Enhanced Tight Plugging Water-Based Drilling Fluid Technology for Hard and Brittle Shales in Junggar Basin
-
摘要:
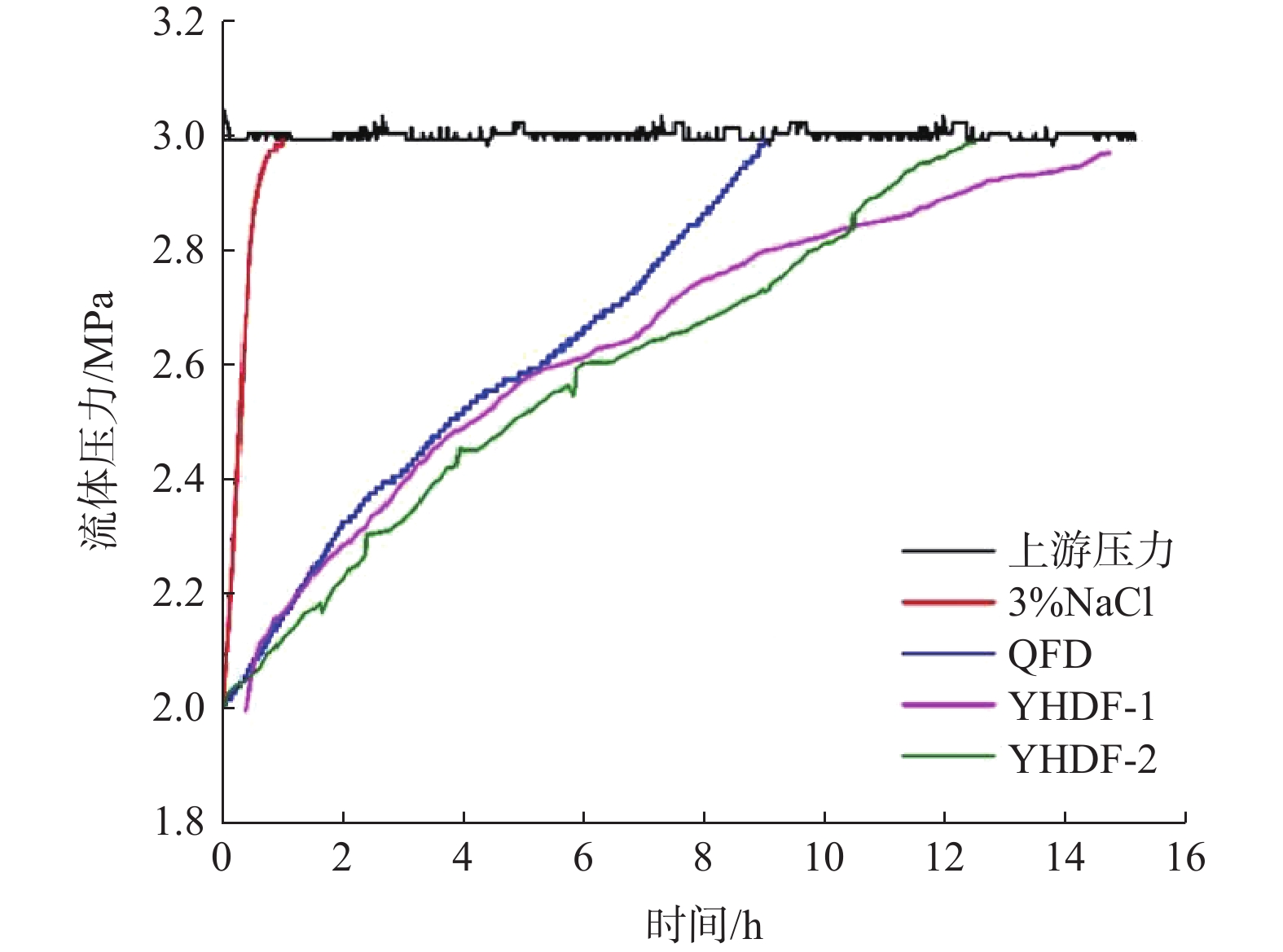
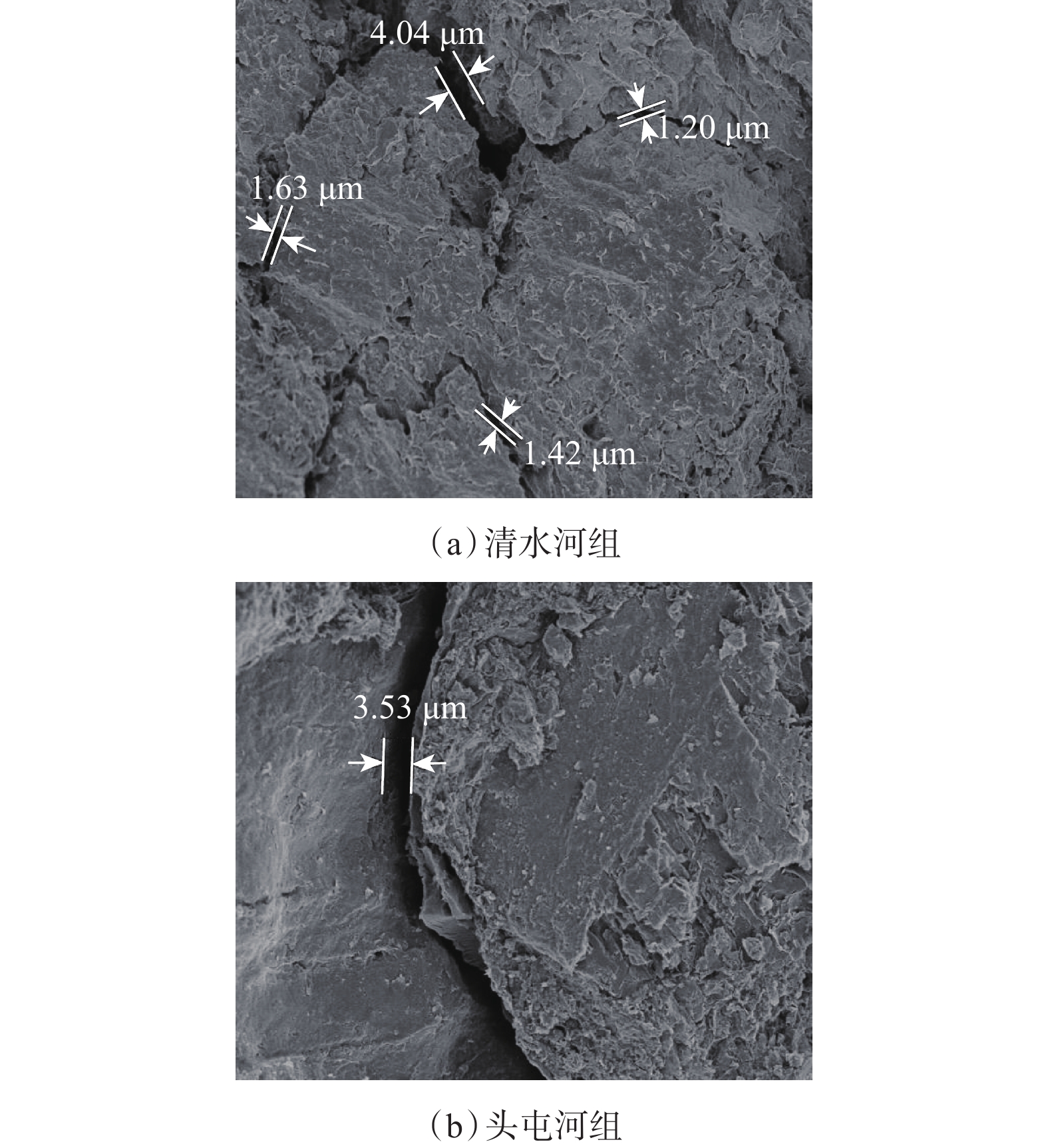
为解决准噶尔盆地硬脆性页岩地层井壁失稳的问题,在分析准噶尔盆地硬脆性页岩矿物组成与组构特征的基础上,根据多元协同井壁稳定理论,提出了以多尺度致密封堵为核心的协同稳定井壁技术对策,构建了多尺度致密封堵水基钻井液YHDF-1和YHDF-2。矿物组成和组构特征分析结果得知,准噶尔盆地硬脆性页岩地层井壁失稳与“微裂缝–裂隙–孔隙”的多尺度特征密切相关,加强封堵微纳米尺度缝隙,提高抑制页岩表面水化的能力,发挥合理密度钻井液有效应力支撑井壁的作用,才能协同强化稳定井壁。性能评价结果表明,多尺度致密封堵水基钻井液YHDF-1和YHDF-2可耐150 ℃高温,其400 mD砂盘的PPA滤失量分别为17.8和13.2 mL,可使页岩的渗透率降低90%以上。钻井液YHDF-1和YHDF-2分别在准噶尔盆地的D-72井和D-12井进行了现场试验,钻井过程中均未出现井壁失稳现象,试验井段平均井径扩大率均小于10.0%,电测均一次成功。研究和现场试验结果表明,多尺度致密封堵水基钻井液YHDF-1和YHDF-2具有优异的封堵防塌性能,可以解决准噶尔盆地硬脆性页岩地层井壁失稳的问题。
Abstract:In order to solve the problem of wellbore instability in hard and brittle shale formations in Junggar Basin, the characteristics of mineral compositions and structural fabric of shale were analyzed, and the technology strategy with multi-scale tight plugging as the core was proposed according to the multivariate synergistic principle for wellbore stability. Furthermore, water-based drilling fluids (YHDF-1, YHDF-2) with multi-scale tight plugging were developed. From the analysis results of the mineral compositions and structural fabric characteristics, it is known that the wellbore instability of hard and brittle shales was closely related to its multi-scale characteristics of “microfracture–fissure–pore”. Therefore, the wellbore stability could be enhanced by plugging micro-nano scale fractures, improving shale hydration inhibitive ability, and offering effective stress support of drilling fluids with reasonable density. Performance evaluation results showed that YHDF-1 and YHDF-2 drilling fluids could withstand a high temperature up to 150 °C, and their PPA filtration volumes in a 400 mD sand disc were 17.8 mL and 13.2 mL respectively, with the shale permeability reduced by above 90%. YHDF-1 and YHDF-2 drilling fluids were applied in the drilling operation of Well D-72 and D-12 in Junggar Basin, and no wellbore instability occurred during the drilling process. The average well diameter enlargement rate was lower than 10% in all the test well sections, and the electrical logging was achieved successfully at a time. Research and field tests show that YHDF-1 and YHDF-2 drilling fluids exhibit excellent performance in plugging and collapse prevention, and can be used to deal with the wellbore instability of hard and brittle shale in Junggar Basin.
-
-
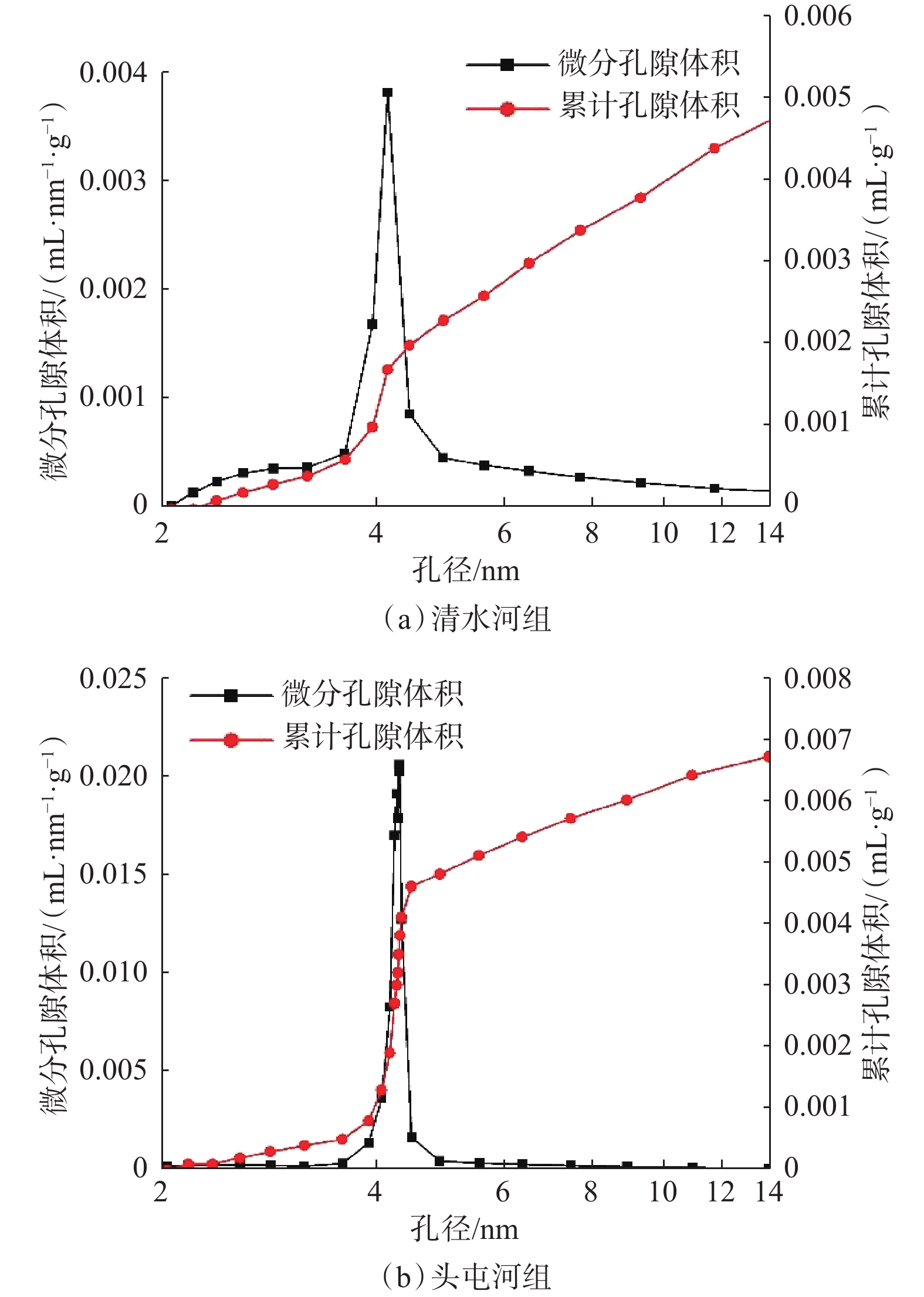
表 1 准噶尔盆地清水河组、头屯河组页岩全岩矿物分析结果
Table 1 Whole-rock mineral analysis results of shales from Qingshuihe Formation and Toutunhe Formation in Junggar Basin
地层 全岩矿物含量,% 脆性
指数石英 斜长石 方解石 白云石 菱铁矿 赤铁矿 黏土矿物 清水
河组30 8 2 3 1 3 53 0.4839 32 9 2 4 2 51 0.5424 34 7 1 5 4 49 0.5763 头屯
河组34 15 10 3 3 4 31 0.6667 33 13 8 3 5 38 0.6111 29 11 10 5 2 8 35 0.4833 表 2 准噶尔盆地清水河组、头屯河组页岩黏土矿物分 析结果
Table 2 Clay mineral analysis results of shales of Qingshuihe Formation and Toutunhe Formation in Junggar Basin
地层 黏土矿物相对含量,% 高岭石 绿泥石 伊利石 伊/蒙混层 间层比 清水河组 1 0 2 97 75 1 0 1 98 70 2 0 1 97 75 头屯河组 2 3 7 88 65 2 3 9 86 65 2 3 5 90 70 表 3 钻井液流变性和滤失性评价结果
Table 3 Evaluation results of rheology and filtration of drilling fluids
配方 测试
条件表观黏度/
(mPa·s)塑性黏度/
(mPa·s)动切力/
Pa静切力/
PaAPI滤失量/mL 高温高压滤失量/mL pH值 YHDF-1 老化前 78.0 63.5 14.5 3.5/8.5 1.6 11 老化后 64.0 54.0 10.0 2.5/7.5 1.4 5.8 10 YHDF-2 老化前 78.0 64.0 14.0 6.0/12.0 2.0 11 老化后 74.0 63.0 11.0 5.0/9.5 1.4 6.4 10 注:老化条件为在温度150 ℃下滚动16 h,高温高压滤失量测试条件为150 ℃/3.5 MPa。 -
[1] 陈建平,王绪龙,邓春萍,等. 准噶尔盆地油气源、油气分布与油气系统[J]. 地质学报,2016,90(3):421–450. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.03.002 CHEN Jianping, WANG Xulong, DENG Chunping, et al. Oil and gas source, occurrence and petroleum system in the Junggar Basin, Northwest China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2016, 90(3): 421–450. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.03.002
[2] 张雄,余进,毛俊,等. 准噶尔盆地玛东油田水平井高性能油基钻井液技术[J]. 石油钻探技术,2020,48(6):21–27. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2020106 ZHANG Xiong, YU Jin, MAO Jun, et al. High-performance oil-based drilling fluid technology for horizontal wells in the Madong Oilfield, Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2020, 48(6): 21–27. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2020106
[3] 张尚明,程中疆,金萍,等. 准噶尔盆地西北缘车排7井区八道湾组顶部有利储层分布预测[J]. 特种油气藏,2021,28(3):40–46. doi: 1 ZHANG Shangming, CHENG Zhongjiang, JIN Ping, et al. Prediction of favorable reservoir distribution on the top of Badaowan For-mation in Wellblock Chepai7, northwestern margin, Junggar Ba-sin[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2021, 28(3): 40–46. doi: 1
[4] 付超胜,敖天,余加水,等. 强封堵防塌剂 XZ-OSD 在准噶尔盆地南缘山前构造带的现场应用[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2021,38(4):469–473. doi: 10.12358/j.issn.1001-5620.2021.04.011 FU Chaosheng, AO Tian, YU Jiashui, et al. Field application of a plugging borehole wall anti-collapse agent XZ-OSD in the piedmont structural belt on the south margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2021, 38(4): 469–473. doi: 10.12358/j.issn.1001-5620.2021.04.011
[5] 张凤奇,鲁雪松,卓勤功,等. 准噶尔盆地南缘下组合储层异常高压成因机制及演化特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2020,41(5):1004–1016. doi: 10.11743/ogg20200511 ZHANG Fengqi, LU Xuesong, ZHUO Qingong, et al. Genetic mechanism and evolution characteristics of overpressure in the lower play at the southern margin of the Junggar Basin, Northwestern China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(5): 1004–1016. doi: 10.11743/ogg20200511
[6] 梁舒艺,洪扬,崔立杰. 盆腹区张扭断裂带与盆缘造山带成因关系及油气成藏控制:以准噶尔盆地盆1井西凹陷东环带侏罗系为例[J]. 断块油气田,2021,28(6):805–809. doi: 10.6056/dkyqt202106016 LIANG Shuyi,HONG Yang,CUI Lijie. Genetic relationship between transtensional fault zones in the hinterland of the basin and orogenic belts in the margin of the basin and its control on hydrocarbon accumulation:a case study of Jurassic in the east belt around Pen-1 well west sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2021, 28(6): 805–809. doi: 10.6056/dkyqt202106016
[7] 李忠慧,楼一珊,王兆峰,等. 地层压力预测技术在准噶尔盆地钻井中的应用[J]. 天然气工业,2009,29(8):66–68. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2009.08.021 LI Zhonghui, LOU Yishan, WANG Zhaofeng, et al. Application of formation pressure prediction technology to drilling in Junggar Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2009, 29(8): 66–68. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2009.08.021
[8] 伊明,黄志强,张景虹,等. 准噶尔盆地南缘高泉构造三维地质力学建模及深探井风险应用[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2021,43(1):21–28. YI Ming, HUANG Zhiqiang, ZHANG Jinghong, et al. Three-dimensional geomechanical modeling of Gaoquan structure along the southern margin of the Junggar Basin and its application to the risk evaluation of deep exploration wells[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2021, 43(1): 21–28.
[9] 路宗羽,赵飞,雷鸣,等. 新疆玛湖油田砂砾岩致密油水平井钻井关键技术[J]. 石油钻探技术,2019,47(2):9–14. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2019029 LU Zongyu, ZHAO Fei, LEI Ming, et al. Key technologies for drilling horizontal wells in glutenite tight oil reservoirs in the Mahu Oilfield of Xinjiang[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2019, 47(2): 9–14. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2019029
[10] 余加水,周玉东,辛小亮,等. 准噶尔盆地超深井达探1井钻井液技术[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2016,33(4):60–64. YU Jiashui, ZHOU Yudong, XIN Xiaoliang, et al. Drilling fluid technology used in drilling ultra deep well Datan-1 in Junggar Basin[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2016, 33(4): 60–64.
[11] 刘四海. 准噶尔盆地南缘山前构造复杂地层钻井液技术[J]. 石油钻探技术,2003,31(4):33–34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0890.2003.04.015 LIU Sihai. Drilling fluid technologies for complex formations of piedmont structure in the southern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2003, 31(4): 33–34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0890.2003.04.015
[12] 邱春阳,吴晓文,秦涛,等. 准噶尔盆地永进油田井壁稳定钻井液技术研究[J]. 鲁东大学学报(自然科学版),2015(4):375–379. QIU Chunyang, WU Xiaowen, QIN Tao, et al. Drilling fluid technology about borehole stability in Yongjin Oilfield in Junggar Basin[J]. Ludong University Journal(Natural Science Edition), 2015(4): 375–379.
[13] 邱正松,徐加放,吕开河,等. “多元协同”稳定井壁新理论[J]. 石油学报,2007,28(2):117–119. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2007.02.024 QIU Zhengsong, XU Jiafang, LYU Kaihe, et al. A multivariate cooperation principle for well-bore stabilization[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2007, 28(2): 117–119. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2007.02.024
[14] LIU Junyi, QIU Zhengsong, HUANG Weian. Novel latex particles and aluminum complexes as potential shale stabilizer in water-based drilling fluids[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2015, 135: 433–441. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2015.10.003
[15] 王志远,黄维安,范宇,等. 长宁区块强封堵油基钻井液技术研究及应用[J]. 石油钻探技术,2021,49(5):31–38. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2021039 WANG Zhiyuan, HUANG Weian, FAN Yu, et al. Technical research and application of oil base drilling fluid with strong plugging property in Changning Block[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2021, 49(5): 31–38. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2021039
[16] CAI Jihua, CHENEVERT M E, SHARMA M M, et al. Decreasing water invasion into Atoka shale using nonmodified silica nanoparticles[J]. SPE Drilling & Completion, 2012, 27(1): 103–112.
[17] 石崇东,王万庆,史配铭,等. 盐池区块深层页岩气水平井钻井关键技术研究[J]. 石油钻探技术,2021,49(6):23–28. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2021007 SHI Chongdong, WANG Wanqing, SHI Peiming, et al. Research on key drilling technology for horizontal wells in the deep shale gas reservoirs in Yanchi Block[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2021, 49(6): 23–28. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2021007
[18] 于盟,王健,王斐. 适用于辽河致密油地层的高性能钻井液技术[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2020,37(5):578–584. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2020.05.007 YU Meng, WANG Jian, WANG Fei. High performance drilling fluid technology for tight oil formation drilling in Liaohe Oilfield[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2020, 37(5): 578–584. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2020.05.007
[19] 柴金鹏. 准噶尔盆地硬脆性页岩地层防塌钻井液技术研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2018: 26−28. CHAI Jinpeng. Study on anti-sloughing drilling fluid technology for brittle shale formations in Junggar Basin[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum(East China), 2018: 26−28.
[20] 钟汉毅. 聚胺强抑制剂研制及其作用机理研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2012: 108−109. ZHONG Hanyi. Development and mechanism study on high performance polyamine inhibitor in water-based drilling fluid[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum(East China), 2012: 108−109.
[21] 刘均一,郭保雨. 页岩气水平井强化井壁水基钻井液研究[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版),2019,34(2):86–92. LIU Junyi, GUO Baoyu. Study on water-based drilling fluid for strengthening wellbore of horizontal shale gas wells[J]. Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 34(2): 86–92.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 刘献博,薛亮,刘敏,王智明,张峥,邵天宇. 连续波钻井液脉冲发生器压力波波形优化研究. 石油机械. 2020(12): 44-51 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)



 下载:
下载: