Hydraulic Fracture Initiation and Extending Tests in Deep Shale Gas Formations and Fracturing Design Optimization
-
摘要:
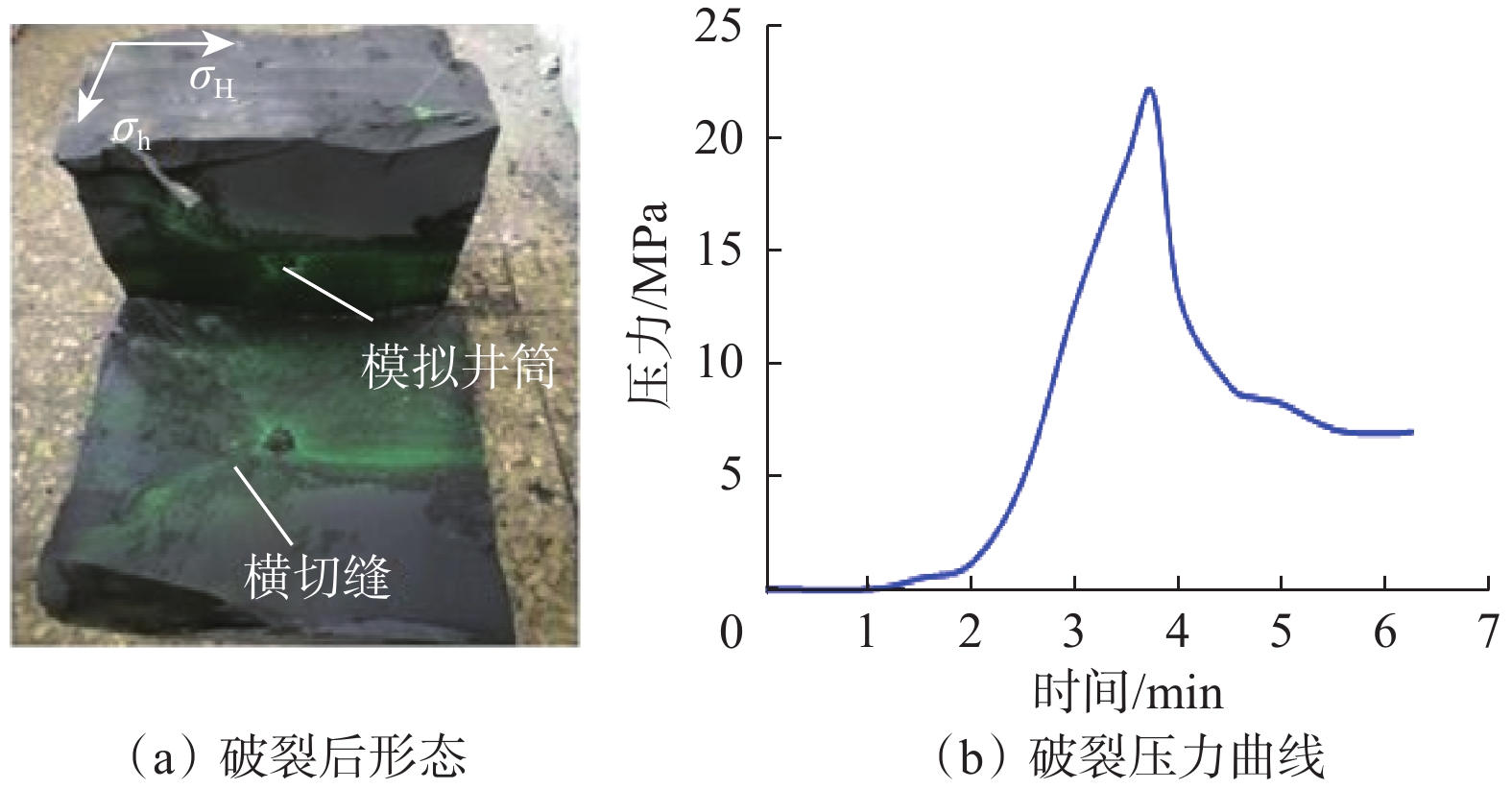
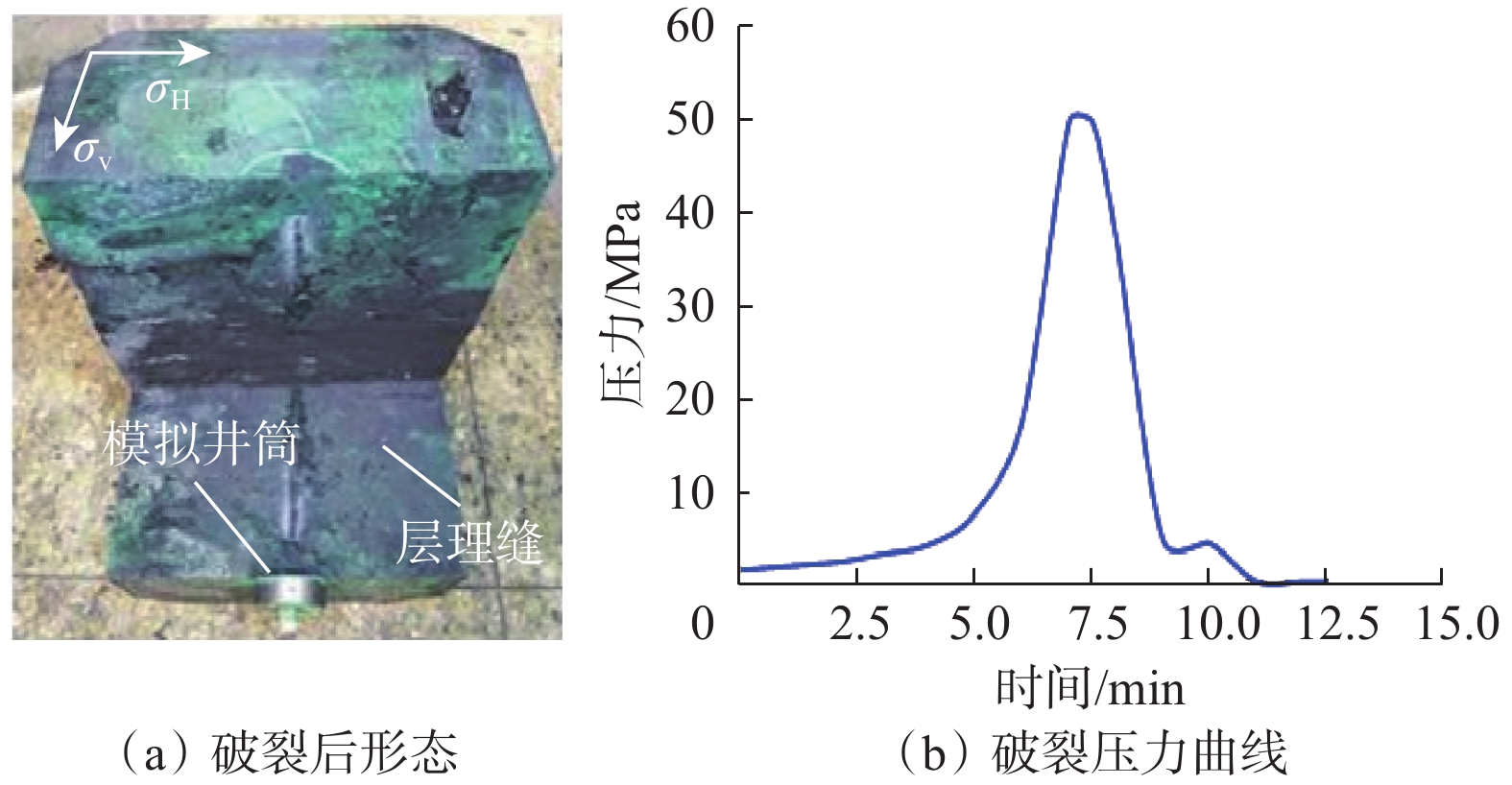
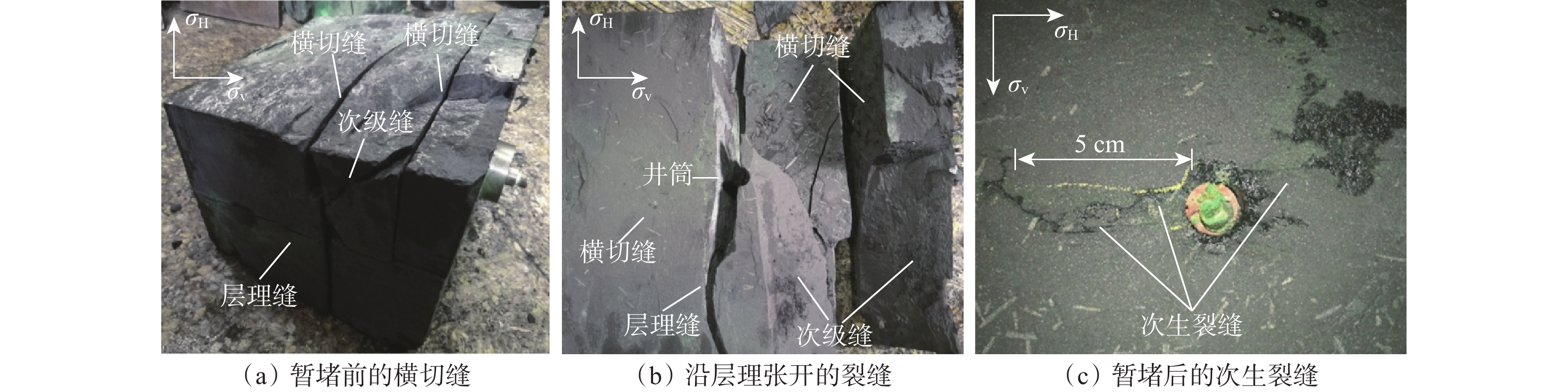
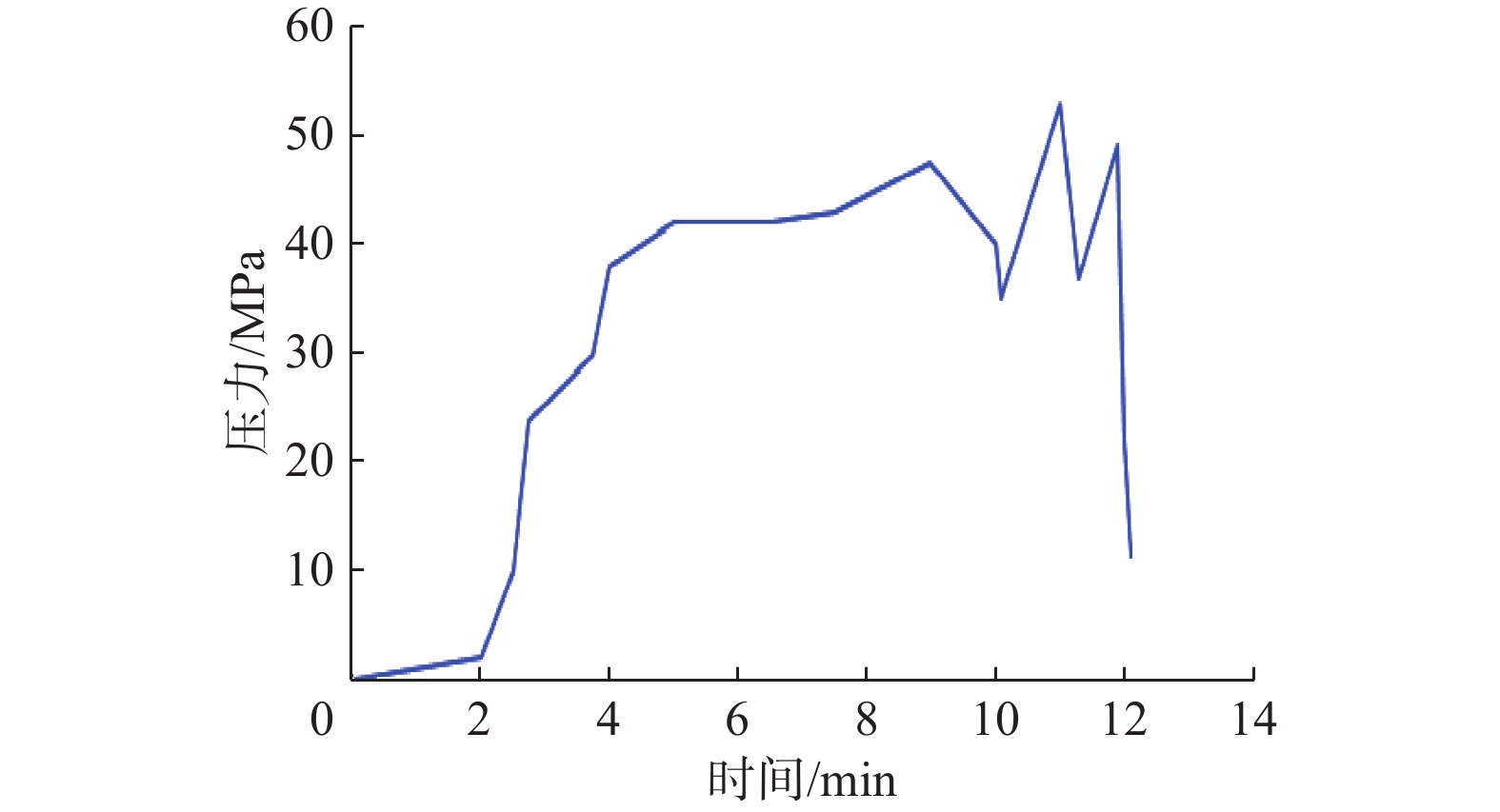
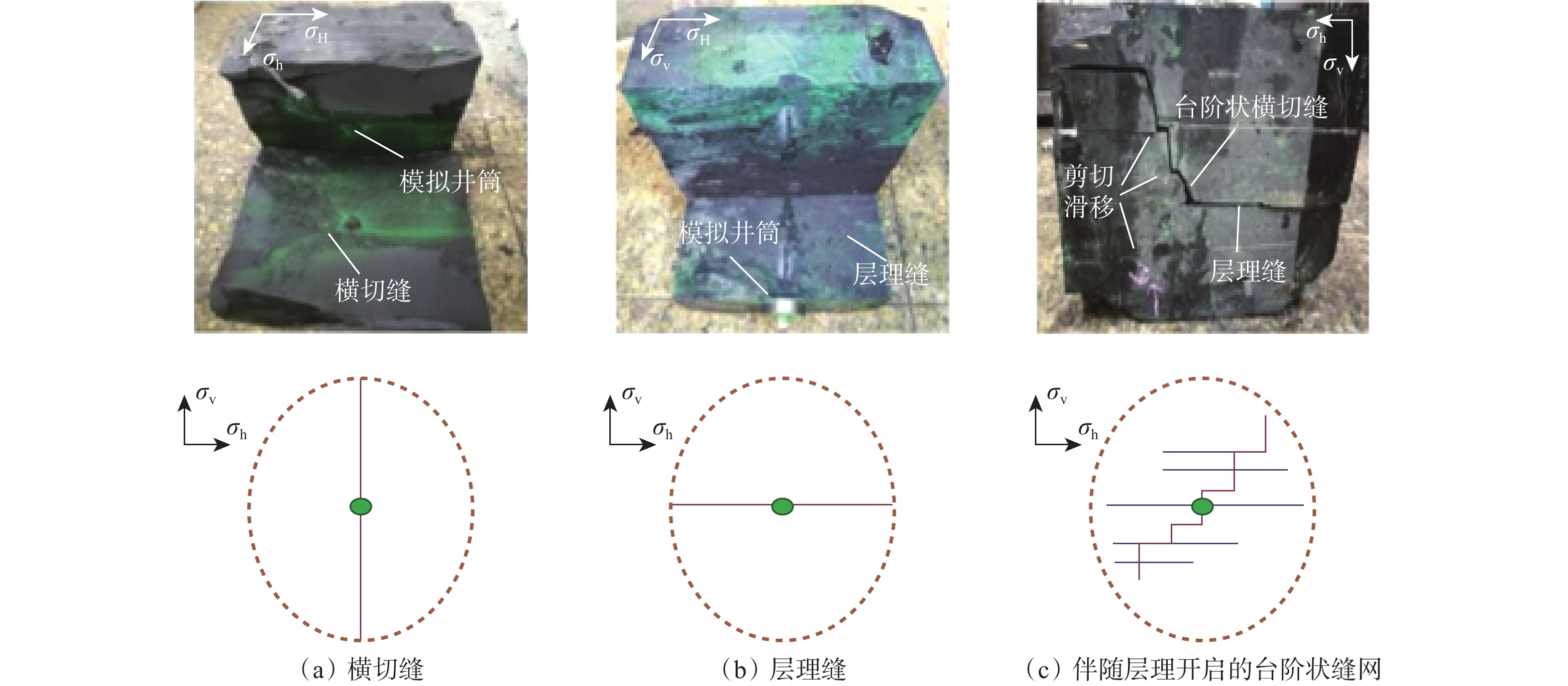
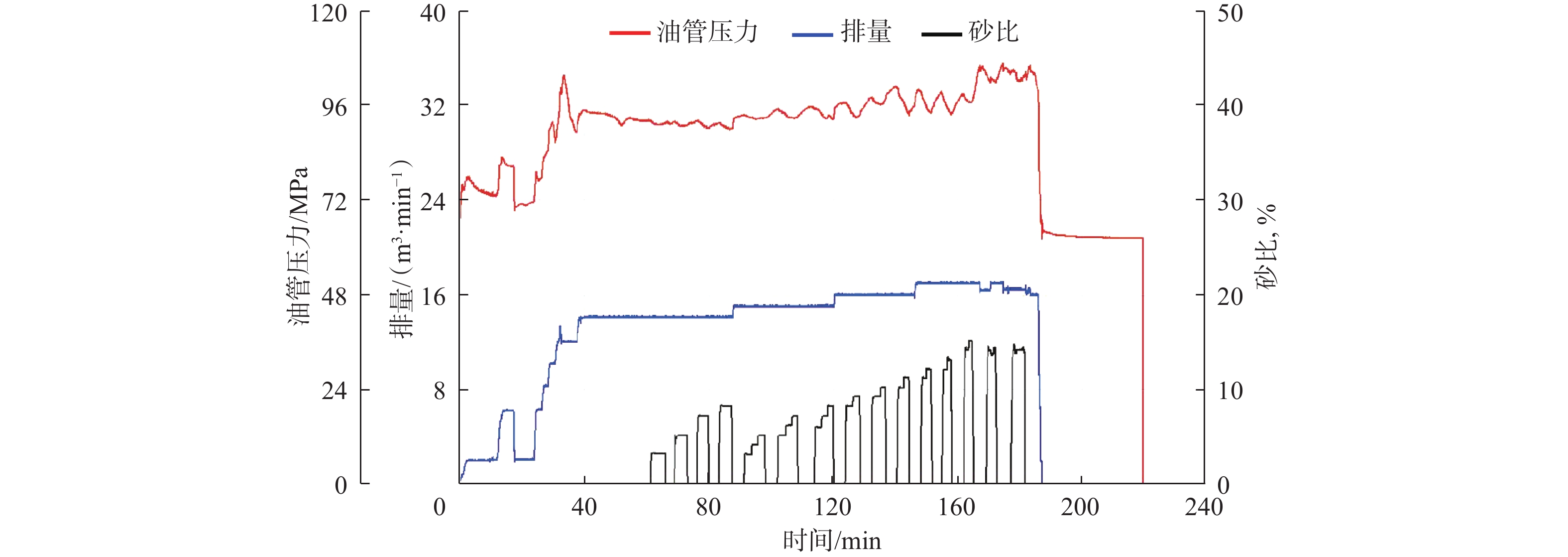
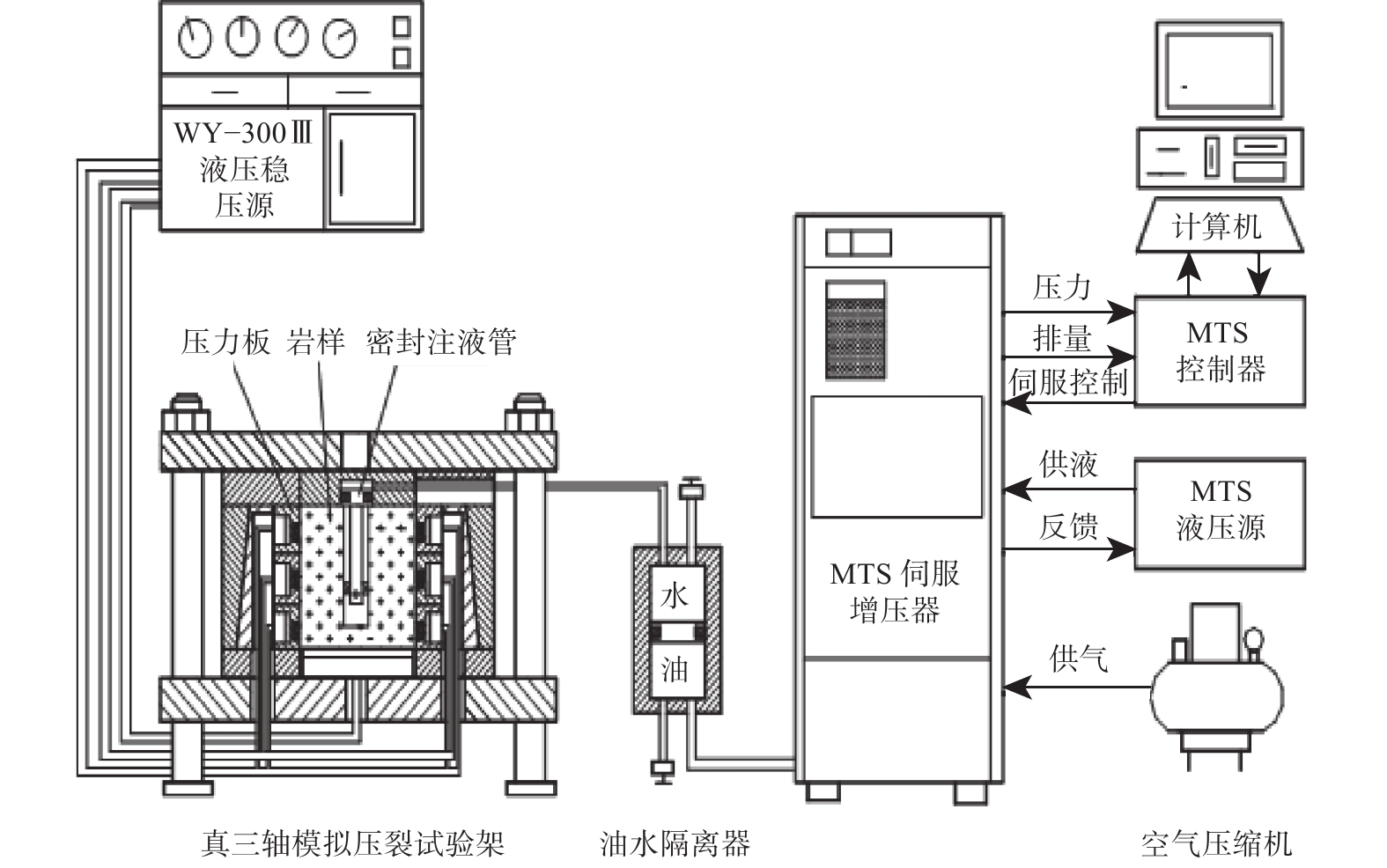
受地质构造、成岩作用等多方面因素影响,深层页岩的层理发育程度、脆性指数、岩石力学特性、最小水平主应力梯度及水平应力差都与中深层页岩有明显差异,使人工裂缝起裂压力更高,裂缝复杂程度更低,从而极大地影响了深层页岩气地层的体积压裂设计和安全施工。为此,利用大尺寸岩样,模拟研究了深层页岩气地层的水平应力差、压裂流体黏度、施工排量等地层和工艺参数及缝内暂堵措施对人工裂缝的起裂与扩展特征的影响规律。研究发现,裂缝起裂与扩展特性受层理胶结强弱、水平应力差及前置液黏度等因素影响较大,压裂裂缝容易沿层理起裂导致早期憋压超压,从而使施工失败,高应力差条件下裂缝扩展形态相对简单,前置中黏压裂液、缝内暂堵等措施有利于裂缝多次破裂、产生次生裂缝使裂缝复杂化。在此基础上,提出了密切割分段、短簇距射孔、组合液体及变排量施工等压裂优化设计方案,现场应用后深层页岩气产量获得了重要突破。
Abstract:Due to geological structure, diagenesis and other factors, deep shale presents different characteristics compared with that in medium-deep formations in terms of bedding development degree, brittleness index, rock mechanical characteristics, in-situ stress gradient and horizontal stress difference. Taken together, theseresult in higher fracture initiation pressure and less complicated fractures geometry and greatly affect fracturing volume design and operation safety in deep shale gas formations. Experimental study on the initiation and expansion characteristics of artificial fractures was conducted. A large cubic rock sample (300 mm×300 mm×300 mm) was used to investigate the influential effects of horizontal stress difference, viscosity of fracturing fluid and pumping flow rate, and the temporary blocking within fractures in hydraulic fracturing. The investigation showed that fracture initiation and propagation are largely affected by those factors as strength of bedding cementation, horizontal stress difference and pad viscosity. Fractures are prone to initiate along bedding planes, resulting in early overpressure and operation failure. Fracture growth pattern is relatively simple under high stress difference, but measures such as using medium-level viscous fracturing fluid to temporarily block flow within fractures can help the generation of multiple fractures and secondary fractures for more complex fracture networks. On this basis, the design optimization of fracturing that incorporates techniques such as densely subdivided stages, short cluster perforations, fluids combination and variable flow rate operation were advanced, and an important breakthrough was made in deep shale gas production after the field application of the optimized design features.
-
Keywords:
- deep shale gas /
- fracture initiation /
- fracture extending /
- simulation test /
- fracturing design /
- filed test
-
-
表 1 裂缝起裂与扩展物理模拟试验方案
Table 1 Physical simulation experiment scheme of fracture initiation and extending
岩心号 水平应力差/
MPa排量/
(mL·min–1)液体黏度/
(mPa·s)备注 1# 6 40 3 2# 40 30 3# 9 40 3 4# 40 30 5# 9 40 3 6# 40 30 7# 6 12 3 100目支撑剂 8# 9 12 3 9# 7 30 3 10# 6 30 3 11# 9 30 30 表 2 川东南地区2口深层页岩气井压裂施工参数与压裂改造效果
Table 2 Parameters and effect of fracturing job of 2 deep shale gas wells in the southeast Sichuan
井号 垂深/m 斜深/m 水平段长/m 簇间距/m 压裂段数 单段砂量/m3 粉陶比例,% 排量/(m3·min–1) 无阻流量/(104 m3·d–1) X1 4 096 5 322 1 103 21.70 17 71.2 20.8 15~17 22.0 X2 4 145 5 685 1 520 22.50 20 78.7 19.4 15~18 18.2 -
[1] 曾义金, 陈作, 卞晓冰. 川东南深层页岩气分段压裂技术的突破与认识[J]. 天然气工业, 2016, 36(1): 61–67. ZENG Yijin, CHEN Zuo, BIAN Xiaobing. Breakthrough and understanding of staged fracturing technology implemented in Southeast Sichuan deep shale gas play[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2016, 36(1): 61–67.
[2] 陈作, 曾义金. 深层页岩气分段压裂技术现状与发展建议[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2016, 44(1): 6–11. CHEN Zuo, ZENG Yijin. Present situations and prospects of multi-stage fracturing technology for deep shale gas development[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2016, 44(1): 6–11.
[3] 王海涛, 蒋廷学, 卞晓冰, 等. 深层页岩压裂工艺优化与现场试验[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2016, 44(2): 76–81. WANG Haitao, JIANG Tingxue, BIAN Xiaobing, et al. Optimization and field application of hydraulic fracturing techniques in deep shale gas reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2016, 44(2): 76–81.
[4] 柳占立, 庄茁, 孟庆国, 等. 页岩气高效开采的力学问题与挑战[J]. 力学学报, 2017, 49(3): 507–516. LIU Zhanli, ZHUANG Zhuo, MENG Qingguo, et al. Problems and challengs of mecanics in shale gas efficient exploition[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2017, 49(3): 507–516.
[5] 张旭, 蒋廷学, 贾长贵, 等. 页岩气储层水力压裂物理模拟试验研究[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2013, 41(2): 70–74. ZHANG Xu, JIANG Tingxue, JIA Changgui, et al. Physical simulation of hydraulic fracturing of shale gas reservoir[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2013, 41(2): 70–74.
[6] 郭印同, 杨春和, 贾长贵, 等. 页岩水力压裂物理模拟与裂缝表征方法研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2014, 33(1): 52–59. GUO Yintong, YANG Chunhe, JIA Changgui, et al. Research on hydraulic fracturing physical simulation of shale and fracture characterization methods[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2014, 33(1): 52–59.
[7] 曹学军,王明贵,康杰,等. 四川盆地威荣区块深层页岩气水平井压裂改造工艺[J]. 天然气工业, 2019, 39(7): 81–87. CAO Xuejun,WANG Minggui,KANG Jie,et al. Fracturing technologies of deep shale gas horizontal wells in the Weirong Block, Southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2019, 39(7): 81–87.
[8] 冯国强,赵立强,卞晓冰,等. 深层页岩气水平井多尺度裂缝压裂技术[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2017, 45(6): 77–82. FENG Guoqiang,ZHAO Liqiang,BIAN Xiaobing,et al. Multi-scale hydraulic fracturing of horizontal well in deep shale gas plays[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2017, 45(6): 77–82.
[9] 路保平. 中国石化页岩气工程技术进步及展望[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2013, 41(5): 1–8. LU Baoping. Sinopec engineering technical advance and its developing tendency in shale gas[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2013, 41(5): 1–8.
[10] 曾义金. 页岩气开发的地质与工程一体化技术[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2014, 42(1): 1–6. ZENG Yijin. Integration technology of geology engineering for shale gas development[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2014, 42(1): 1–6.
[11] 陈作, 薛承瑾, 蒋廷学, 等. 页岩气井体积压裂技术在我国的应用建议[J]. 天然气工业, 2010, 30(10): 30–32. CHEN Zuo, XUE Chengjin, JIANG Tingxue, et al. Proposals for the application of fracturing by stimulated reservoir volume(SRV) in shale gas wells in China[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2010, 30(10): 30–32.
[12] GRIESER W V, TALLEY C A. Post-frac production analysis of horizontal completions in CANA Woodford shale[R].SPE 151223, 2012.
[13] POPE C D, PALISCH T T, LOLON E, et al. Improving stimulation effectiveness: field results in the Haynesville shale[R]. SPE 134165, 2010.
[14] 贾长贵, 路保平, 蒋廷学, 等. DY2HF深层页岩气水平井分段压裂技术[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2014, 42(2): 85–90. JIA Changgui, LU Baoping, JIANG Tingxue, et al. Multi-stage horizontal well fracturing technology in deep shale gas well DY2HF[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2014, 42(2): 85–90.
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 任向海,李楠,李晶辉,杨志,彭振华,丁雯. 大排量深抽减载抽油泵研制. 重庆科技学院学报(自然科学版). 2024(02): 116-120 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 秦飞,王禧文,丁保东,曹畅,高晨豪,郭继香. 塔河油田稠油开发经济效益评价. 天然气与石油. 2023(04): 144-150 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘玉国,杨利萍,彭振华,曹畅,丁保东. 塔河油田抽油机效能提升技术研究与应用. 石油石化节能与计量. 2023(10): 1-5 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 尹丹,罗日蕾. 空心抽油杆杆式电加热技术在高含蜡井的应用. 石油石化节能. 2022(07): 33-36 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 杜坤,王鹏,李杨,蒋海岩,白玉. 塔河油田典型深抽工艺研究. 辽宁石油化工大学学报. 2019(05): 45-52 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)



 下载:
下载: