Simulation Study on the Key Parameters Affecting Pressure-Controlled Drainage Effect
-
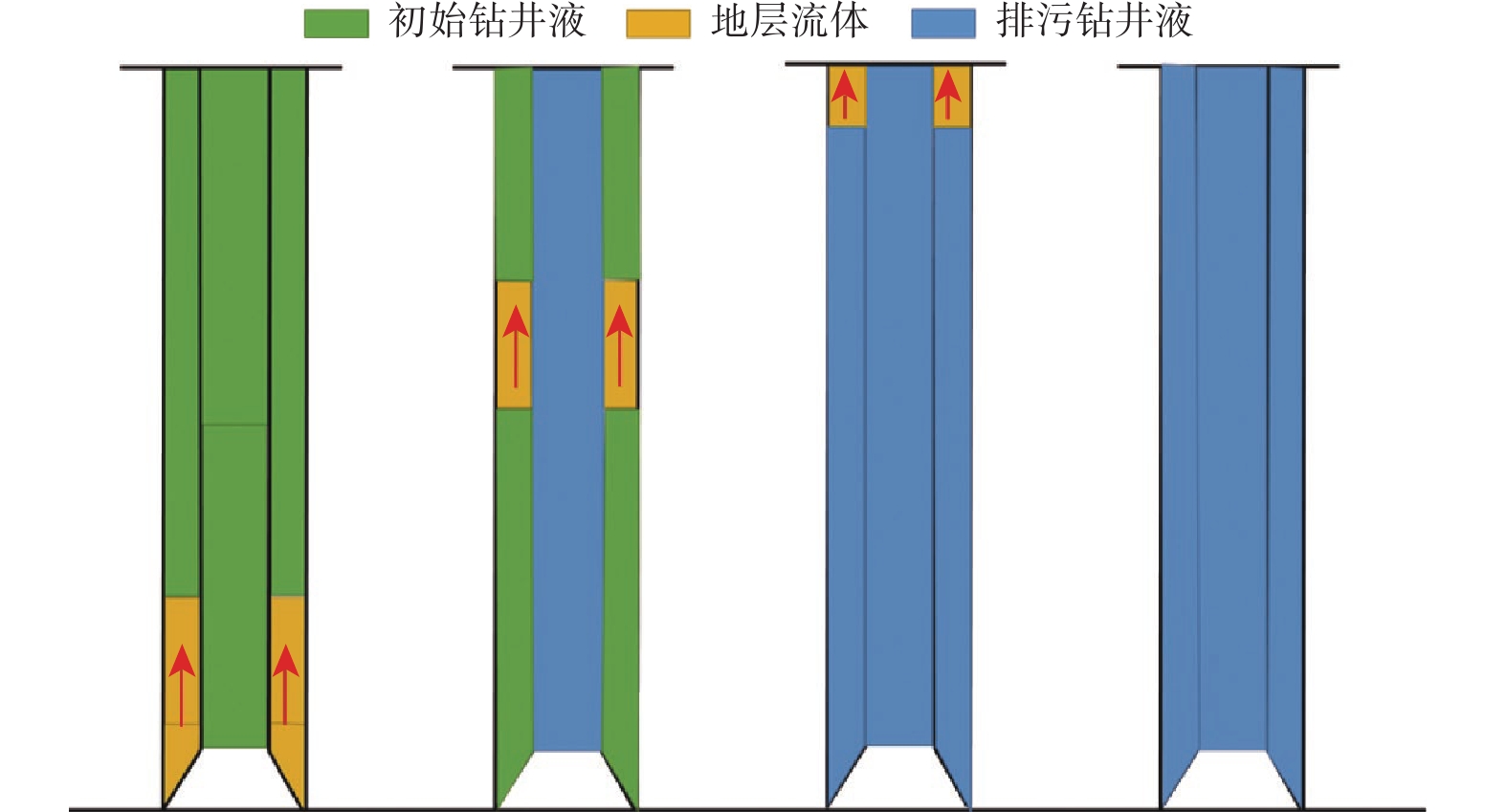
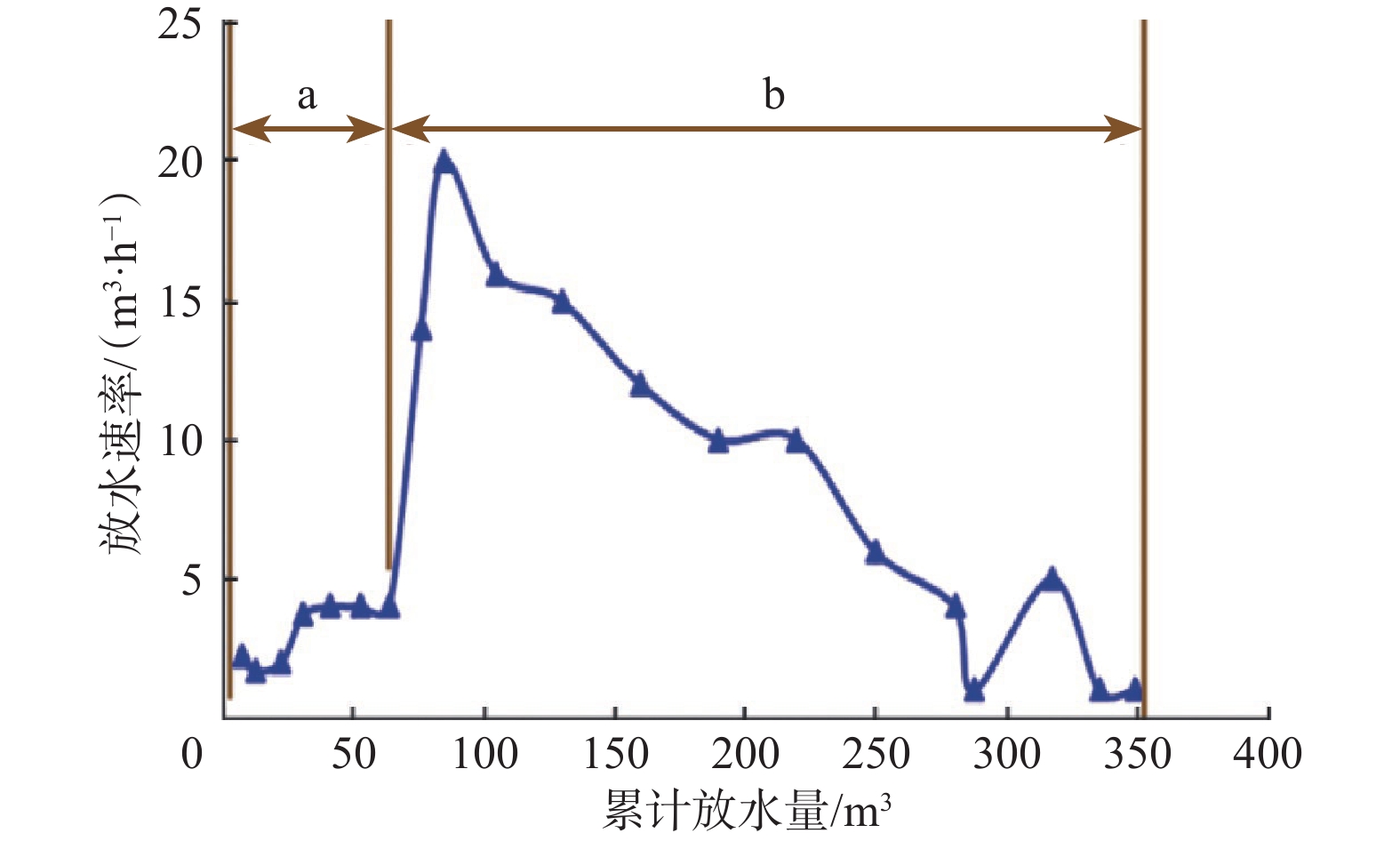
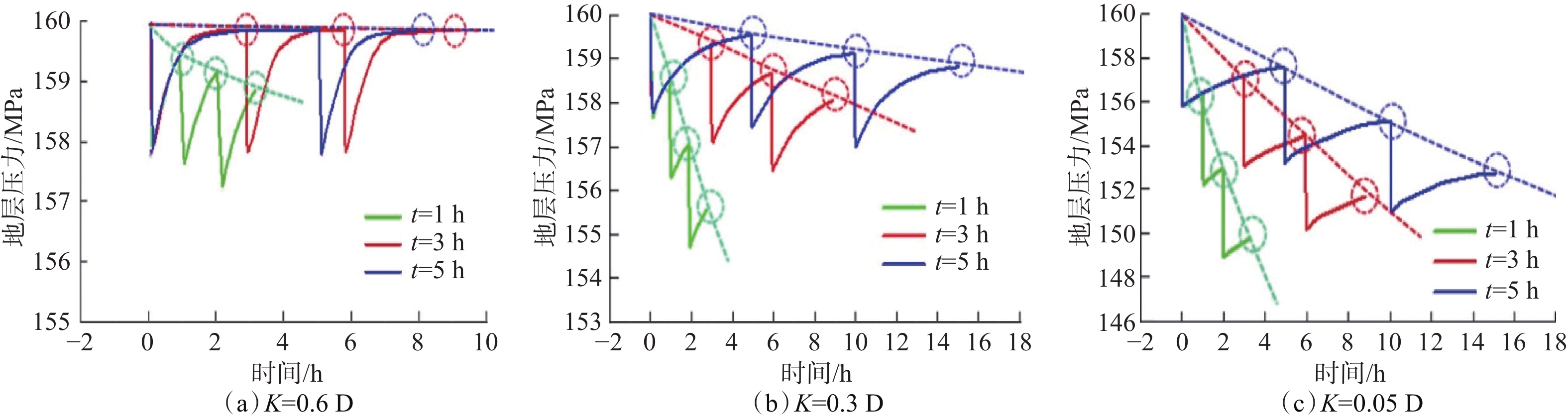
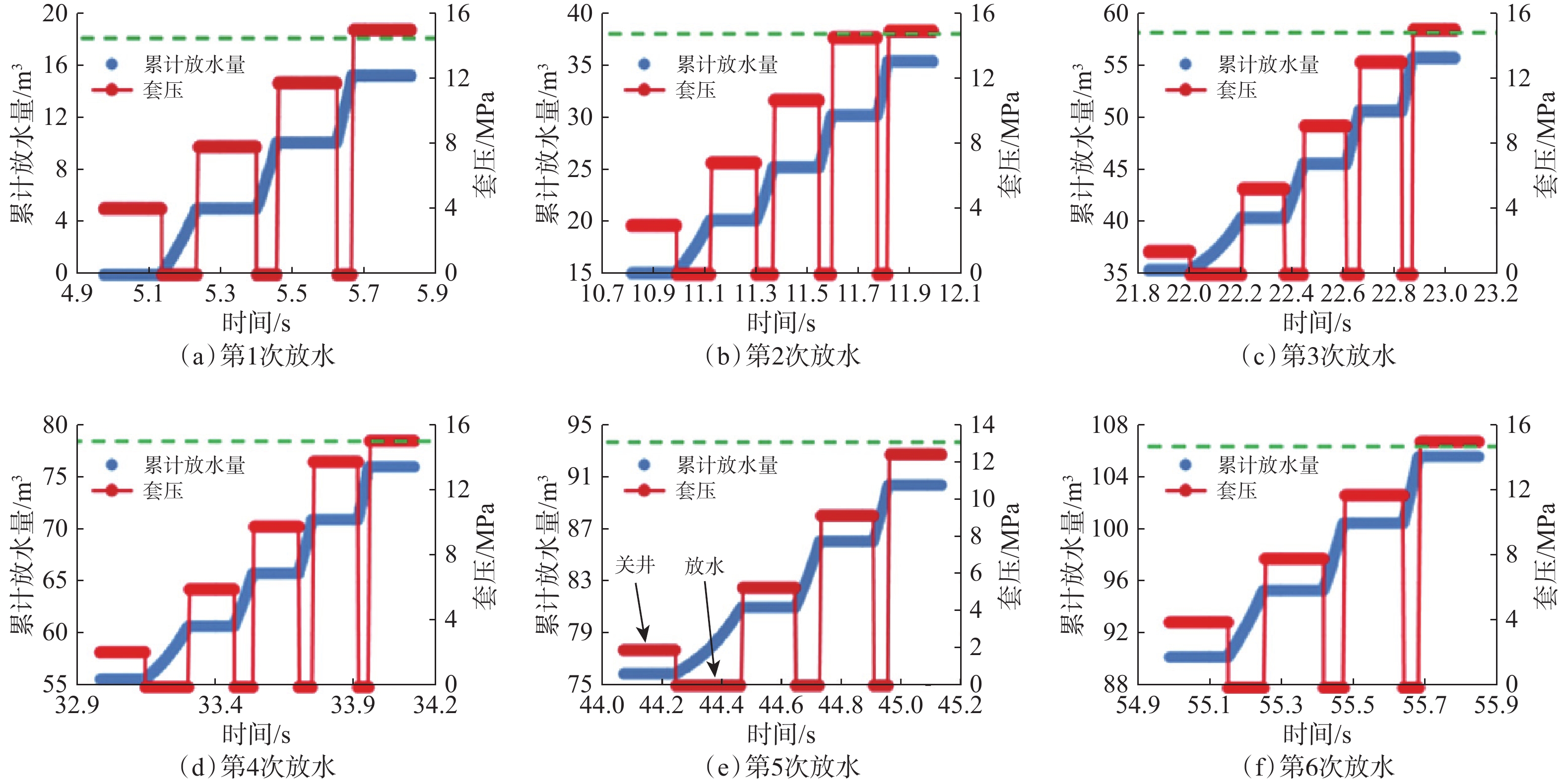
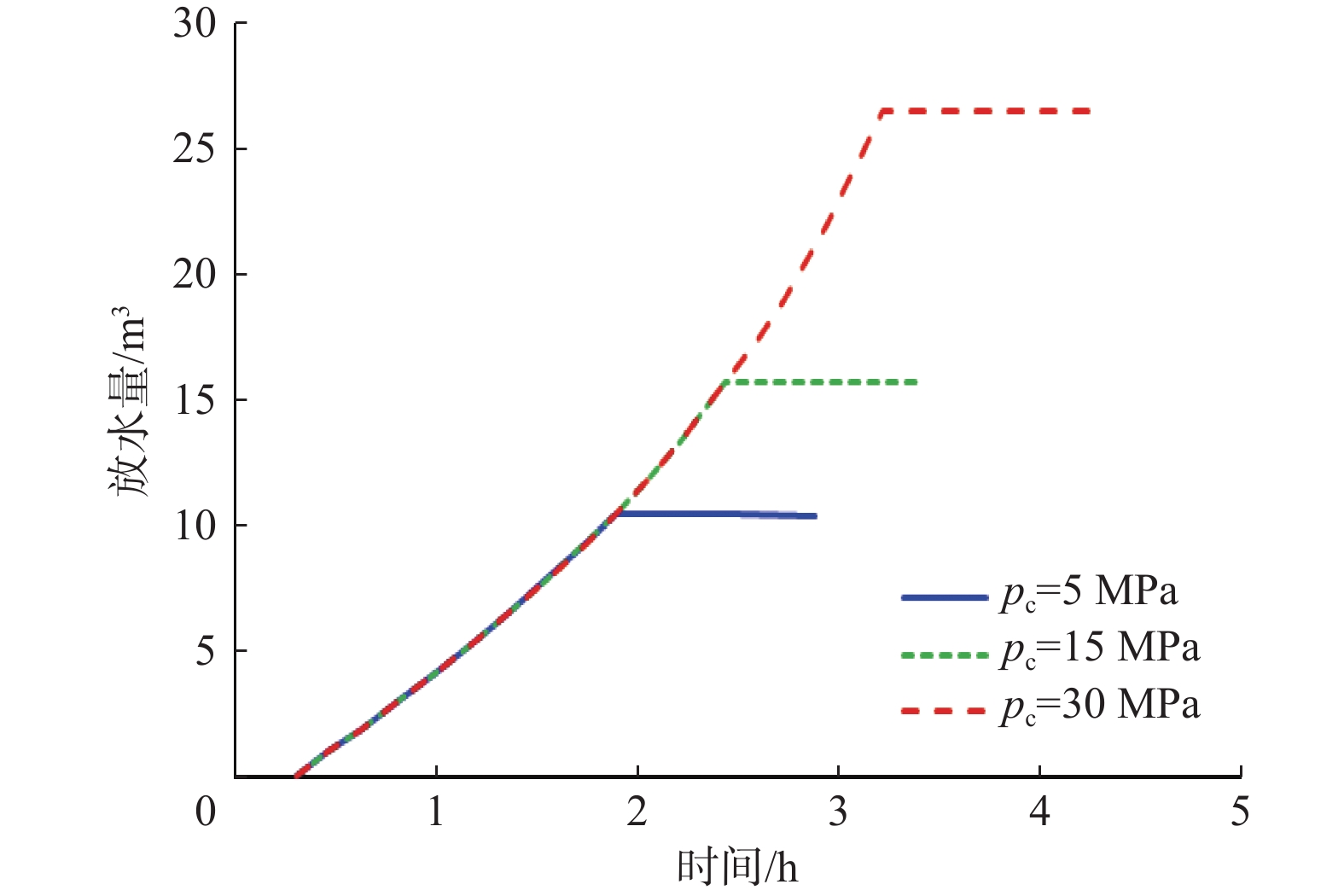
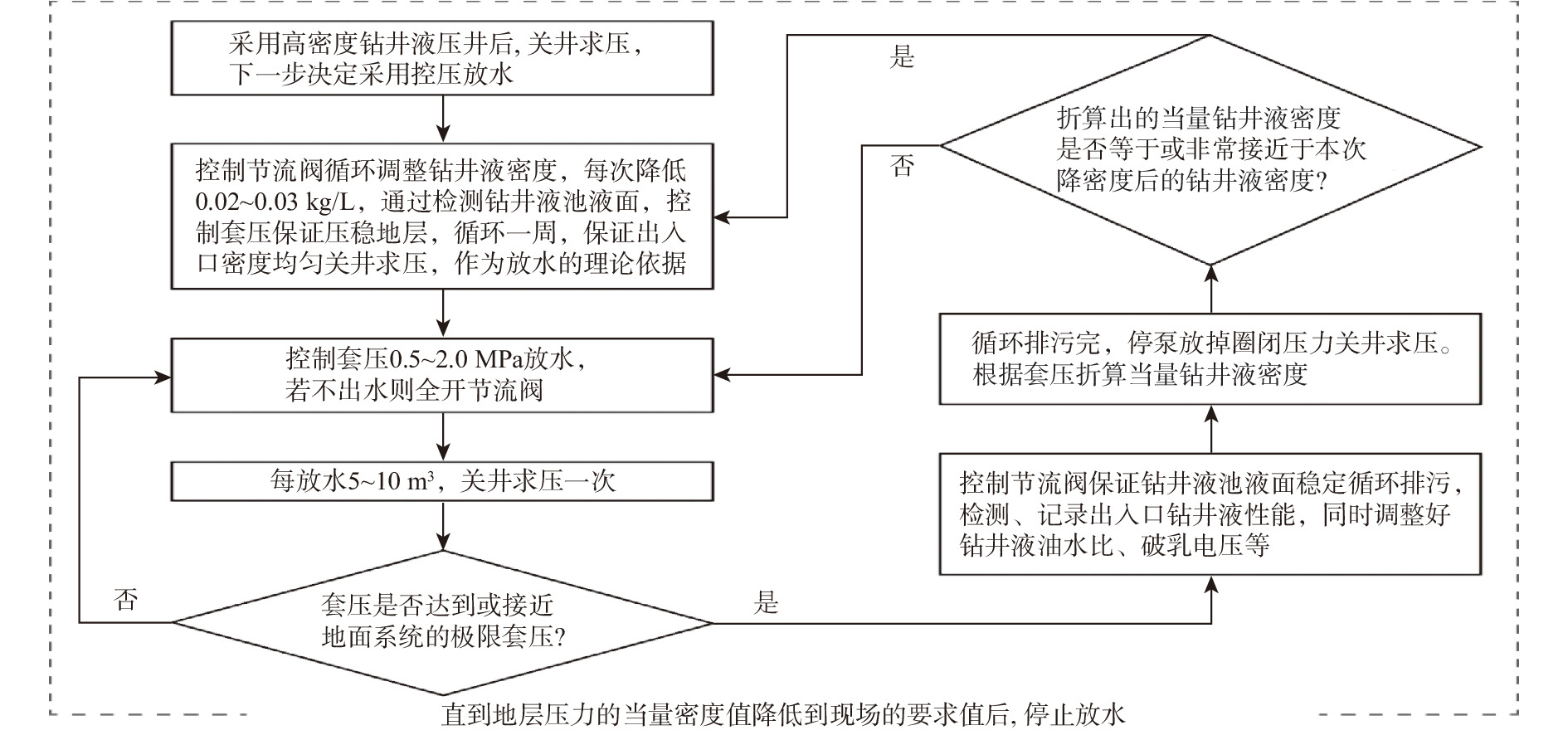
摘要: 控压放水可以有效降低高压盐水层的地层压力,但不清楚施工过程中一些关键参数对控压放水效果的影响程度。为此,分析了控压放水的技术特征、工艺特点,总结了控压放水的工艺流程;基于地层盐水渗流和井筒流动理论,考虑关井期间地层压力的恢复,建立了参数动态变化、可以模拟控压放水全过程的数学模型。以塔里木油田克深A井为例,进行了模拟计算,模拟结果与实测结果误差较小。分析影响放水效果和周期的关键参数发现:关井时间越短,地层压力下降速度越快;节流阀承压极限从5 MPa提高至15 MPa,循环排污次数可以减少一半;当地层渗透率较低时,前7次放水效果显著,因此确定试放水时间为7 d。根据研究结果提出了相应的改进措施,以便更好地控制关键施工参数,提高控压放水效果。Abstract: Pressure-controlled drainage can effectively reduce formation pressure in a high-pressure brine layer, but the influence of some key parameters on its effect in operating process is still unclear. The characteristics of pressure-controlled drainage technology were analyzed, and its technological process was summarized. On the basis of the seepage theory of formation brine and wellbore flow theory, a mathematical model with dynamic parameters was built taking into consideration the formation pressure recovery in the shut-in period to simulate the entire process of pressure-controlled drainage. Taking Well Keshen A in Tarim Oilfield as an example, simulations were conducted and the results by simulation and measurement were analyzed. It was found that the error between them was small. The analysis of key parameters affecting the effects and cycles of water drainage showed that the shorter the shut-in time, the quicker the decline in formation pressure. When the pressure-bearing limit of throttle was raised from 5 MPa to 15 MPa, the number of times for cyclic sewage disposal could be reduced by half. However, when the formation permeability was low, the effects of the first seven operations of water drainage were remarkable, and thus the period for trial drainage was set to seven days. According to the above results, relevant improving measures were put forward to better control the key operational parameters, so as to enhance the effects of pressure-controlled drainage.
-
-
-
[1] 孙谦, 任娜. 塔里木山前构造克深905井盐层控压放水应用及探讨[J/OL]. 中国科技期刊数据库: 工业A, 2017: 304. (2017-01-02) [2020-12-20]. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/71899X/201701/epub1000000680083.html. SUN Qian, REN Na. Application and discussion of stratum pressure-controlled drainage in Well Keshen 905, Tarim Piedmont structure[J/OL]. China Science and Technology Journal Database: Industry A, 2017: 304. (2017-01-02) [2020-12-20]. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/71899X/201701/epub1000000680083.html.
[2] 田径. 钻遇盐膏层高压盐水的井控技术[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学, 2012. TIAN Jing. Drilling well control technology of high pressure brine in salt-paste layer[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2012.
[3] 程天辉,何选蓬,王燕新,等. 复合盐层控压放水技术在克深905井的应用[J]. 钻采工艺,2017,40(4):108–109. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1006-768X.2017.04.35 CHENG Tianhui, HE Xuanpeng, WANG Yanxin, et al. Application of compound stratum pressure-controlled drainage technology in Well Kesheng 905[J]. Drilling & Production Technology, 2017, 40(4): 108–109. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1006-768X.2017.04.35
[4] 梁红军,李军,李卫东,等. 高压盐水层控压放水室内实验研究[J]. 钻采工艺,2019,42(2):21–23. LIANG Hongjun, LI Jun, LI Weidong, et al. Experimental study on controlled pressure discharge of high pressure brine out of formations[J]. Drilling & Production Technology, 2019, 42(2): 21–23.
[5] 张朝举,李军,杨宏伟,等. 高压盐水层控压放水模拟计算研究[J]. 钻采工艺,2021,44(3):1–4. ZHANG Chaoju, LI Jun, YANG Hongwei, et al. Simulation computation of pressure-controlled water drainage in high-pressure brine layer[J]. Drilling & Production Technology, 2021, 44(3): 1–4.
[6] 宋付权,刘慈群. 低渗透多孔介质中新型渗流模型[J]. 新疆石油地质,2001,22(1):56–58. SONG Fuquan, LIU Ciqun. A new percolation model used for low permeability porous medium[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2001, 22(1): 56–58.
[7] 段慕白,李皋,孟英峰,等. 气体钻井地层动态出水量预测计算模型[J]. 天然气工业,2016,36(6):66–71. DUAN Mubai, LI Gao, MENG Yingfeng, et al. A prediction and calculation model for dynamic formation water yield in gas drilling[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2016, 36(6): 66–71.
[8] 李祖光, 蒋宏伟, 翟应虎, 等. 气体钻井地层出水量理论模型[J]. 辽宁工程技术大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 28(增刊1): 8-10. LI Zuguang, JIANG Hongwei, ZHAI Yinghu, et al. Water output model in gas drilling[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical Univer-sity(Natural Science), 2009, 28(supplement1): 8-10.
[9] 吴建发,郭建春,赵金洲,等. 有水气井井底出水量计算方法研究[J]. 西南石油大学学报,2003,25(6):27–30. WU Jianfa, GUO Jianchun, ZHAO Jinzhou, et al. Study on calculation of water inflow rate of bottom hole of gas well with water[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum Institute, 2003, 25(6): 27–30.
[10] 金业权,李成,吴谦. 深水钻井井涌余量计算方法及压井方法选择[J]. 天然气工业,2016,36(7):68–73. JIN Yequan, LI Cheng, WU Qian. Methodology for kick tolerance calculation and well killing in deepwater drilling[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2016, 36(7): 68–73.
[11] 李黔,杨先伦,伍贤柱. 压井过程中井底压力的控制方法[J]. 天然气工业,2013,33(9):87–90. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2013.09.015 LI Qian, YANG Xianlun, WU Xianzhu. A method of controlling the bottomhole pressures in well killing[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2013, 33(9): 87–90. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2013.09.015
[12] 李晓平. 利用气井压力恢复资料求产能方程和排泄半径[J]. 断块油气田,2001,8(1):24–26,67. LI Xiaoping. Determining deliverability equation and drainage radius using pressure buildup data of gas well[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2001, 8(1): 24–26,67.
[13] 付晓飞,贾茹,王海学,等. 断层-盖层封闭性定量评价:以塔里木盆地库车坳陷大北—克拉苏构造带为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2015,42(3):300–309. FU Xiaofei, JIA Ru, WANG Haixue, et al. Quantitative evaluation of fault-caprock sealing capacity: a case from Dabei-Kelasu Structural Belt in Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2015, 42(3): 300–309.
[14] 张锦荣,陈安明,周玉仓. 塔里木深井盐膏层钻井技术[J]. 石油钻探技术,2003,31(6):25–27. ZHANG Jinrong, CHEN Anming, ZHOU Yucang. The drilling technology for penetrating carbonate formation in Tarim deep wells[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2003, 31(6): 25–27.
[15] 刘伟,周英操,石希天,等. 塔里木油田库车山前超高压盐水层精细控压钻井技术[J]. 石油钻探技术,2020,48(2):23–28. LIU Wei, ZHOU Yingcao, SHI Xitian, et al. Precise managed pressure drilling technology for ultra-high pressure brine layer in the Kuqa Piedmont of the Tarim Oilfield[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2020, 48(2): 23–28.
[16] 许安明,吴超,尚江伟,等. 面积深度法在库车坳陷北部盐下构造变形研究中的应用[J]. 天然气工业,2015,35(6):37–42. XU Anming, WU Chao, SHANG Jiangwei, et al. Application of area-depth method in studies on the deformation of subsalt structures in the northern Kuqa Depression[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2015, 35(6): 37–42.
[17] 刘伟,李牧,何思龙,等. 库车山前超高压盐水层控压固井实践与认识[J]. 钻采工艺,2020,43(5):31–33. LIU Wei,LI Mu,HE Silong,et al. Practice and understanding of managed pressure cementing for ultra-high pressure brine formation in the Kuche Piedmont[J]. Drilling & Production Technology, 2020, 43(5): 31–33.
[18] 江同文,孙雄伟. 中国深层天然气开发现状及技术发展趋势[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2020,42(5):610–621. JIANG Tongwen,SUN Xiongwei. Development status and technology development trend of deep natural gas in China [J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2020, 42(5): 610–621.
[19] 罗威,倪玲梅. 致密砂岩有效储层形成演化的主控因素:以库车坳陷巴什基奇克组砂岩储层为例[J]. 断块油气田,2020,27(1):7–12. LUO Wei,NI Lingmei. Main controlling factors of formation and evolution of effective reservoir in tight sandstone: taking Bashijiqike Formation sandstone reservoir in Kuqa Depression as an exam-ple[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2020, 27(1): 7–12.
[20] 王学龙,何选蓬,刘先锋,等. 塔里木克深9气田复杂超深井钻井关键技术[J]. 石油钻探技术,2020,48(1):15–20. WANG Xuelong, HE Xuanpeng, LIU Xianfeng, et al. Key drilling technologies for complex ultra-deep wells in the Tarim Keshen 9 Gas Field[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2020, 48(1): 15–20.
[21] 王建华,闫丽丽,谢盛,等. 塔里木油田库车山前高压盐水层油基钻井液技术[J]. 石油钻探技术,2020,48(2):29–33. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2020007 WANG Jianhua, YAN Lili, XIE Sheng, et al. Oil-based drilling fluid technology for high pressure brine layer in Kuqa Piedmont of the Tarim Oilfield[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2020, 48(2): 29–33. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2020007
-
期刊类型引用(23)
1. 车继勇,丁鹏,王红月,马永刚. 组合钻具定向钻井造斜及提速技术方法. 设备管理与维修. 2024(08): 98-100 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 熊浪豪,巢世伟,柏尚宇,陈君,范乘浪,崔建峰. E Zhanbyrshy-3井钻井实践及技术难点分析. 内蒙古石油化工. 2023(05): 63-66+120 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 汪伟,柳贡慧,李军,查春青,连威,夏铭莉. 脉动式扭转冲击钻井工具工作特性分析与测试. 石油钻探技术. 2022(05): 63-69 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 宋周成,翟文宝,邓昌松,徐杨,徐席明,汪鑫,文涛. 富满油田超深井井身结构优化技术与应用. 钻采工艺. 2022(06): 36-41 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王涛,刘锋报,罗威,晏智航,陆海瑛,郭斌. 塔里木油田防漏堵漏技术进展与发展建议. 石油钻探技术. 2021(01): 28-33 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 崔月明,史海民,张清. 吉林油田致密油水平井优快钻井完井技术. 石油钻探技术. 2021(02): 9-13 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 苏崭,王博,盖京明,李玮,赵欢,陈冰邓. 复合式扭力冲击器在坚硬地层中的应用. 中国煤炭地质. 2021(05): 47-50+57 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 张强,饶志华,秦世利,金勇. 南海东部深层古近系高效开发技术探索与实践. 石油化工应用. 2021(06): 34-38 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 李银婷,董小虎. 顺北油田钻井参数强化的提速效果评价. 钻探工程. 2021(07): 72-78 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 陈冬毅,徐鲲,张作伟,吕广,张鑫,郭小明. 恒压恒扭工具在渤海油田中的应用. 科学技术创新. 2021(22): 153-154 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 严德,张玉山,宋玲安,陈彬,李彬,刘保波. 深水高温高压井钻井技术探索与实践. 中国石油和化工标准与质量. 2021(13): 193-194 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 张喆,闫楚旋,冯震,脱直霖,石朝龙. 塔里木油田HLHT区块优快钻井技术研究. 云南化工. 2021(10): 127-129 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 李双贵,于洋,樊艳芳,曾德智. 顺北油气田超深井井身结构优化设计. 石油钻探技术. 2020(02): 6-11 .  本站查看
本站查看
14. 袁国栋,王鸿远,陈宗琦,母亚军,席宝滨. 塔里木盆地满深1井超深井钻井关键技术. 石油钻探技术. 2020(04): 21-27 .  本站查看
本站查看
15. 张智亮,王威,伊明,刘强. 井下安全监控系统设计与实现. 石油钻探技术. 2020(06): 65-70 .  本站查看
本站查看
16. 周波,汪海阁,张富成,纪国栋,韩泽龙,武强. 温度压力对岩石可钻性和破岩效率影响实验. 石油钻采工艺. 2020(05): 547-552 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 李林涛,万小勇,黄传艳,潘丽娟,郭知龙,曹宗波,张伟博. 双向卡瓦可回收高温高压封隔器的研制与应用. 石油机械. 2019(03): 81-86 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 路宗羽,赵飞,雷鸣,邹灵战,石建刚,卓鲁斌. 新疆玛湖油田砂砾岩致密油水平井钻井关键技术. 石油钻探技术. 2019(02): 9-14 .  本站查看
本站查看
19. 江波,任茂,王希勇. 彭州气田PZ115井钻井提速配套技术. 探矿工程(岩土钻掘工程). 2019(08): 73-78 .  百度学术
百度学术
20. 郑振国,黎红胜,赵海艳,温慧芸,孙东方. 哥伦比亚Matambo区块深井钻井关键技术. 石油钻探技术. 2018(02): 30-37 .  本站查看
本站查看
21. 丁红,宋朝晖,袁鑫伟,邢战,张宏阜,张仪. 哈拉哈塘超深定向井钻井技术. 石油钻探技术. 2018(04): 30-35 .  本站查看
本站查看
22. 李世昌,闫立鹏,李建冰,白文路,杨秀丽,闫天宇. 自循环粒子射流钻井提速工具机理研究. 中国锰业. 2018(03): 98-102 .  百度学术
百度学术
23. 陈养龙,席宝滨,晁文学,朱伟厚. 顺北区块Ⅰ号断裂带钻井分层提速技术. 断块油气田. 2018(05): 649-652 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)



 下载:
下载: