Research and Field Test on Energy Storage Fracturing Mechanism of Horizontal Wells in Ultra-Low Permeability Reservoirs
-
摘要:
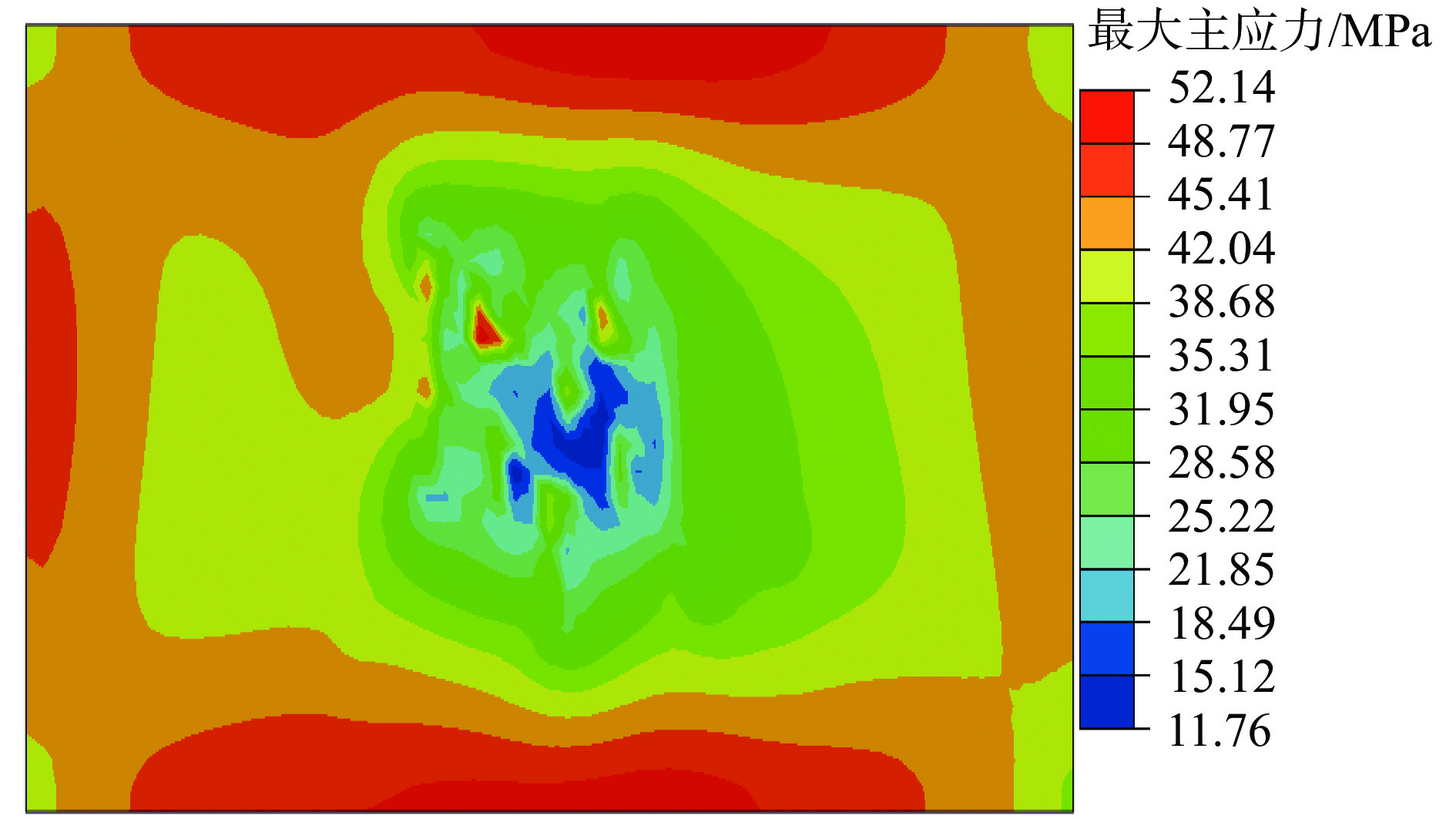
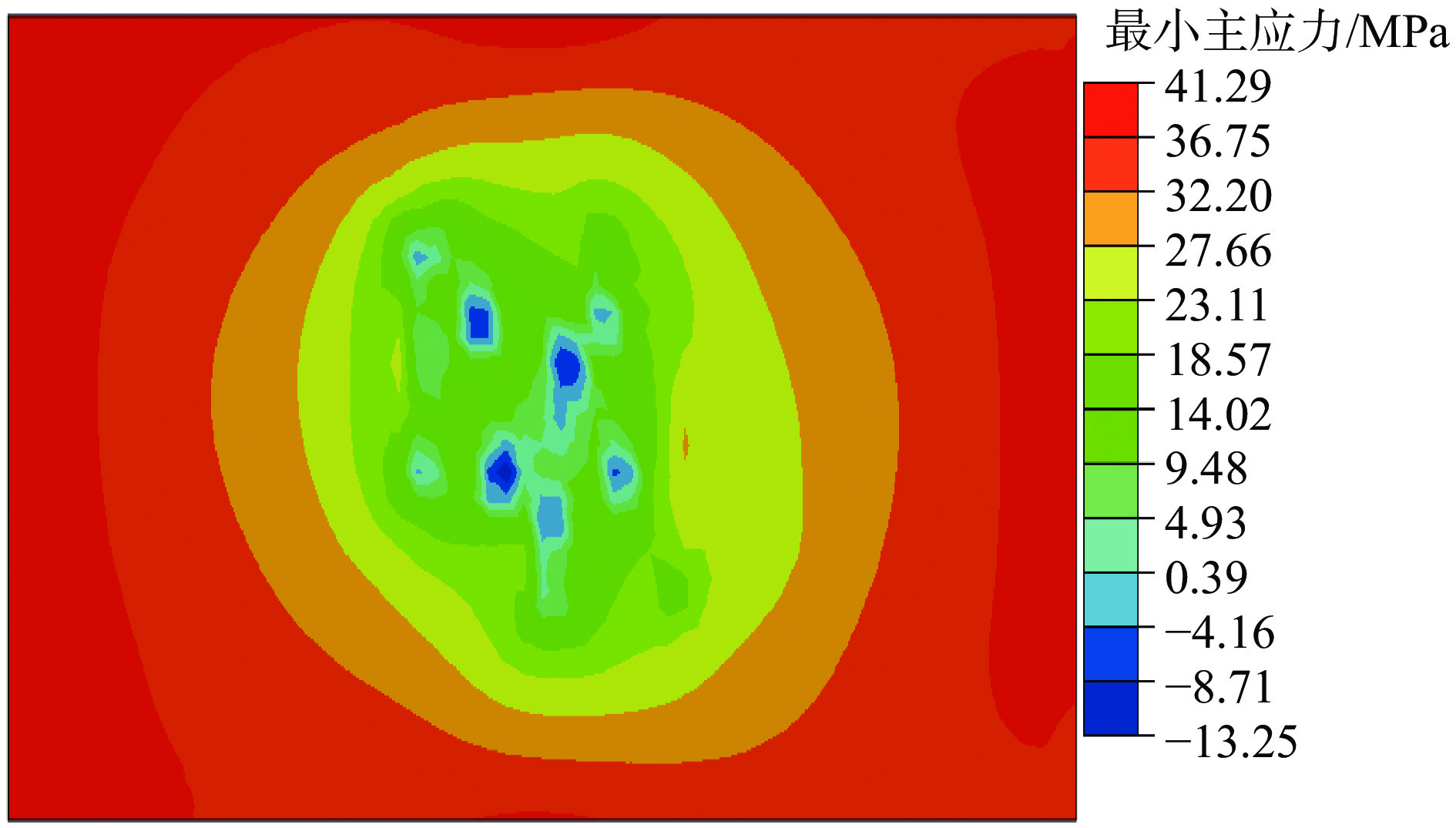
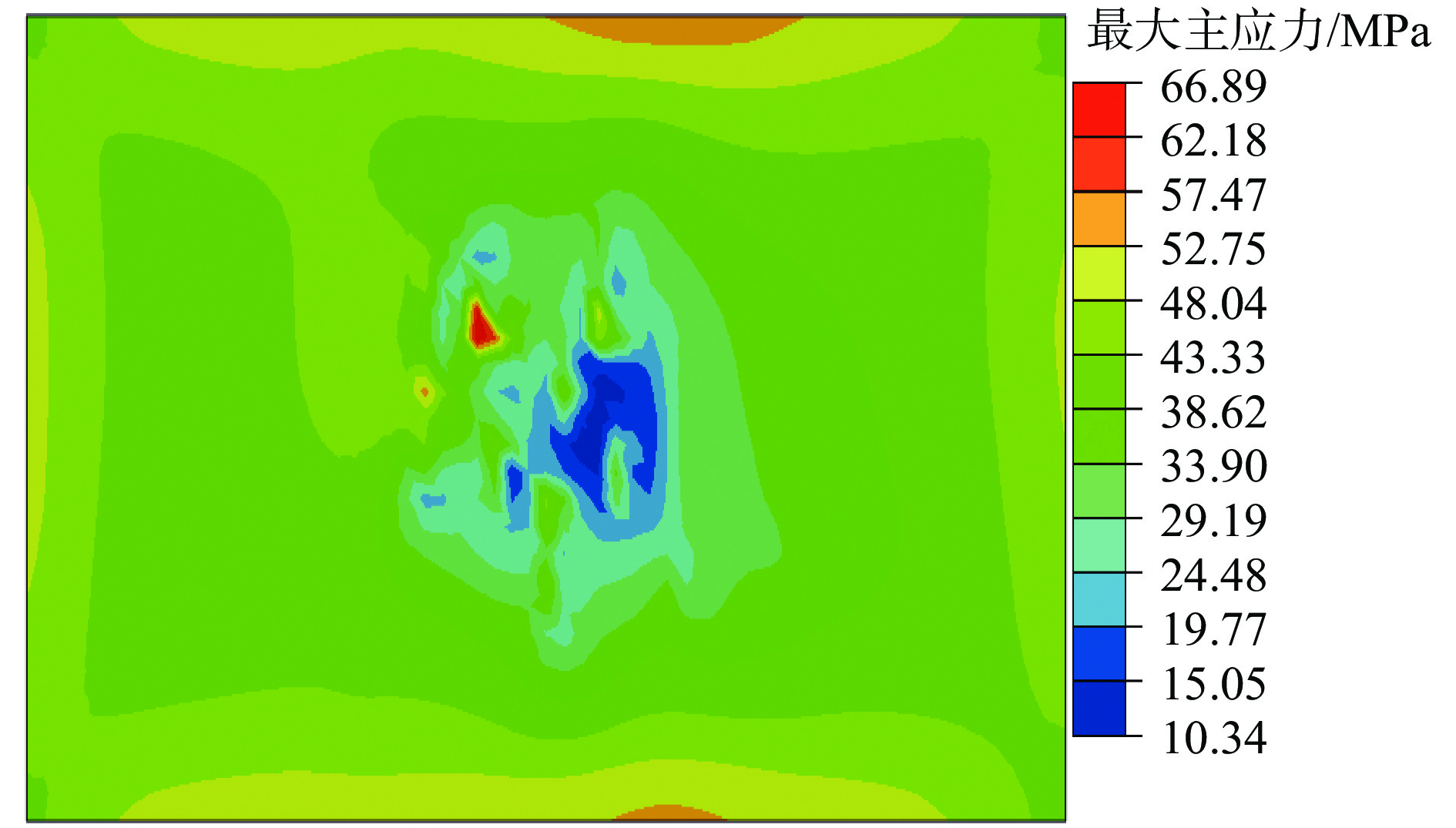
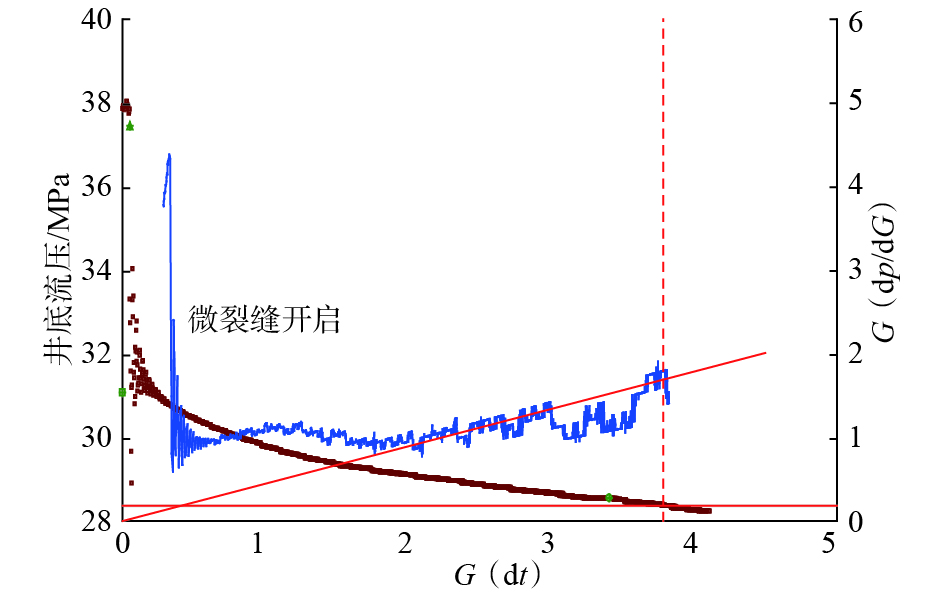
针对超低渗透油藏部分水平井生产一段时间后,出现单井产能降低的问题,开展了超低渗透油藏水平井储能压裂机理研究与现场试验。根据岩石破坏机理,进行了室内储能压裂模拟试验,利用声发射信号检测储能压裂对试件内部的破坏情况,并采用有限元法计算近井地带地应力变化情况。试验及数值模拟结果表明:在高孔隙压力作用下,天然裂缝面错动痕迹明显,憋压过程中试件内部产生了大量微破裂;压裂后焖井过程中,一段时间内地应力场受到影响。研究表明,压裂前注入适量的驱油压裂液,压裂后焖井进行渗吸扩散,可以有效补充地层能量,同时结合优化后的体积压裂重复改造技术,能够进一步增大压裂改造体积和裂缝复杂程度。该技术对能量亏空、裂缝闭合导致的低产水平井提高产量具有较好的适应性,可为同类超低渗透油藏重复压裂提供技术参考。
Abstract:After the production of some horizontal wells in ultra-low permeability reservoirs for a period of time, the production capacity from those wells start to decrease. A research and test on energy storage fracturing mechanism of horizontal wells in ultra-low permeability reservoir have been carried out. According to the failure mechanism of the rock, the laboratory simulated energy storage fracturing experiment was performed, in which the failure of the rock sample within the specimen was detected by acoustic emission. In addition, the stresses change near a wellbore was calculated through finite element method. Experimental and numerical simulation results showed that natural fracture surface has obvious dislocation traces, and a large number of microfractures are produced in the specimen during building up of high pore pressure. During well soaking process after fracturing, in-situ stress field is disturbed for a period of time. The research results showed that the injection of appropriate amount of oil displacement fracturing fluid before fracturing treatment and the imbibition and diffusion by well soaking after fracturing could effectively provide supplement energy in the formation. At the same time, the treated volume and complexity of fractures could be further increased when combined with the optimized volume refracturing. This technology has a good effect in increasing the production of low production horizontal wells due to energy deficit and fracture closure, and it has some reference value for the same ultra-low permeability reservoirs.
-
-
表 1 储能压裂前后各参数的变化情况
Table 1 Changes of parameters before and after energy storage fracturing
条件 渗透率/mD 孔隙度,% 单井产量/(t∙d–1) 采收率,% 压裂前 0.30 11.50 1.18 6.77 压裂后 27.80 19.50 4.60 17.00 -
[1] 张红妮,陈井亭. 低渗透油田蓄能整体压裂技术研究:以吉林油田外围井区为例[J]. 非常规油气, 2015, 2(5): 55–60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-8471.2015.05.010 ZHANG Hongni, CHEN Jingting. Insights into energy storage bulk fracturing technology for low-permeability oilfields: a case study of peripheral wellblock of Jilin Oilfield[J]. Unconventional Oil & Gas, 2015, 2(5): 55–60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-8471.2015.05.010
[2] 修书志,贾元钊,张斌,等. 巨厚低渗砂砾岩储层控缝高蓄能缝网压裂技术研究及应用[J]. 中外能源, 2016, 21(10): 58–63. XIU Shuzhi, JIA Yuanzhao, ZHANG Bin, et al. Research and application of height control-energizing-network fracturing technology in extremely-thick low permeability glutenite reservoirs[J]. Sino-Global Energy, 2016, 21(10): 58–63.
[3] 王益维,张士诚,李宗田,等. 深层低渗透储层压裂裂缝处理技术[J]. 特种油气藏, 2010, 17(6): 87–89. WANG Yiwei, ZHANG Shicheng, LI Zongtian, et al. Induced fracture treating technology for deep low permeability reservoirs[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2010, 17(6): 87–89.
[4] 吴忠宝,李莉,阎逸群. 超低渗油藏体积压裂与渗吸采油开发新模式[J]. 断块油气田, 2019, 26(4): 491–494. WU Zhongbao, LI Li, YAN Yiqun. New development pattern of network fracturing and imbibition oil recovery for super-low permeability oil reservoirs[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2019, 26(4): 491–494.
[5] 刘雄,王磊,王方,等. 致密油藏水平井体积压裂产能影响因素分析[J]. 特种油气藏, 2016, 23(2): 85–88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2016.02.020 LIU Xiong, WANG Lei, WANG Fang, et al. Sensitivity analysis of volume-fractured horizontal well productivity in tight reservoir[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2016, 23(2): 85–88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2016.02.020
[6] 王文东,赵广渊,苏玉亮,等. 致密油藏体积压裂技术应用[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2013, 34(3): 345–348. WANG Wendong, ZHAO Guangyuan, SU Yuliang, et al. Application of network fracturing technology to tight oil reservoirs[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2013, 34(3): 345–348.
[7] 李川,张翔,杜现飞,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地致密油应力循环压裂技术[J]. 石油钻采工艺, 2018, 40(4): 494–498. LI Chuan, ZHANG Xiang, DU Xianfei, et al. Stress-cycle fracturing technology suitable for tight oil reservoirs in the Ordos Basin[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2018, 40(4): 494–498.
[8] 何海波. 致密油水平井缝网增能重复压裂技术实践[J]. 特种油气藏, 2018, 25(4): 170–174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2018.04.034 He Haibo. Practice of re-fracturing with network energization for horizontal well in tight oil reservoir[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2018, 25(4): 170–174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2018.04.034
[9] 李宪文,刘顺,陈强,等. 考虑复杂裂缝网络的致密油藏水平井体积压裂改造效果评价[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2019, 47(6): 73–82. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2019126 LI Xianwen, LIU Shun, CHEN Qiang, et al. An evaluation of the stimulation effect of horizontal well volumetric fracturing in tight reservoirs with complex fracture networks[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2019, 47(6): 73–82. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2019126
[10] 雷林,张龙胜,熊炜,等. 武隆区块常压页岩气水平井分段压裂技术[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2019, 47(1): 76–82. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2018129 LEI Lin, ZHANG Longsheng, XIONG Wei, et al. Multi-stage fracturing technology of normally pressured shale gas in horizontal wells in the Wulong Block[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2019, 47(1): 76–82. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2018129
[11] 杨同玉,魏辽,冯丽莹,等. 水平井趾端压裂关键工具设计与试验[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2018, 46(4): 54–58. YANG Tongyu, WEI Liao, FENG Liying, et al. Design and test of key tools in horizontal well toe-end fracturing[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2018, 46(4): 54–58.
[12] 田磊,何建军,杨振周,等. 二氧化碳蓄能压裂技术在吉林油田的应用[J]. 钻井液与完井液, 2015, 32(6): 78–80, 84. TIAN Lei, HE Jianjun, YANG Zhenzhou, et al. Application of CO2 energized fracturing fluid technology in Jilin Oilfield[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2015, 32(6): 78–80, 84.




 下载:
下载: