃)15%HCl ≤90 005 57.24 057 59.35 059 56.31 平均值 57.63 胶凝酸
(180 ℃)20%HCl ≤80 076 32.28 078 30.76 平均值 31.52 注:试验条件为压力16 MPa、搅拌速度60 r/min、110SS钢片(油管相同材质),反应时间4 h。 表 4 YS-1井与MS-1井酸压测试效果对比
Table 4 Comparison of acid fracturing effects of Well YS-1 and Well MS-1
井号 储层中深/
m储层温度/
℃地压压力
系数入井液量/
m3入井酸量/
m3动态缝长/
m酸蚀缝长/
m平均缝宽/
cm平均裂缝导流能力/
(mD·m)日产气量/
104m3MS-1 8081.00 178.84 1.10 183.50 142.00 56.00 37.40 0.27 9.40 1.04 YS-1 8774.50 210.00 1.10 450.00 350.00 72.60 41.20 0.44 11.20 3.28 -
[1] 郭旭升,蔡勋育,刘金连,等. 中国石化 “十三五” 天然气勘探进展与前景展望[J]. 天然气工业,2021,41(8):12–22. GUO Xusheng, CAI Xunyu, LIU Jinlian, et al. Natural gas exploration progress of Sinopec during the 13th Five-Year Plan and prospect forecast during the 14th Five-Year Plan[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(8): 12–22.
[2] 何治亮,金晓辉,沃玉进,等. 中国海相超深层碳酸盐岩油气成藏特点及勘探领域[J]. 中国石油勘探,2016,21(1):3–14. HE Zhiliang, JIN Xiaohui, WO Yujin, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation characteristics and exploration domains of ultra-deep marine carbonates in China[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2016, 21(1): 3–14.
[3] 孙斌,张培先,高全芳,等. 川东南南川地区茅口组一段碳酸盐岩储层特征及富集模式[J]. 非常规油气,2022,9(3):21–31. SUN Bin, ZHANG Peixian, GAO Quanfang, et al. Reservoir properties and accumulation mode of carbonate rocks in Mao1 Member of Nanchuan Area in southeast Sichuan[J]. Unconventional Oil & Gas, 2022, 9(3): 21–31.
[4] 马永生,蔡勋育,李慧莉,等. 深层–超深层碳酸盐岩储层发育机理新认识与特深层油气勘探方向[J]. 地学前缘,2023,30(6):1–13. MA Yongsheng, CAI Xunyu, LI Huili, et al. New insights into the formation mechanism of deep-ultra-deep carbonate reservoirs and the direction of oil and gas exploration in extra-deep strata[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2023, 30(6): 1–13.
[5] 孙自明,卞昌蓉,张荣强,等. 四川盆地东南部震旦系灯影组四段台缘带天然气勘探前景[J]. 现代地质,2022,36(4):979–987. SUN Ziming, BIAN Changrong, ZHANG Rongqiang, et al. Natural gas exploration prospect of the platform marginal zone of the fourth member of Sinian Dengying Formation in southeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(4): 979–987.
[6] 林永茂, 缪尉杰, 刘林,等. 川西南靖和1井茅口组立体酸压技术[J]. 石油钻探技术,2022,50(2):105–112. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2022009 LIN Yongmao, MIAO Weijie, LIU Lin, et al. 3D acid fracturing technology in Maokou Formation of Well Jinghe 1 in Southwestern Sichuan[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2022, 50(2): 105–112. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2022009
[7] 曾义金. 海相碳酸盐岩超深油气井安全高效钻井关键技术[J]. 石油钻探技术,2019,47(3):25–33. ZENG Yijin. Key technologies for safe and efficient drilling of marine carbonate ultra-deep oil and gas wells[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2019, 47(3): 25–33.
[8] 马永生,黎茂稳,蔡勋育,等. 中国海相深层油气富集机理与勘探开发:研究现状、关键技术瓶颈与基础科学问题[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2020,41(4):655–672. MA Yongsheng, LI Maowen, CAI Xunyu, et al. Mechanisms and exploitation of deep marine petroleum accumulations in China: advances, technological bottlenecks and basic scientific problems[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(4): 655–672.
[9] 苏镖,龙刚,许小强,等. 超深高温高压高含硫气井的安全完井投产技术:以四川盆地元坝气田为例[J]. 天然气工业,2014,34(7):60–64. SU Biao, LONG Gang, XU Xiaoqiang, et al. Safe completion and production technologies of a gas well with ultra depth, high temperature, high pressure and high H2S content: a case from the Yuanba Gas Field in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(7): 60–64.
[10] 孙玉炳. 高温高压气井完井技术难点与对策[J]. 中国石油和化工标准与质量,2021,41(22):197–198. SUN Yubing. Difficulties and countermeasures of completion for HT/HP gas wells[J]. China Petroleum and Chemical Standard and Quality, 2021, 41(22): 197–198.
[11] 贾学钰. 川西海相酸性气井试气工艺技术[J]. 石油地质与工程,2014,28(4):129–131. JIA Xueyu. Gas testing technology for marine acidic gas wells in western Sichuan[J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2014, 28(4): 129–131.
[12] 王勇军. 四川盆地元坝深层致密砂岩气藏超高压压裂测试工艺技术探索[J]. 天然气勘探与开发,2016,39(2):54–57. WANG Yongjun. Technology of ultra-high pressure fracturing test for deep and tight sandstone gas reservoirs, Yuanba Block[J]. Natural Gas Exploration and Development, 2016, 39(2): 54–57.
[13] 许小强,陈琛,戚斌,等. 川东北高温高压含硫超深气井测试技术实践[J]. 钻采工艺,2009,32(3):53–55. XU Xiaoqiang, CHEN Chen, QI Bin, et al. Well testing technology on high temperature and high pressure sulfurous ultra-deep reservoirs in northeast Sichuan[J]. Drilling & Production Technology, 2009, 32(3): 53–55.
[14] 杨廷玉,黎洪. 川东北高含硫气井测试作业安全控制技术浅谈[J]. 油气井测试,2012,21(3):72–74. YANG Tingyu, LI Hong. A brief discussion on security control technology of gas well testing operation containing high sulfur in northeastern Sichuan Gas Field[J]. Well Testing, 2012, 21(3): 72–74.
[15] 崔龙兵,樊凌云,邹伟,等. 顺北油田超深井可回收式套管封隔器失效因素分析及改进对策[J]. 油气井测试,2022,31(1):22–26. CUI Longbing, FAN Lingyun, ZOU Wei, et al. Failure factor analysis and improvement countermeasures of recyclable casing packer in ultra-deep wells in Shunbei Oilfield[J]. Well Testing, 2022, 31(1): 22–26.
[16] 卢刚,唐蜜,王毅. 超深酸性气藏APR测试事故分析及测试工艺优化研究[J]. 内蒙古石油化工,2016,42(8):31–33. LU Gang, TANG Mi, WANG Yi. Analysis of APR testing accidents in ultra deep acidic gas reservoirs and research on testing process optimization[J]. Inner Mongolia Petrochemical Industry, 2016, 42(8): 31–33.
[17] 刘洪涛,刘举,刘会锋,等. 塔里木盆地超深层油气藏试油与储层改造技术进展及发展方向[J]. 天然气工业,2020,40(11):76–88. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2020.11.009 LIU Hongtao, LIU Ju, LIU Huifeng, et al. Progress and development direction of production test and reservoir stimulation technologies for ultra-deep oil and gas reservoirs in Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(11): 76–88. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2020.11.009
[18] 周生福,崔龙兵,刘练,等. 顺北油田三高油气井完井测试封隔器影响因素及对策[J]. 油气井测试,2019,28(3):37–41. ZHOU Shengfu, CUI Longbing, LIU Lian, et al. Influencing factors of completion test packer and countermeasure for 3-high oil and gas well in Shunbei Oilfield[J]. Well Testing, 2019, 28(3): 37–41.
[19] 陈科,胡桂林,张超伟. 川东北RTTS封隔器失封原因及对策[J]. 天然气技术与经济,2012,6(3):48–51. CHEN Ke, HU Guilin, ZHANG Chaowei. Causes of RTTS packer failure and the countermeasures in northeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Technology and Economy, 2012, 6(3): 48–51.
[20] 王立军. RTTS封隔器胶筒问题浅析[J]. 油气井测试,2010,19(1):54–55. WANG Lijun. Analysis of problems about rubber element of RTTS packer[J]. Well Testing, 2010, 19(1): 54–55.
[21] 曹阳,贾宝,熊昕东,等. 元坝超深含硫气井测试事故分析与预防措施[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2012,34(6):49–52. CAO Yang, JIA Bao, XIONG Xindong, et al. Testing accident analysis and preventive measures for ultra-deep sulfur-bearing gas wells in Yuanba Gas Field[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2012, 34(6): 49–52.
[22] 王宴滨,石小磊,高德利,等. 深层高温高压气井完井测试管柱失效分析:以顺南地区某井为例[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2022,44(3):302–308. WANG Yanbin, SHI Xiaolei, GAO Deli, et al. Failure analysis of completion test string for deep high-temperature and high-pressure gas well: a case study on a well in Shunnan area[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2022, 44(3): 302–308.
[23] 汤火林,张天翊,黄刚,等. 高密度压井液环境下某井APR测试替喷技术[J]. 油气井测试,2023,32(3):17–21. TANG Huolin, ZHANG Tianyi, HUANG Gang, et al. APR testing bullheading technique in high-density well killing fluid environment[J]. Well Testing, 2023, 32(3): 17–21.
[24] 吴建军,龙学,黄力,等. 元坝1-侧1井高温高压高含硫超深大斜度井测试技术[J]. 钻采工艺,2012,35(3):34–35. WU Jianjun, LONG Xue, HUANG Li, et al. Gas test technique for super-deep well YB1-C1 with HTHP and high sour[J]. Drilling & Production Technology, 2012, 35(3): 34–35.
[25] 杨波,范蓉,罗凌睿. 川西含硫气井测试工艺技术及应用[J]. 天然气技术与经济,2018,12(4):42–44. YANG Bo, FAN Rong, LUO Lingrui. Well testing technologies and their application to sour gas wells, western Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Technology and Economy, 2018, 12(4): 42–44.
[26] 纪松,宫建. 高温高压井测试联作射孔技术研究及应用[J]. 复杂油气藏,2013,6(3):76–78. JI Song, GONG Jian. Research and application of perforating and testing combination technology in high temperature and high pressure well[J]. Complex Hydrocarbon Reservoirs, 2013, 6(3): 76–78.
[27] 张明江,张果. 川东北高温、高压、高含硫气井测试地面控制应用技术研究[J]. 油气井测试,2009,18(1):56–57. ZHANG Mingjiang, ZHANG Guo. Technology study on surface controlling of well test in gas wells with high temperature, high pressure and high sulfur content in north-east of Sichuan[J]. Well Testing, 2009, 18(1): 56–57.
[28] 崔龙兵,刘练,周生福,等. 顺北油田“三高”油气井试井工艺技术[J]. 油气井测试,2020,29(3):57–63. CUI Longbing, LIU Lian, ZHOU Shengfu, et al. Well test processes of oil and gas wells with “three highs” in Shunbei Oilfield[J]. Well Testing, 2020, 29(3): 57–63.
[29] 丁士东,赵向阳. 中国石化重点探区钻井完井技术新进展与发展建议[J]. 石油钻探技术,2020,48(4):11–20. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2020069 DING Shidong, ZHAO Xiangyang. New progress and development suggestions for drilling and completion technologies in Sinopec key exploration areas[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2020, 48(4): 11–20. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2020069
[30] 马健,杨永华,何颂根,等. 川西超深海相碳酸盐岩超高压分段酸压技术实践[J]. 钻采工艺,2021,44(1):57–60. MA Jian, YANG Yonghua, HE Songgen, et al. Practice of ultra-high-pressure staged acid fracturing in western Sichuan ultra-deep marine carbonate[J]. Drilling & Production Technology, 2021, 44(1): 57–60.
[31] 陈宗琦,刘湘华,白彬珍,等. 顺北油气田特深井钻井完井技术进展与发展思考[J]. 石油钻探技术,2022,50(4):1–10. CHEN Zongqi, LIU Xianghua, BAI Binzhen, et al. Technical progress and development consideration of drilling and completion engineering for ultra-deep wells in the Shunbei Oil & Gas Field[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2022, 50(4): 1–10.
[32] 罗伟,林永茂,李海涛. 碳酸盐岩储层射孔穿深的影响规律[J]. 爆破器材,2020,49(1):49–53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8352.2020.01.010 LUO Wei, LIN Yongmao, LI Haitao. Dependence of perforating penetration depth on properties of carbonate reservoir[J]. Explosive Materials, 2020, 49(1): 49–53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8352.2020.01.010
[33] SY/T 5440—2000 天然气井试井技术规范[S]. SY/T 5440—2000 Technical specifications for natural gas well test[S].



 下载:
下载: