The Standard Division of Tight Oil Reservoirs in Chang 6-8 Members of Changqing Oilfield based on CQ Index
-
摘要:
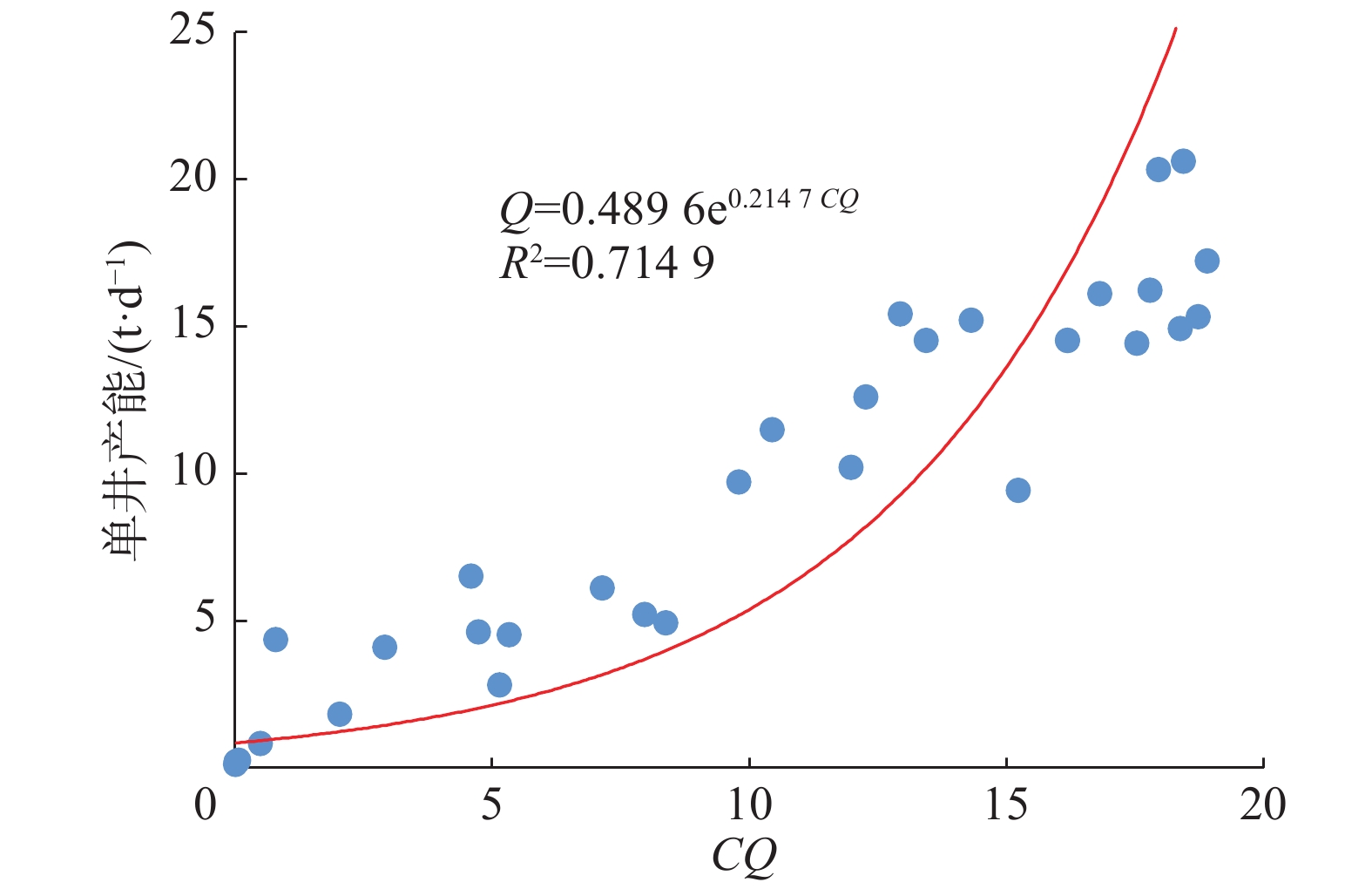
鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系长6—长8段致密油储层具有低孔、低渗、低压和低产等特征,为了优选单井剖面的地质甜点、工程甜点,针对长6—长8段致密油储层的地质特性,提出了一种划分致密油储层标准的实用方法。首先计算或提取储层的最小水平主应力、破裂压力、脆性指数、孔隙度、渗透率及含水饱和度等参数,建立储层完井品质综合评价指标CQ;然后基于CQ和单井产能的关系图版,将储层划分为好、中、差3个等级,并根据CQ值优选射孔压裂层段。利用该方法对长庆油田陇东地区L375井进行了储层划分,划分结果与试油结果对比表明,基于CQ指标优选出的射孔压裂位置与实际高中低产井段完全相符。研究表明,该方法满足优选致密油射孔压裂位置和寻找地质甜点、工程甜点的要求,可以用于区块储层的划分。
Abstract:The tight oil reservoirs in the Chang 6-8 Member of the Triassic Yanchang Formation in the Ordos Basin are characterized by low porosity, low permeability, low pressure and low production. In order to optimize the geological engineering sweet spots on the single-well section, a practical method for standard division of tight oil reservoirs has been proposed in accordance with the geological characteristics of Chang 6-8 tight oil reservoir. The first step involved calculating and extracting the minimum horizontal principal stress, fracture pressure, brittleness index, porosity, permeability and water saturation of reservoir etc. This allows them to establish the comprehensive evaluation index of the reservoir completion quality (CQ), and then, to classify the reservoirs “good, medium and bad” based on the relationship chart of CQ and single well productivity. And then to optimize the perforating and fracturing intervals in terms of the CQ value. Using this method, reservoir division was performed in Well L375 of the Changqing Longdong Area, and the comparison of division result and the oil test result showed that the perforating/fracturing interval optimized by the CQ index was completely consistent with the actual intervals of high, medium and low production-yields. Study results also indicated that this method could meet the requirements for optimizing the perforating/fracturing intervals of tight oil and and for identifying engineering geological sweet spots, and can be used for a classification standard for block reservoirs.
-
-
表 1 L375井延长组致密油射孔压裂优选层段
Table 1 Optimized intervals for perforating/fracturing in Yanchang tight oil formation of Well L375
小层编号 储层井段/m 解释结论 CQ 优选射孔井段/m S 排序 65 2 475.00~2 483.50 油层 186.49 2 478.00~2 482.00 192.417 1 60 2 366.50~2 373.50 油层 105.15 2 369.38~2 373.38 149.429 2 69 2 500.38~2 507.00 油层 94.00 2 500.62~2 504.62 122.245 3 55 2 333.00~2 335.88 油层 83.14 2 333.00~2 335.88 113.843 4 58 2 355.75~2 360.00 油层 61.41 2 356.12~2 360.00 77.703 5 67 2 488.75~2 491.88 油层 50.57 2 488.75~2 491.88 68.576 6 66 2 484.50~2 485.50 油层 26.92 2 484.50~2 485.50 34.627 7 52 2 293.38~2 295.75 油层 18.00 2 293.38~2 295.75 21.524 8 68 2 495.38~2 497.00 干层 0.09 2 495.38~2 497.00 0.096 9 51 2 285.00~2 287.88 干层 0.08 2 285.00~2 287.88 0.090 10 表 2 L375井实际射孔位置与通过CQ指标所优选射孔位置对比
Table 2 Comparison of actual perforation position and optimized perforation position by CQ index in Well L375
层位 CQ 优选射孔位置/m 实际射孔位置/m 产油量/(t·d–1) 储层划分结果 长7 61.41 2 356.13~2 360.00 2 358.24 32.47 优质储层 105.15 2 369.38~2 373.38 2 370.28 长8 186.49 2 478.00~2 482.00 2 478.00~2 481.00 21.59 优质储层 50.57 2 488.75~2 491.88 2 489.00~2 491.00 -
[1] 黄鑫,董秀成,肖春跃,等. 非常规油气勘探开发现状及发展前景[J]. 天然气与石油, 2012, 30(6): 38–41. HUANG Xin, DONG Xiucheng, XIAO Chunyue, et al. Present situation and development prospect of unconventional oil and gas exploration and development[J]. Natural Gas and Oil, 2012, 30(6): 38–41.
[2] 杨双定. 鄂尔多斯盆地致密砂岩气层测井评价新技术[J]. 天然气工业, 2005, 25(9): 45–47. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2005.09.015 YANG Shuangding. New methods of log evaluation of the tight sandstone gas reservoirs in E’erduosi Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2005, 25(9): 45–47. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2005.09.015
[3] 楼一珊, 金业权.岩石力学与石油工程[M].北京: 石油工业出版社, 2006. LOU Yishan, JIN Yequan. Rock mechanics and petroleum engineering[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2006.
[4] 王团. 致密砂岩储层中优质储层的划分及识别方法研究[J]. 国外测井技术, 2015(3): 26–29. WANG Tuan. Research on the division and identification of high-quality reservoir in tight sandstone reservoir[J]. World Well Logging Technology, 2015(3): 26–29.
[5] 杜金虎,刘合,马德胜,等. 试论中国陆相致密油有效开发技术[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(2): 198–204. doi: 10.11698/PED.2014.02.09 DU Jinhu, LIU He, MA Desheng, et al. Discussion on effective development techniques for continental tight oil in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(2): 198–204. doi: 10.11698/PED.2014.02.09
[6] 赖锦,王贵文,范卓颖,等. 非常规油气储层脆性指数测井评价方法研究进展[J]. 石油科学通报, 2016, 1(3): 330–341. LAI Jin, WANG Guiwen, FAN Zhuoying, et al. Research progress in brittleness index evaluation methods with logging data in unconventional oil and gas reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Science Bulletin, 2016, 1(3): 330–341.
[7] 夏宏泉,杨双定,弓浩浩,等. 岩石脆性实验及压裂缝高度与宽度测井预测[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 35(4): 81–89. doi: 10.3863/j.issn.1674-5086.2013.04.011 XIA Hongquan, YANG Shuangding, GONG Haohao, et al. Research on rock brittleness experiment and logging prediction of hydraulic fracture height & width[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition), 2013, 35(4): 81–89. doi: 10.3863/j.issn.1674-5086.2013.04.011
[8] 林英松,葛洪魁,王顺昌. 岩石动静力学参数的试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 1998, 17(2): 216–222. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.1998.02.019 LIN Yingsong, GE Hongkui, WANG Shunchang. Testing study on dynamic and static elastic parameters of rocks[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 1998, 17(2): 216–222. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.1998.02.019
[9] 周新桂,张林炎,范昆,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地现今地应力测量及其在油气开发中的应用[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 24(3): 7–12. ZHOU Xingui, ZHANG Linyan, FAN Kun, et al. Measurement of the present earth stress of Ordos Basin and its applications in oil and gas exploitation[J]. Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University (Natural Science Edition), 2009, 24(3): 7–12.
[10] 夏宏泉,刘畅,李高仁,等. 基于测井资料的TIV地层水平地应力计算方法[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2019, 47(6): 67–72. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2019130 XIA Hongquan, LIU Chang, LI Gaoren, et al. A logging data-based calculation method for the horizontal TIV formation in-situ stress[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniquest, 2019, 47(6): 67–72. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2019130
[11] 李传亮,孔祥言. 油井压裂过程中岩石破裂压力计算公式的理论研究[J]. 石油钻采工艺, 2000, 22(2): 54–56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7393.2000.02.014 LI Chuanliang, KONG Xiangyan. A theoretical study on rock breakdown pressure calculation equations of fracturing process[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2000, 22(2): 54–56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7393.2000.02.014
[12] HIGGINS S, GOODWIN S, DONALD A, et al. Anisotropic stress models improve completion design in the Baxter Shale[R]. SPE 115736, 2008.
[13] 李映艳,钱根葆,高阳,等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷百口泉组砾岩致密油藏地质“甜点”分级标准及应用[J]. 东北石油大学学报, 2018, 42(6): 85–94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4107.2018.06.009 LI Yingyan, QIAN Genbao, GAO Yang, et al. Identification criterion of the geological "sweet point" of conglomerate tight reservoir and its application of Baikouquan Formation in Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 2018, 42(6): 85–94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4107.2018.06.009
[14] 夏宏泉,文晓峰,冯春珍,等. 基于测井信息的致密油层射孔优化选层方法研究[J]. 测井技术, 2017, 41(3): 353–357. XIA Hongquan, WEN Xiaofeng, FENG Chunzhen, et al. Optimal selecting interval method of tight oil reservoir perforating based on well logging information[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2017, 41(3): 353–357.
[15] 吴飞鹏,蒲春生,陈德春,等. 射孔油井产能计算模型研究[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2008, 36(1): 69–72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0890.2008.01.019 WU Feipeng, PU Chunsheng, CHEN Dechun, et al. Productivity calculation model of perforated oil wells[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2008, 36(1): 69–72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0890.2008.01.019
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 李朋,张艳玉,孙晓飞,李冬冬,刘洋,陈会娟. SAGD循环预热割缝筛管参数影响规律研究. 工程热物理学报. 2020(04): 940-947 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 薛衡,黄祖熹,王贺华,安永生,刘榧,成一,何冰,刘卡. Ahdeb油田水平井控水完井及一体化耦合模型. 石油与天然气地质. 2019(02): 423-429 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李朋,张艳玉,孙晓飞,陈会娟,刘洋. 稠油油藏双管水平井注汽井筒参数预测新模型. 特种油气藏. 2019(04): 85-90 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李朋,张艳玉,孙晓飞,刘洋,谢孟珂,王朝,陈会娟. SAGD循环预热注汽参数影响规律数值模拟. 中南大学学报(自然科学版). 2019(11): 2896-2905 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 陈会娟,李明忠,狄勤丰,刘春苗. 多点注汽水平井井筒出流规律数值模拟. 石油学报. 2017(06): 696-704 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 徐磊. 稠油热采井防砂筛管热稳定性优化仿真分析. 北京石油化工学院学报. 2016(02): 40-45 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)




 下载:
下载: