Research on a Nano-Composite Cement Slurry System Suitable for Low-Temperature Formations
-
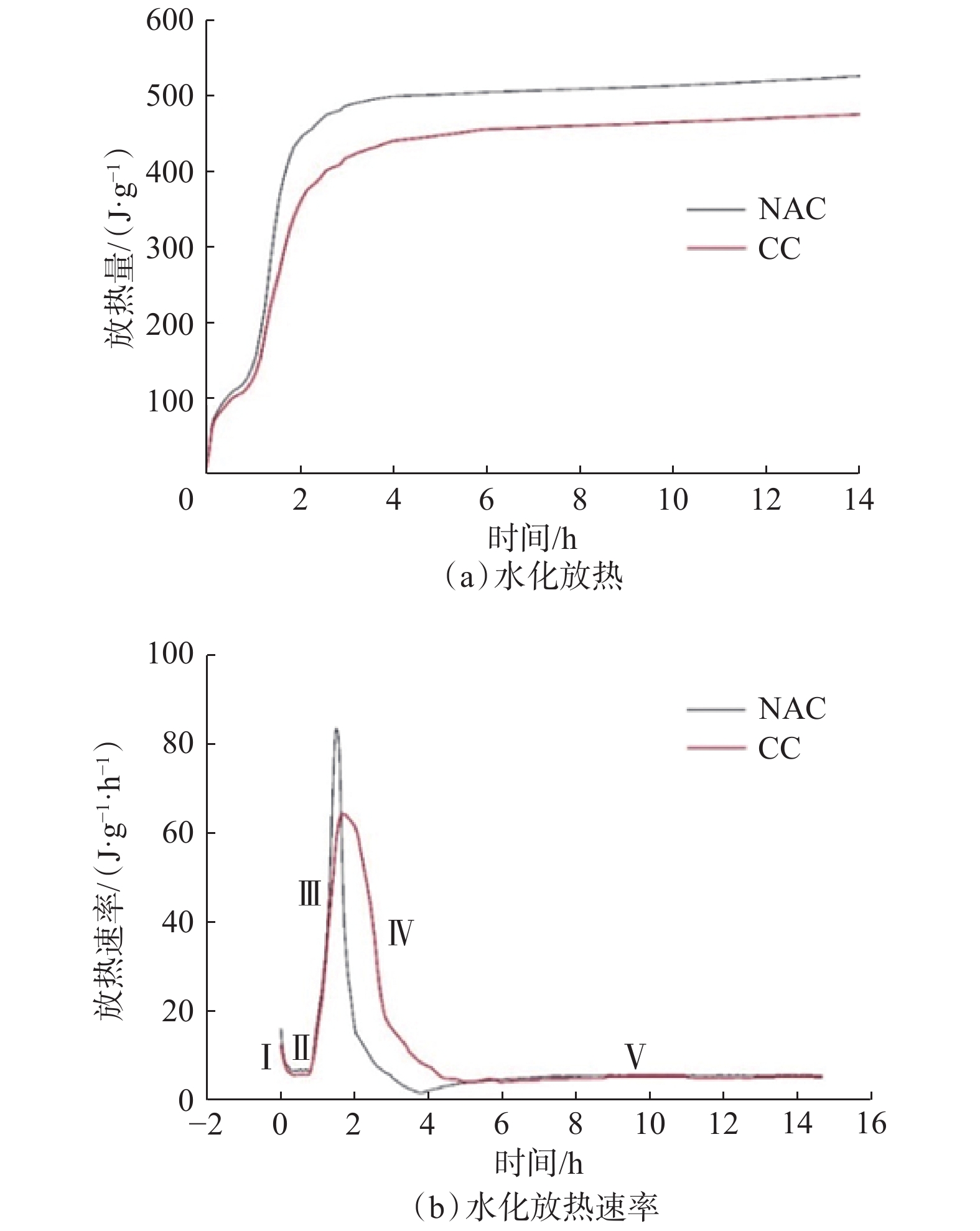
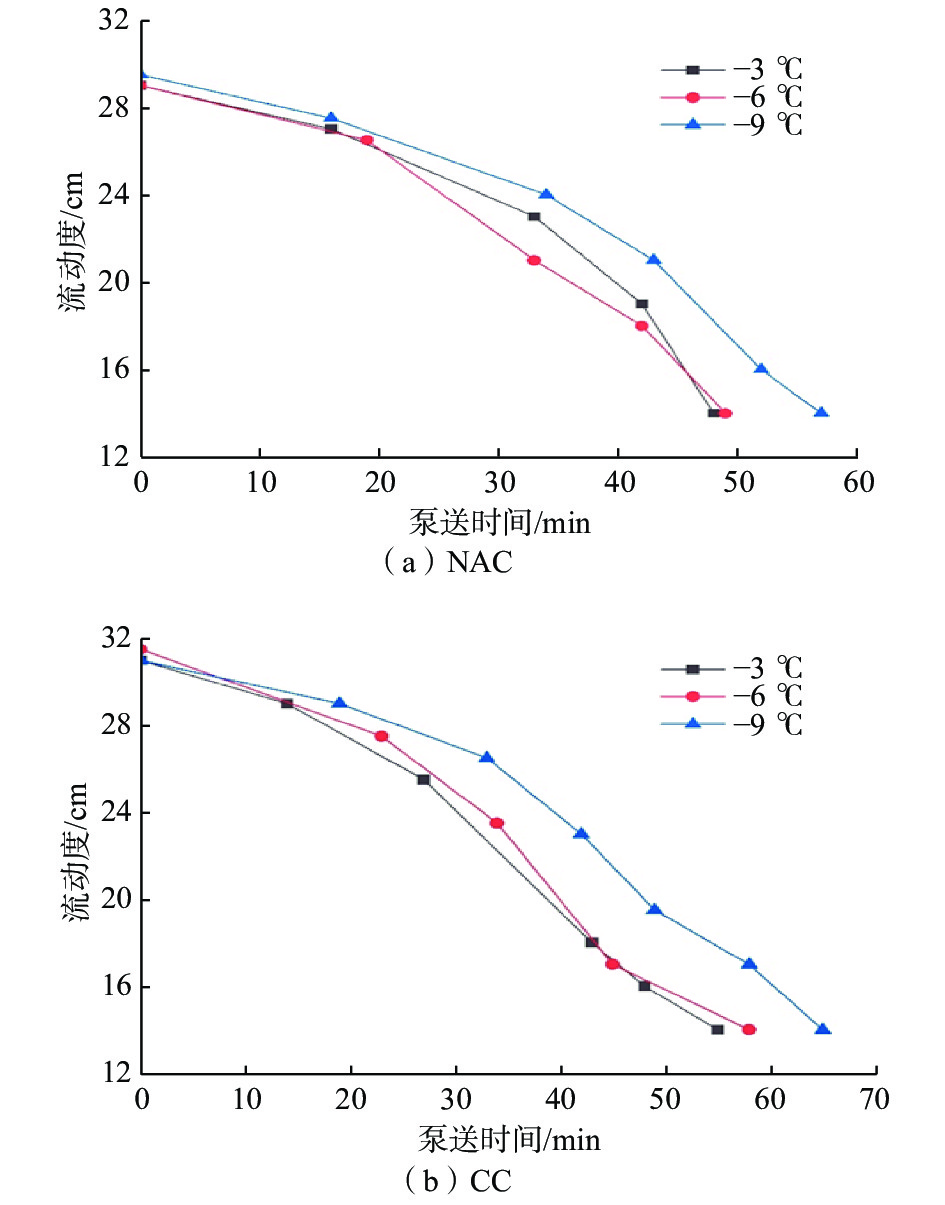
摘要: 为解决低温地层钻探过程中的井壁坍塌和井漏问题,研制了适用于低温地层的纳米复合水泥浆。采用宏观试验与微观分析相结合的方法,研究了低温下纳米Al2O3对硅酸盐–硫铝酸盐复合水泥浆性能和水化过程的影响;以普通硅酸盐水泥与硫铝酸盐水泥复合产生的水化协同效应为基础,结合纳米Al2O3、防冻剂EG、减水剂JS-1和早强剂TEOA,配制了纳米复合水泥浆NAC;采用扫描电镜、X射线衍射和水化放热试验相结合的方法,研究了NAC的低温水化过程及水化机理。试验得知,温度为–9 ℃时,纳米复合水泥浆具有良好的初始流动性,可泵期为57 min,初、终凝时间分别为84和101 min,24 h抗压强度为6.9 MPa。研究结果表明,NAC具有直角稠化效应,低温下性能优越,能够满足钻进低温地层时的护壁堵漏要求。Abstract: In order to solve the problems of borehole wall collapse and well leakage in low-temperature drilling, a nano-composite cement slurry system suitable for low-temperature formations was designed. Combining the macroscopic test with microscopic analysis, the influence of nano-Al2O3 at low temperatures on the performance of silicate-sulphoaluminate composite cement slurry and the hydration process was studied. Based on the synergistic effect of hydration generated from the composite of ordinary silicate cement and sulphoaluminate cement, a nano-composite cement (NAC) was developed in conjunction with the nano-Al2O3, antifreeze agent EG, water reducing agent JS-1, and hardening accelerating agent TEOA. In addition, the low-temperature hydration process of NAC and its mechanism were studied through a combination of the scanning electron microscope (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and exothermic experiments of hydration. Experimental results showed that the nano-composite cement slurry had good initial fluidity at −9 ℃ with a pumpable period of 57 min, a 24-hour compressive strength of 6.9 MPa, and an initial and final setting time of 84 min and 101 min, respectively. The results of the study indicated that NAC had the right-angle thickening effect and superior performance at low temperatures, capable of meeting the requirements of borehole wall protection and loss circulation control in low-temperature formations.
-
-
表 1 纳米Al2O3对复合水泥浆性能的影响试验结果
Table 1 The effect of nano Al2O3 on the properties of composite cement slurry
纳米Al2O3
加量,%初始流动度/
cm可泵期/
min初凝时间/
min终凝时间/
min24 h抗压
强度/MPa0 21 26 40 106 3.3 0.1 23 38 65 119 5.7 0.3 22 29 51 99 6.2 0.5 20 13 50 97 5.8 表 2 减水剂对纳米复合水泥浆性能的影响试验结果
Table 2 The effect of water reducing agent on the properties of nano-composite cement slurry
减水剂 加量,
%初始流动度/
cm可泵期/
min初凝时间/
min终凝时间/
min22.0 29 51 99 JS-1 0.1 27.0 43 144 197 0.3 35.0 103 265 354 0.5 33.0 89 186 246 NS 0.1 26.0 97 224 641 0.3 27.0 168 1 143 1 472 0.5 29.0 229 957 1 383 PAS 0.1 28.0 53 212 517 0.3 32.0 79 267 678 0.5 34.5 81 186 450 表 3 早强剂对纳米复合水泥浆性能的影响试验结果
Table 3 The effect of hardening accelerating agent on the properties of nano-composite cement slurry
早强剂 加量,
%初始流动
度/cm可泵期/
min初凝时
间/min终凝时
间/min24 h抗压
强度/MPa33.0 89 186 246 6.1 TEOA 0.02 32.0 75 114 135 7.8 0.06 30.0 67 94 105 8.2 0.10 33.0 81 126 172 7.6 CaCl2 1.00 32.0 184 329 457 4.6 3.00 29.5 104 231 351 5.1 5.00 30.0 117 273 364 4.8 Na2SO4 0.50 31.5 52 77 96 6.3 1.50 31.0 43 72 99 6.5 2.50 30.5 37 64 89 6.7 表 4 NAC的正交试验结果(–9 ℃)
Table 4 Results of orthogonal test of NAC (–9 ℃)
序号 A B C D 初始流动度/cm 可泵期/min 凝结时间/min 24 h抗压强度/MPa 初凝 终凝 1 0.5 0.2% 0.05% 0.4% 27.0 52 88 121 9.3 2 0.5 0.3% 0.06% 0.5% 31.0 53 159 208 9.1 3 0.5 0.4% 0.07% 0.6% 29.5 63 75 89 9.4 4 0.6 0.2% 0.06% 0.6% 31.0 60 139 219 7.7 5 0.6 0.3% 0.07% 0.4% 30.5 58 80 154 8.1 6 0.6 0.4% 0.05% 0.5% 30.5 60 144 238 8.8 7 0.7 0.2% 0.07% 0.5% 35.0 92 156 231 6.8 8 0.7 0.3% 0.05% 0.6% 33.0 75 178 234 7.3 9 0.7 0.4% 0.06% 0.4% 31.0 52 199 226 7.5 -
[1] 牛洪波,于政廉,孙菁,等. 天然气水合物动力学抑制剂与水分子相互作用研究[J]. 石油钻探技术,2019,47(4):29–34. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2019037 NIU Hongbo, YU Zhenglian, SUN Jing, et al. The interaction between gas hydrate kinetics inhibitors and water molecules[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2019, 47(4): 29–34. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2019037
[2] 张川,王胜,陈礼仪,等. 用于冻土区天然气水合物钻探的聚合物钻井液低温流变响应[J]. 天然气工业,2016,36(2):92–97. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2016.02.013 ZHANG Chuan, WANG Sheng, CHEN Liyi, et al. Low-temperature rheological response characteristics of the polymer drilling fluid developed for permafrost gas hydrate exploration[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2016, 36(2): 92–97. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2016.02.013
[3] 田野,符军放,宋维凯,等. 一种新型超深水低温早强剂[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2019,36(2):224–228. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2019.02.016 TIAN Ye, FU Junfang, SONG Weikai, et al. A new low temperature early strength agent for ultradeep water operation[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2019, 36(2): 224–228. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2019.02.016
[4] 何瑞兵,董平华,李治衡,等. 生物灰低密度水泥浆体系室内研究[J]. 长江大学学报(自然科学版),2020,17(3):43–47. HE Ruibing, DONG Pinghua, LI Zhiheng, et al. Laboratory study on low temperature and low density cement slurry system of biological ash[J]. Journal of Yangtze University(Natural Science Edition), 2020, 17(3): 43–47.
[5] 刘浩亚,鲍洪志,赵卫. –18 ℃下冻土区负温水泥浆水化微观过程研究[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2019,36(1):77–81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2019.01.015 LIU Haoya, BAO Hongzhi, ZHAO Wei. Study on microscopic hydration process of a cold temperature cement slurry used in Frozen Areas at –18 ℃[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2019, 36(1): 77–81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2019.01.015
[6] 丁向群,赵欣悦,徐晓婉,等. 矿物掺合料对硫铝酸盐水泥–普通硅酸盐水泥复合体系性能的影响[J]. 新型建筑材料,2020,47(3):40–44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-702X.2020.03.011 DING Xiangqun, ZHAO Xinyue, XU Xiaowan, et al. Effect of admixtures on properties of sulphoaluminate cement-common Portland cement composite system[J]. New Building Materials, 2020, 47(3): 40–44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-702X.2020.03.011
[7] 张鑫,邱瑞军,侯淑鹏,等. 硅酸盐-硫铝酸盐水泥混合体系浆液流变特性试验研究[J]. 混凝土,2019(8):72–76, 81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3550.2019.08.017 ZHANG Xin, QIU Ruijun, HOU Shupeng, et al. Experimental study on the rheological behavior of silicate-sulphoaluminate mixed cement system[J]. Concrete, 2019(8): 72–76, 81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3550.2019.08.017
[8] WANG Sheng, WANG Jingfei, YUAN Chaopeng, et al. Development of the nano-composite cement: application in regulating grouting in complex ground conditions[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2018, 15(7): 1572–1584. doi: 10.1007/s11629-017-4729-9
[9] WANG Sheng, JIAN Liming, SHU Zhihong, et al. Preparation, properties and hydration process of low temperature nano-composite cement slurry[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 205: 434–442. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.02.049
[10] 詹培敏,孙斌祥,何智海,等. 纳米碳酸钙对水泥基材料性能影响的研究进展[J]. 硅酸盐通报,2018,37(3):881–887, 910. ZHAN Peimin, SUN Binxiang, HE Zhihai, et al. Research progress of effect of nano-calcium carbonate on the properties of cement-based materials[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2018, 37(3): 881–887, 910.
[11] ALOMAYRI T. Experimental study of the microstructural and mechanical properties of geopolymer paste with nano material (Al2O3)[J]. Journal of Building Engineering, 2019, 25: 100788. doi: 10.1016/j.jobe.2019.100788
[12] LU Xiaolei, YE Zhengmao, ZHANG Lina, et al. The influence of ethanol- diisopropanolamine on the hydration and mechanical properties of Portland cement[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 135: 484–489. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.12.191
[13] 姚嘉诚,延永东,徐鹏飞,等. 水泥基渗透结晶型防水材料和纳米二氧化硅改性混凝土自修复性能的研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报,2020,39(6):1772–1777. YAO Jiacheng, YAN Yongdong, XU Pengfei, et al. Self-healing properties of concrete modified by cementitious capillary crystalline waterproofing and nano-silica[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2020, 39(6): 1772–1777.
[14] SINGH N B, SARVAHI R, SINGH N P, et al. Effect of temperature on the hydration of ordinary Portland cement in the presence of a superplasticizer[J]. Thermochim Acta, 1994, 247(2): 381–388. doi: 10.1016/0040-6031(94)80138-X
[15] HU Qinang, ABOUSTAIT M, KIM T, et al. Direct three-dimensional observation of the microstructure and chemistry of C3S hydration[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2016, 88: 157–169. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2016.07.006
[16] BERGER S, COUMES C C D, BESCOP P L, et al. Influence of a thermal cycle at early age on the hydration of calcium sulphoaluminate cements with variable gypsum contents[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2011, 41(2): 149–160. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2010.10.001
[17] LI Laibo, CHEN Mingxu, GUO Xiangyang, et al. Early-age hydration characteristics and kinetics of Portland cement pastes with super low w/c ratios using ice particles as mixing water[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2020, 9(4): 8407–8428. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.05.082
[18] TELESCA A, MARROCCOLI M, PACE M L, et al. A hydration study of various calcium sulphoaluminate cements[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2014, 53: 224–232. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2014.07.002
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 冷光耀. 空气和CO_2辅助蒸汽吞吐室内实验研究. 油田化学. 2018(03): 447-450+479 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: