Key Drilling Technologies for Ultra-Deep Extended Reach Horizontal Well in Enping 21−4 Oilfield, Eastern South China Sea
-
摘要:
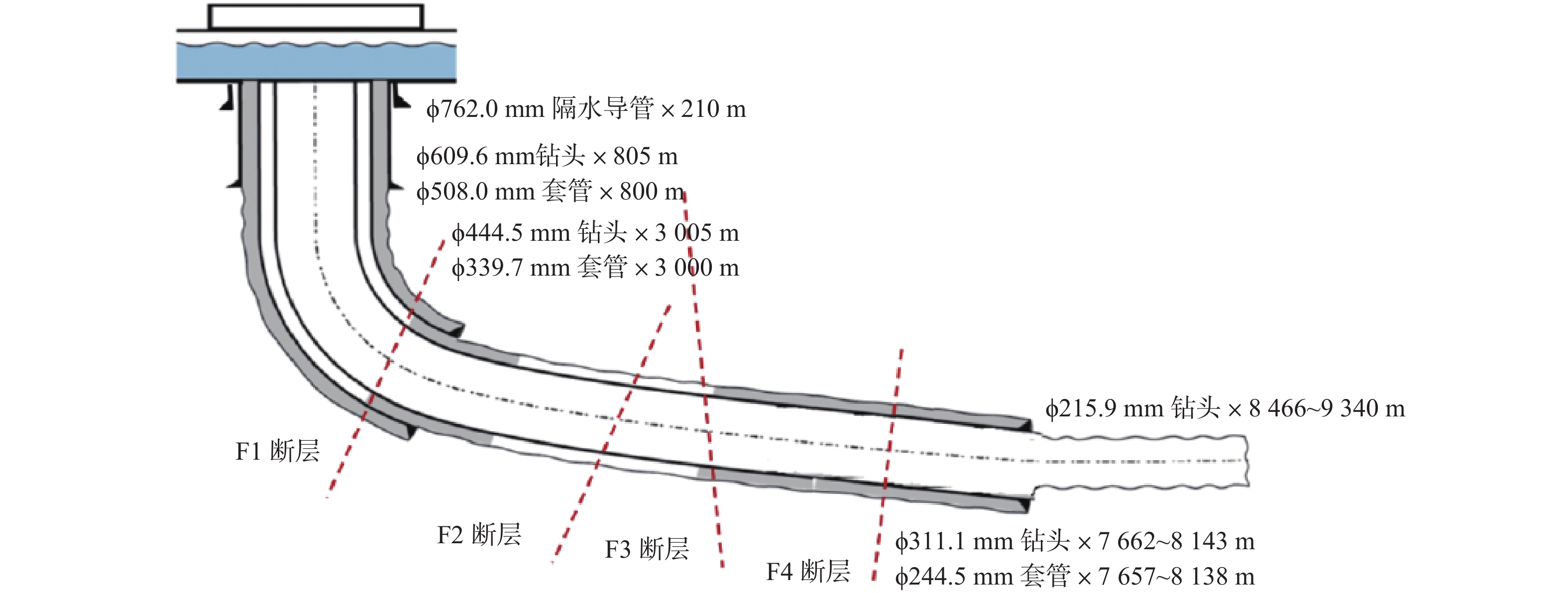
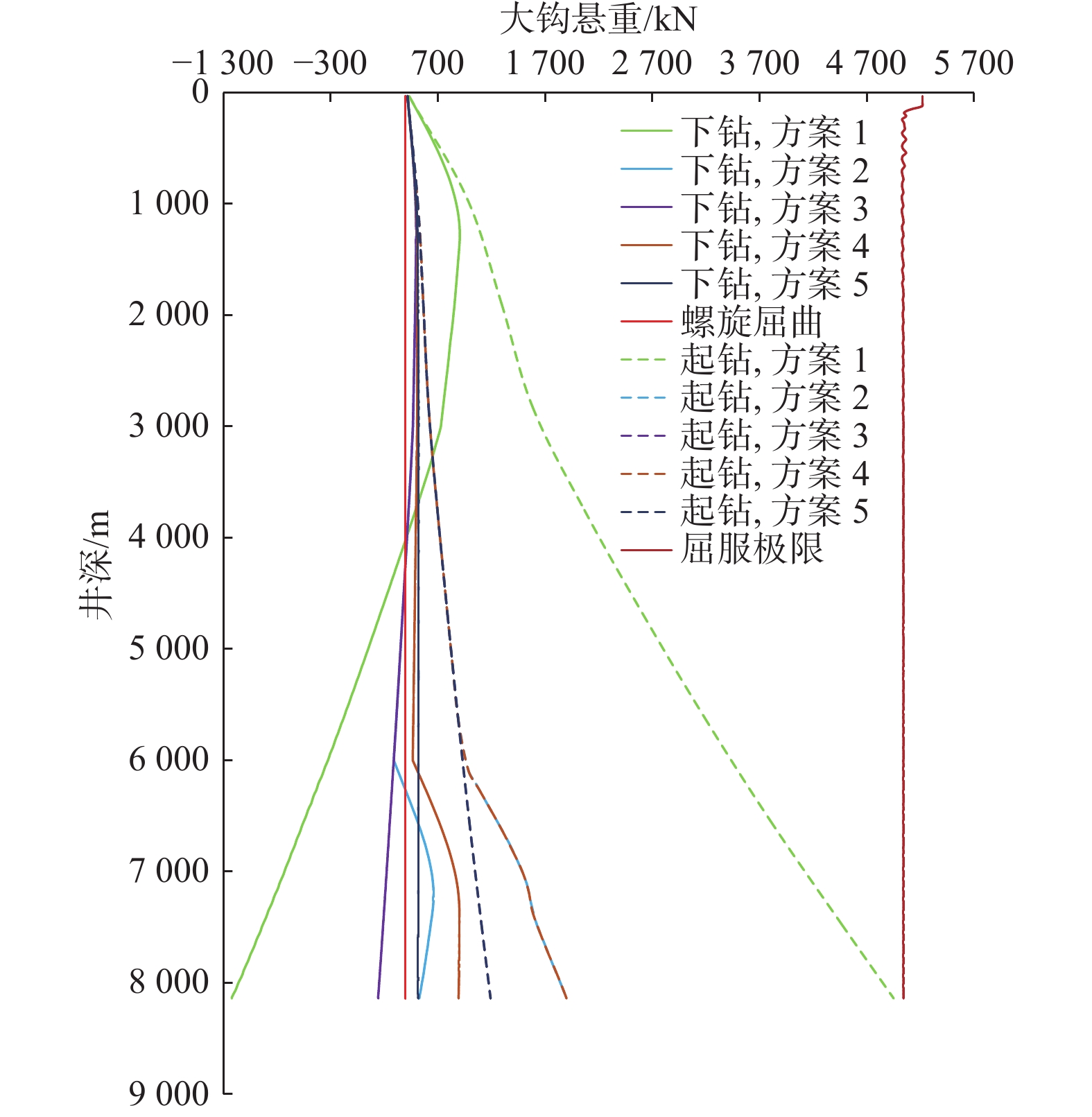
恩平21−4油田位于南海东部海域,储量规模小,为满足其经济高效开发的需求,部署了2口超深大位移井。针对超深大位移井钻完井过程中存在的井漏风险高、井眼轨迹控制困难、井眼清洁难度大、安全作业密度窗口窄和摩阻扭矩高等技术难点,开展了井眼轨道优化设计及井眼轨迹精准控制、钻井液和水泥浆体系优化设计、套管安全下入、动态监测辅助诊断技术和完井管柱抗磨减阻技术等技术攻关研究,形成了超深大位移井钻完井关键技术,确保了2口超深大位移井顺利完钻和投产。其中恩平21−4−A1H井完钻井深9 508.00 m,水平位移8 689.00 m,水垂比4.43,创我国海上油气田井深最深纪录。恩平21−4油田超深大位移井钻完井关键技术不但丰富完善了我国大位移井技术体系,也为万米级边际油田高效开发提供了有力的技术支撑。
Abstract:The Enping 21−4 Oilfield, located in the eastern part of the South China Sea, has limited reserves. In order to meet the needs of economic and efficient development, two ultra-deep extended reach wells have been deployed.To address the challenges such as high risk of lost circulation, difficult trajectory control, poor wellbore cleaning efficiency, narrow safety density window, and high friction and torque in the ultra-deep extended reach wells during drilling and completion, a series of technologies were developed and applied. These technologies include wellbore trajectory design and precise control, drilling fluid and cement slurry system optimization, safe casing running, dynamic monitoring auxiliary diagnosis technology, and anti-wear friction-reducing completion strings solution. These innovations establish the key drilling and completion technologies for ultra-deep extended reach wells, ensuring the smooth drilling and production of these two wells. Notably, Well Enping 21−4−A1H achieved a total depth of 9 508.0 m with a horizontal displacement of 8 689.0 m, and the ratio of horizontal displacement to vertical depth is 4.43, which sets a new record for the deepest offshore oil and gas well in China. The key technologies for drilling and completion of ultra-deep extended reach wells applied in Enping 21−4 Oilfield not only enrich and improve the technical system of China’s extended reach wells but also provide robust technical support for the efficient development of 10 000-meter-class marginal oilfields.
-
-
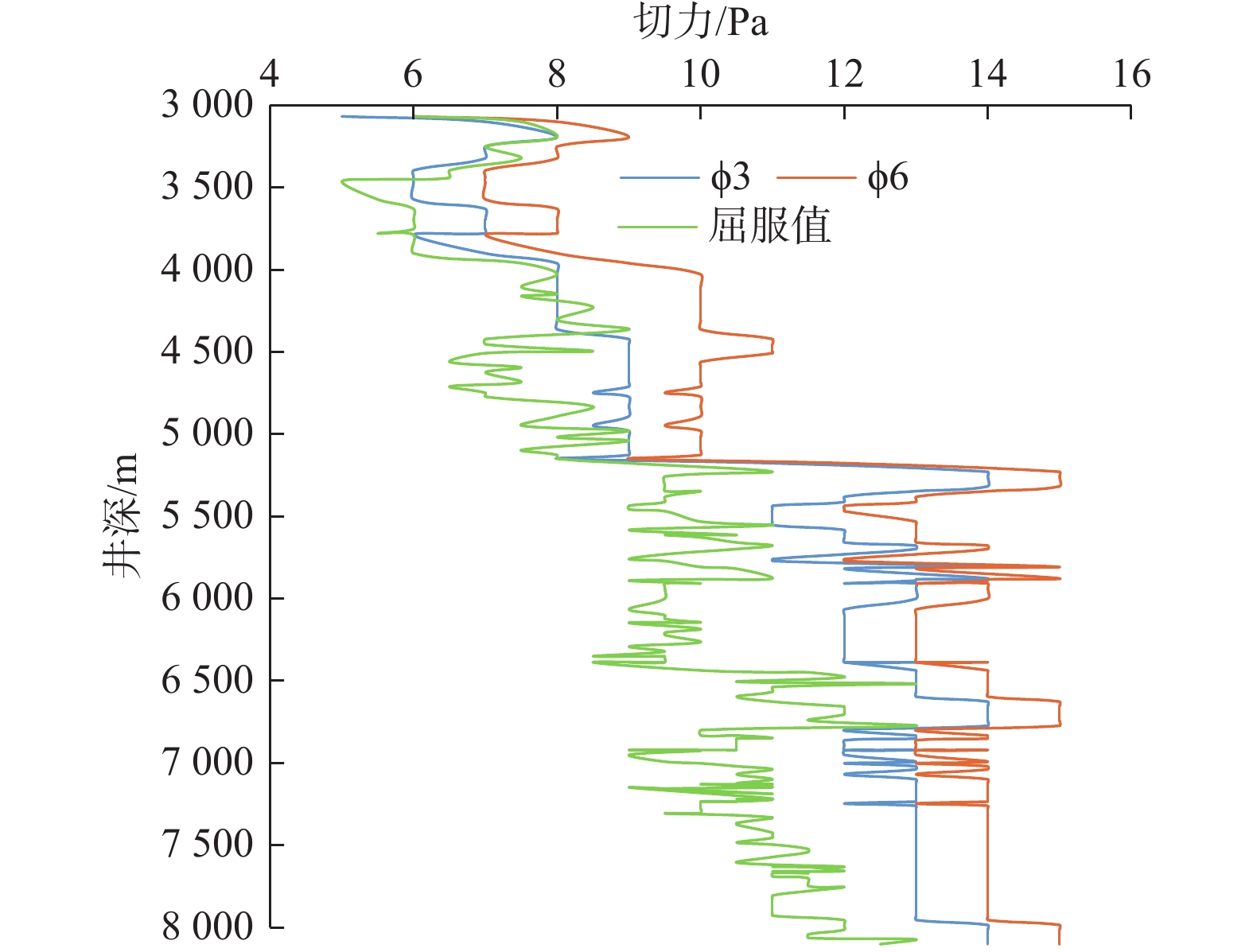
表 1 合成基钻井液与常规油基钻井液模拟ECD和摩阻系数对比
Table 1 Comparison of simulated ECD and friction coefficient between synthetic-based drilling fluid and conventional oil-based drilling fluid
井眼/mm ECD/(kg·L−1) 摩阻系数 合成基
钻井液常规油基
钻井液合成基
钻井液常规油基
钻井液311.1 1.45 1.52 0.17~0.20 0.20~0.25 215.9 1.48 1.58 0.15~0.18 0.18~0.22 表 2 固井水泥浆体系首浆和尾浆性能
Table 2 Properties of head and tail cementing slurry
水泥浆 密度/(kg·L−1) 黏度计读数 API滤失/mL 稠化时间①/h 自由液,% 造浆率② 抗压强度③/kPa 首浆 1.28 6/9/36/50/63 102 14.3 0 299.62 1 584.7 尾浆 1.50 5/8/64/109/155 48 9.5 0 129.41 13 986.7 注:①测试温度为90℃;②单位为L/100kg水泥;③测试条件为温度80 ℃、候凝时间48 h。 表 3 2口超深大位移井创造钻完井纪录情况
Table 3 Drilling and completion records of 2 ultra-deep extended reach wells
序号 纪录范围 纪录名称 现纪录 1 全国 海上井深最深(生产井) 9 508 m 2 全国 水平位移最大 8 689 m 3 全国 ϕ311.1 mm井段最长 8 131 m 4 全国 ϕ244.5 mm套管下深最深 8 125 m 5 中国海油 井深最深(生产井) 9 508 m 6 中国海油 水平位移最大的井 8 689 m 7 中国海油 ϕ311.1 mm井段最长 8 131 m 8 中国海油 ϕ244.5 mm套管下深最深井 8 125 m 9 中国海油 裸眼段最长 5 124 m 10 中国海油 9 501~10 000 m井深水平井
最短钻井周期107.83 d 11 中国海油 9 501~10 000 m井深防砂水平井
最短作业周期(仅下筛管)7.54 d 12 中国海油 8 501~9 000 m井深水平井
最短钻井周期81.05 d 13 中国海油 8 501~9 000 m井深防砂水平井
最短作业周期(仅下筛管)7.50 d -
[1] 吴林强,张涛,徐晶晶,等. 全球海洋油气勘探开发特征及趋势分析[J]. 国际石油经济,2019,27(3):29–36. WU Linqiang, ZHANG Tao, XU Jingjing, et al. Characteristics and trends of global offshore oil and gas exploration and develop-ment[J]. International Petroleum Economics, 2019, 27(3): 29–36.
[2] 杨进,李磊,宋宇,等. 中国海洋油气钻井技术发展现状及展望[J]. 石油学报,2023,44(12):2308–2318. YANG Jin, LI Lei, SONG Yu, et al. Current status and prospects of offshore oil and gas drilling technology development in China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2023, 44(12): 2308–2318.
[3] 杨进,傅超,刘书杰,等. 中国深水钻井关键技术与装备现状及展望[J]. 世界石油工业,2024,31(4):69–80. YANG Jin, FU Chao, LIU Shujie, et al. Current status and prospects of key technologies and equipment for deepwater drilling in China[J]. World Petroleum Industry, 2024, 31(4): 69–80.
[4] 张海山. 中国海洋石油大位移井钻井技术现状及展望[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2023,45(1):1–11. ZHANG Haishan. Status and prospect of CNOOC’s extended reach well drilling technologies[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2023, 45(1): 1–11.
[5] 黄熠,刘和兴,刘智勤,等. 南海西部浅层大位移水平井钻井关键技术与实践[J]. 中国海上油气,2023,35(6):115–123. HUANG Yi, LIU Hexing, LIU Zhiqin, et al. Key drilling technologies and practices of shallow extended reach well in western South China Sea[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2023, 35(6): 115–123.
[6] 张磊,张羽臣,董平华,等. 渤海油田浅层大位移水平井钻井关键技术研究[J]. 非常规油气,2022,9(1):10–17. ZHANG Lei, ZHANG Yuchen, DONG Pinghua, et al. Research on key drilling technology of shallow extended reach horizontal well in Bohai Oilfield[J]. Unconventional Oil & Gas, 2022, 9(1): 10–17.
[7] 林四元,张杰,韩成,等. 东方气田浅部储层大位移水平井钻井关键技术[J]. 石油钻探技术,2019,47(5):17–21. LIN Siyuan, ZHANG Jie, HAN Cheng, et al. Key technology for horizontal well of extended reach drilling in the shallow reservoirs of the Dongfang Gas Field[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2019, 47(5): 17–21.
[8] 魏宏安,张武辇,唐海雄. 超大水垂比大位移井钻井技术[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2005,27(1):1–5. WEI Hongan, ZHANG Wunian, TANG Haixiong. Drilling technology of extended-reach well with ultra-high horizontal displacement to vertical depth ratio[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2005, 27(1): 1–5.
[9] MA Tianshou, CHEN Ping, ZHAO Jian. Overview on vertical and directional drilling technologies for the exploration and exploitation of deep petroleum resources[J]. Geomechanics and Geophysics for Geo-Energy and Geo-Resources, 2016, 2(4): 365–395.
[10] 苏义脑,窦修荣. 大位移井钻井概况、工艺难点和对工具仪器的要求[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2003,25(1):6–10. SU Yinao, DOU Xiurong. General condition and technical difficulties of extended reach well drilling and its requirements on tools and instruments[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2003, 25(1): 6–10.
[11] 高德利,黄文君,刁斌斌,等. 复杂结构井定向钻井技术现状及展望[J]. 前瞻科技,2023,2(2):11–21. GAO Deli, HUANG Wenjun, DIAO Binbin, et al. Current status and prospect of directional drilling technologies for complex wells[J]. Science and Technology Foresight, 2023, 2(2): 11–21.
[12] 张强,秦世利,饶志华,等. 南海超大水垂比大位移M井钻井关键技术[J]. 石油钻探技术,2021,49(5):19–25. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2021045 ZHANG Qiang, QIN Shili, RAO Zhihua, et al. Key drilling technologies in extended-reach Well M with ultra-high HD/VD ratio in the South China Sea[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2021, 49(5): 19–25. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2021045
[13] 刘永峰,朱娜,高德利,等. 南海东部大位移井岩屑床动态运移与参数优化[J]. 石油机械,2022,50(6):36–43. LIU Yongfeng, ZHU Na, GAO Deli, et al. Dynamic transportation and parameter optimization of cuttings bed in extended reach wells in the east of South China sea[J]. China Petroleum Machinery, 2022, 50(6): 36–43.
[14] ZHANG Feifei, WANG Yidi, WANG Yuezhi, et al. Modeling of dynamic cuttings transportation during drilling of oil and gas wells by combining 2D CFD and 1D discretization approach[J]. SPE Journal, 2020, 25(3): 1220–1240.
[15] 冯光通,马凤清,曹向峰,等. 高平1井井眼轨道与井身结构设计[J]. 石油钻探技术,2010,38(6):33–36. FENG Guangtong, MA Fengqing, CAO Xiangfeng, et al. The trajectory and casing program design of Well Gaoping 1[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2010, 38(6): 33–36.
[16] 宋执武,高德利,李瑞营. 大位移井轨道设计方法综述及曲线优选[J]. 石油钻探技术,2006,34(5):24–27. SONG Zhiwu, GAO Deli, LI Ruiying. Summary and optimization of extended-reach-well trajectory design methods[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2006, 34(5): 24–27.
[17] MAHMOUD H, HAMZA A, NASSER M S, et al. Hole cleaning and drilling fluid sweeps in horizontal and deviated wells: comprehensive review[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 186: 106748.
[18] GUO Xiaole, WANG Zhiming, LONG Zhihui. Study on three-layer unsteady model of cuttings transport for extended-reach well[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2010, 73(1/2): 171–180.
[19] 谢彬强,邱正松,黄维安,等. 大位移井钻井液关键技术问题[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2012,29(2):76–82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2012.02.025 XIE Binqiang, QIU Zhengsong, HUANG Weian, et al. Summary on key technical issues of drilling fluid for extended reach well[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2012, 29(2): 76–82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2012.02.025
[20] 邢希金,王涛,刘伟,等. 超深大位移井井壁稳定及储层保护技术与应用[J]. 中国海上油气,2023,35(5):154–163. XING Xijin, WANG Tao, LIU Wei, et al. Research and application of drilling risk prevention and control measures in ultra-deep extended-reach wells[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2023, 35(5): 154–163.
[21] 田志欣,王志伟. 全漂浮旋转下套管技术在大位移井中的应用[J]. 石油天然气学报,2018,40(6):53–58. doi: 10.12677/JOGT.2018.406119 TIAN Zhixin, WANG Zhiwei. The application of rotary casing running technology with full-floating in extended reach wells[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2018, 40(6): 53–58. doi: 10.12677/JOGT.2018.406119
[22] HUANG Wenjun, GAO Deli. Combined effects of wellbore curvature, connector, and friction force on tubular buckling behaviors[J]. SPE Journal, 2019, 24(5): 2083–2096. doi: 10.2118/195680-PA
[23] 高德利,黄文君,李鑫. 大位移井钻井延伸极限研究与工程设计方法[J]. 石油钻探技术,2019,47(3):1–8. GAO Deli, HUANG Wenjun, LI Xin. Research on extension limits and engineering design methods for extended reach drilling[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2019, 47(3): 1–8.
[24] 喻贵民,霍宏博,谢涛,等. 渤海超大位移井水平段裸眼延伸极限预测及影响因素分析[J]. 断块油气田,2023,30(2):337–346. YU Guimin, HUO Hongbo, XIE Tao, et al. Prediction of open-hole extension limit and influencing factors analysis of horizontal section of mega-extended-reach well in Bohai Sea[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2023, 30(2): 337–346.
[25] 祝效华,李柯,安家伟. 水平井钻柱动态摩阻扭矩计算与分析[J]. 天然气工业,2018,38(8):75–82. ZHU Xiaohua, LI Ke, AN Jiawei. Calculation and analysis of dynamic drag and torque of horizontal well strings[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2018, 38(8): 75–82.
[26] 汪志明,郭晓乐. 大位移井水力延伸极限研究[J]. 钻采工艺,2008,31(4):1–3. WANG Zhiming, GUO Xiaole. Hydraulic extended limitation of extended-reach well[J]. Drilling & Production Technology, 2008, 31(4): 1–3.



 下载:
下载: