Research and Field Tests of Weighted Fracturing Fluids with Industrial Calcium Chloride and Guar Gum
-
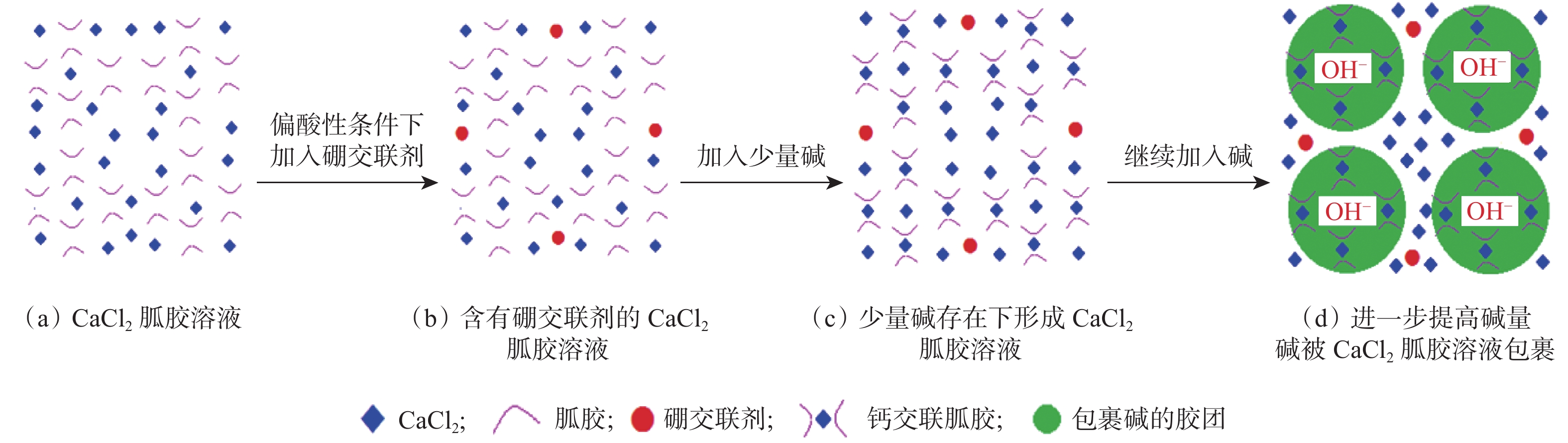
摘要: 为了解决现有加重压裂液体系成本高及加重密度低等问题,采用工业氯化钙作为加重剂,研发了一种低成本加重压裂液技术。在分析硼交联剂在氯化钙胍胶基液中交联受阻机理的基础上,制备了耐高浓度氯化钙溶液的交联剂,可在低pH值环境下使高浓度氯化钙溶液和胍胶基液形成交联冻胶。工业氯化钙加重胍胶压裂液具有加重密度高、基液黏度低和耐温耐剪切性能良好等特点,在温度140 ℃、剪切速率100 s–1条件下剪切2 h后,冻胶黏度大于100 mPa·s。现场试验表明,超深井采用氯化钙加重胍胶压裂液进行压裂施工,施工压力可降低10~15 MPa。研究表明,氯化钙加重胍胶压裂液性能可靠,能够降低超深高应力储层改造施工压力,提高压裂效果,具有现场推广应用价值。Abstract: To solve the problem of high cost and low weighting density in existing weighted fracturing fluid systems, a low-cost technology for weighting the fracturing fluid with industrial calcium chloride was developed. After analyzing the blocking mechanism of boron crosslinking agent in calcium chloride and guar gum base solution, a high-concentration calcium chloride-resistant crosslinker solution was developed. It has the advantage of being able to form crosslinked gel at low pH with high-concentration calcium chloride solution and guar gum base fluid. The industrial calcium chloride weighted guar gum fracturing fluid is characterized by its high weighting density, low base fluid viscosity, strong temperature and shear resistance. After the shearing at 140 °C and with a shearing rate of 100 s–1 for two hours, the gel viscosity was greater than 100 mPa·s. Field tests indicated that the operating pressure can be reduced by 10–15 MPa in ultra-deep wells by using the weighted fracturing fluid with calcium chloride and guar gum. The results showed that fracturing fluid has reliable performance, and could reduce the operational pressure in ultra deep and high stress reservoir reconstructions, and thereby improve the fracturing effect, which has the value of field popularization and application.
-
Keywords:
- weighted fracturing fluid /
- industrial calcium chloride /
- guar gum /
- crosslinker /
- field test
-
-
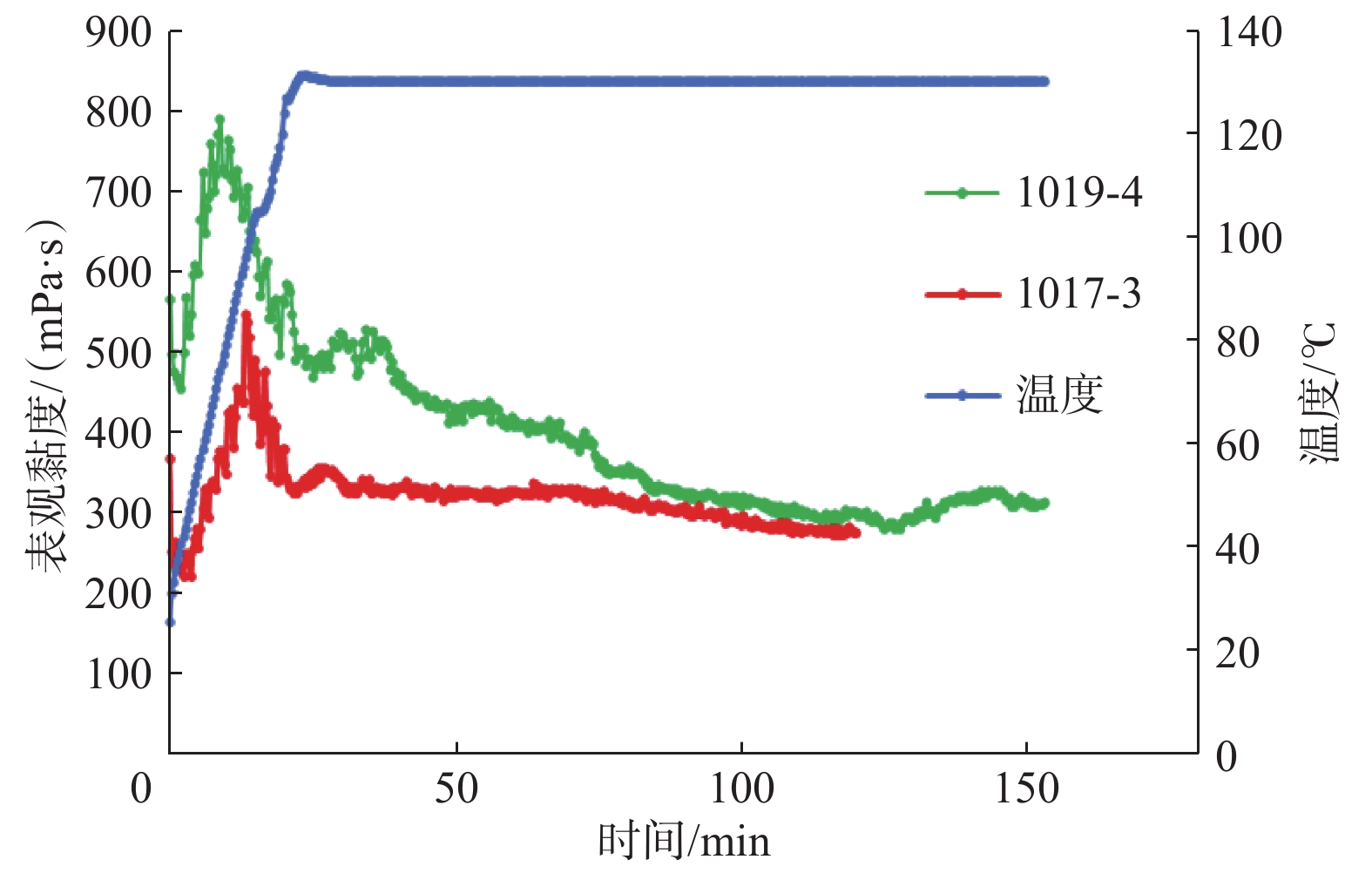
表 1 氯化钙-胍胶交联冻胶剪切试验结果
Table 1 Shear test results of crosslinked gel with calcium chloride and guar gum
试验序号 TEDA5加量,% GZ100加量,% 温度/℃ 剪切不同时间后的黏度/(mPa·s) 0.5 h 1.0 h 1.5 h 2.0 h 2.5 h 3.0 h 1016-2 1.0% 0.2% 130 132 106 108 1016-3 1.0% 0.4% 130 207 210 145 120 105 1016-4 1.0% 0.6% 130 248 270 249 188 1017-1 1.0% 0.8% 140 115 95 1017-2 1.0% 0.6% 140 196 140 111 80 1017-3 1.0% 0.5% 130 325 325 302 272 1019-2 1.0% 0.5% 140 205 204 180 148 1019-4 1.0% 0.5% 130 510 412 323 297 307 262 1020-1 1.2% 0.5% 140 272 177 140 116 表 2 氯化钙加重胍胶压裂液破胶试验结果
Table 2 Gel breaking test results of weighted fracturing fluid with calcium chloride and guar gum
温度/
℃破胶剂
加量,%不同时间下的黏度/(mPa·s) 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h 8 h 50 0.10 冻胶 冻胶 冻胶 稀胶液 稀胶液 0.15 冻胶 冻胶 稀胶液 稀胶液 8.76 0.20 冻胶 稀胶液 稀胶液 10.35 4.67 70 0.10 冻胶 冻胶 冻胶 稀胶液 稀胶液 0.12 冻胶 冻胶 稀胶液 11.23 6.76 0.15 冻胶 稀胶液 11.23 5.46 3.92 90 0.04 冻胶 冻胶 稀冻胶 稀冻胶 稀冻胶 0.06 稀胶液 稀胶液 稀胶液 18.38
(拉丝)9.28
(拉丝)0.08 4.86 4.54 4.46 4.04 3.78 120 0.04 冻胶 冻胶 稀冻胶 稀冻胶 稀冻胶 0.06 稀胶液 13.06
(拉丝)9.69 5.22 0.08 8.11 7.49 6.16 6.00 3.89 表 3 氯化钙加重胍胶压裂液的滤失性能
Table 3 Filtration performance of weighted fracturing fluid with calcium chloride and guar gum
温度/
℃静态滤失系数/
(m·min–0.5)初滤失量/
(m3·m–2)滤失速率/
(m2·min–1)90 4.17×10–4 9.02×10–4 7.22×10–5 140 7.35×10–4 9.04×10–4 1.14×10–4 -
[1] 李鹭光,何海清,范土芝,等. 中国石油油气勘探进展与上游业务发展战略[J]. 中国石油勘探,2020,25(1):1–10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2020.01.001 LI Luguang, HE Haiqing, FAN Tuzhi, et al. Oil and gas exploration progress and upstream development strategy of CNPC[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2020, 25(1): 1–10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2020.01.001
[2] 张宁宁,王青,王建君,等. 近20年世界油气新发现特征与勘探趋势展望[J]. 中国石油勘探,2018,23(1):44–53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2018.01.005 ZHANG Ningning, WANG Qing, WANG Jianjun, et al. Characteristics of oil and gas discoveries in recent 20 years and future exploration in the world[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2018, 23(1): 44–53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2018.01.005
[3] 张光亚,马锋,梁英波,等. 全球深层油气勘探领域及理论技术进展[J]. 石油学报,2015,36(9):1156–1166. ZHANG Guangya, MA Feng, LIANG Yingbo, et al. Domain and theory technology progress of global deep oil and gas exploration[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(9): 1156–1166.
[4] 王招明,李勇,谢会文,等. 库车前陆盆地超深层大油气田形成的地质认识[J]. 中国石油勘探,2016,21(1):37–43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2016.01.004 WANG Zhaoming, LI Yong, XIE Huiwen, et al. Geological understanding on the formation of large-scale ultra-deep oil-gas field in Kuqa foreland basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2016, 21(1): 37–43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2016.01.004
[5] 于京都,郑民,李建忠,等. 我国深层天然气资源潜力、勘探前景与有利方向[J]. 天然气地球科学,2018,29(10):1398–1408. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2018.08.005 YU Jingdu, ZHENG Min, LI Jianzhong, et al. Resource potential, explorative prospect and favorable direction for natural gas in deep formation of China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2018, 29(10): 1398–1408. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2018.08.005
[6] 马开华,谷磊,叶海超. 深层油气勘探开发需求与尾管悬挂器技术进步[J]. 石油钻探技术,2019,47(3):34–40. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2019055 MA Kaihua, GU Lei, YE Haichao. The demands on deep oil/gas exploration & development and the technical advancement of liner hangers[J]. Petroleum Drilling Technology, 2019, 47(3): 34–40. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2019055
[7] 郭建春,苟波,王坤杰,等. 川西下二叠统超深气井网络裂缝酸化优化设计[J]. 天然气工业,2017,37(6):34–41. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2017.06.005 GUO Jianchun, GOU Bo, WANG Kunjie, et al. An optimal design of network-fracture acidification for ultra-deep gas wells in the Lower Permian strata of the western Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2017, 37(6): 34–41. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2017.06.005
[8] 李熙喆,郭振华,胡勇,等. 中国超深层构造型大气田高效开发策略[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2018,45(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(18)30010-7 LI Xizhe, GUO Zhenhua, HU Yong, et al. Efficient development strategies for large ultra-deep structural gas fields in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(1): 111–118. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(18)30010-7
[9] 王学龙,何选蓬,刘先锋,等. 塔里木克深9气田复杂超深井钻井关键技术[J]. 石油钻探技术,2020,48(1):15–20. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2020028 WANG Xuelong, HE Xuanpeng, LIU Xianfeng, et al. Key drilling technologies for complex ultra-deep wells in the Tarim Keshen 9 Gas Field[J]. Petroleum Drilling Technology, 2020, 48(1): 15–20. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2020028
[10] YANG Xiaojiang, MAO Jincheng, ZHANG Wenlong, et al. Tertiary cross-linked and weighted fracturing fluid enables fracture stimulations in ultra high pressure and temperature reservoir[J]. Fuel, 2020, 268: 117222. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.117222
[11] 吕振虎,邬国栋,郑苗,等. 基于溶胀–熟化机理的疏水缔合聚合物速溶压裂液技术[J]. 石油钻探技术,2019,47(4):104–109. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2019018 LYU Zhenhu, WU Guodong, ZHENG Miao, et al. An instantly dissolving fracturing fluid technology using hydrophobic associating polymers based on swelling-curing mechanisms[J]. Petroleum Drilling Technology, 2019, 47(4): 104–109. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2019018
[12] 程兴生,张福祥,徐敏杰,等. 低成本加重瓜胶压裂液的性能与应用[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2011,33(2):91–93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7393.2011.02.023 CHENG Xingsheng, ZHANG Fuxiang, XU Minjie, et al. Performance and application of weighted GHPG fracturing fluid with low cost[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2011, 33(2): 91–93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7393.2011.02.023
[13] 李传增, 张菅, 王现杰, 等.深海油田耐高温加重压裂液体系研究及性能评价[J].海洋工程装备与技术, 2019, 6(增刊1): 116-121. LI Chuanzeng, ZHANG Jian, WANG Xianjie, et al. Research and performance evaluation of high temperature weighted fracturing fluid system in deep sea oilfield[J]. Ocean Engineering Equipment and Technology, 2019, 6 (supplement 1): 116-121.
[14] 施建国,郭粉娟. 低摩阻加重压裂液体系研究及应用[J]. 石油化工应用,2020,39(9):74–78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5285.2020.09.016 SHI Jianguo, GUO Fenjuan. Research and application of low friction fracturing fluid system[J]. Petrochemical Industry Applications, 2020, 39(9): 74–78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5285.2020.09.016
[15] 肖兵,张高群,陈波,等. NaCI、NaBr对HPG压裂液性能的影响[J]. 油田化学,2013,30(1):26–28. XIAO Bing, ZHANG Gaoqun, CHEN Bo, et al. Effect of NaCI and NaBr on the performance of fracturing fluid[J]. Oilfield Chemistry, 2013, 30(1): 26–28.
[16] 董永刚,张菅,裴海华. 耐高温NaBr加重压裂液的研究[J]. 当代化工,2016,45(3):441–443, 446. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2016.03.001 DONG Yonggang, ZHANG Jian, PEI Haihua. Research of heat-resistant sodium bromide weighted fracturing fluid[J]. Contemporary Chemical Industry, 2016, 45(3): 441–443, 446. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2016.03.001
[17] 肖雯,张茂森,李晓倩,等. 加重压裂液体系优选[J]. 承德石油高等专科学校学报,2016,18(4):25–29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9446.2016.04.007 XIAO Wen, ZHANG Maosen, LI Xiaoqian, et al. Properties of heavy fracturing fluid system[J]. Journal of Chengde Petroleum College, 2016, 18(4): 25–29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9446.2016.04.007
[18] QIU Xiaoping, MARTCH W E, MORGENTHALER L N, et al. Design criteria and application of high-density brine-based fracturing fluid for deepwater frac packs[R]. SPE 124704, 2009.
[19] 任占春. 甲酸盐加重瓜胶压裂液体系[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2017,34(1):122–126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2017.01.023 REN Zhanchun. Guar gum fracturing fluids weighted with formates[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2017, 34(1): 122–126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2017.01.023
[20] 王彦玲,张悦,刘飞,等. 复合无机盐加重压裂液研究[J]. 精细石油化工,2017,34(5):6–9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9384.2017.05.002 WANG Yanling, ZHANG Yue, LIU Fei, et al. Research of compound inorganic salt aggravating fracturing fluids[J]. Speciality Petrochemicals, 2017, 34(5): 6–9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9384.2017.05.002
[21] 熊俊杰,赵战江,安琦,等. 硝酸钠加重海水基压裂液性能评价[J]. 油田化学,2019,36(1):43–47. XIONG Junjie, ZHAO Zhanjiang, AN Qi, et al. Performance evaluation of seawater-based fracturing fluid weighted by sodium nitrate[J]. Oilfield Chemistry, 2019, 36(1): 43–47.
-
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 戴文潮,刘奔. 高性能底封拖动分段压裂工具研制及试验. 钻采工艺. 2023(01): 120-125 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 谢斌,陈超峰,马都都,练章华,史君林. 超深高温高压井尾管悬挂器安全性评价新方法. 天然气工业. 2022(09): 93-101 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 郭朝辉,李振,罗恒荣. Φ273.1mm无限极循环尾管悬挂器在元坝气田的应用研究. 石油钻探技术. 2021(05): 64-69 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 古青,宋剑鸣,曹博,马淼,蒋立坤,杨旭,冯治锋. 高温高压尾管悬挂器研制与应用. 石油矿场机械. 2021(06): 51-57 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 高果成. 内嵌卡瓦尾管悬挂器在老井侧钻中的优势综合分析. 钻采工艺. 2020(01): 77-80+12 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 马开华,谷磊,叶海超. 深层油气勘探开发需求与尾管悬挂器技术进步. 石油钻探技术. 2019(03): 34-40 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 朱晓丽,张金法,魏书雷. 尾管用内嵌式卡瓦坐挂机构承载能力分析. 石油矿场机械. 2018(05): 84-87 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 马兰荣,达伟,韩峰,张瑞. 高性能尾管悬挂器关键技术. 断块油气田. 2017(06): 859-862 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 刘珂兵,贾彪,王庆,黄煜鹏. 关于内嵌卡瓦尾管悬挂器的应用探讨. 中国石油和化工标准与质量. 2016(22): 74-75 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 韩峰,崔晓杰,薛占峰,邓同军. 悬挂器坐挂引起的套管二维屈曲失效形式研究. 中国科技论文. 2016(23): 2696-2699+2710 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: