The Establishment and Correction of a Prediction Model for the Repose Angle of a Cuttings Bed in Highly Deviated Well Interval
-
摘要:
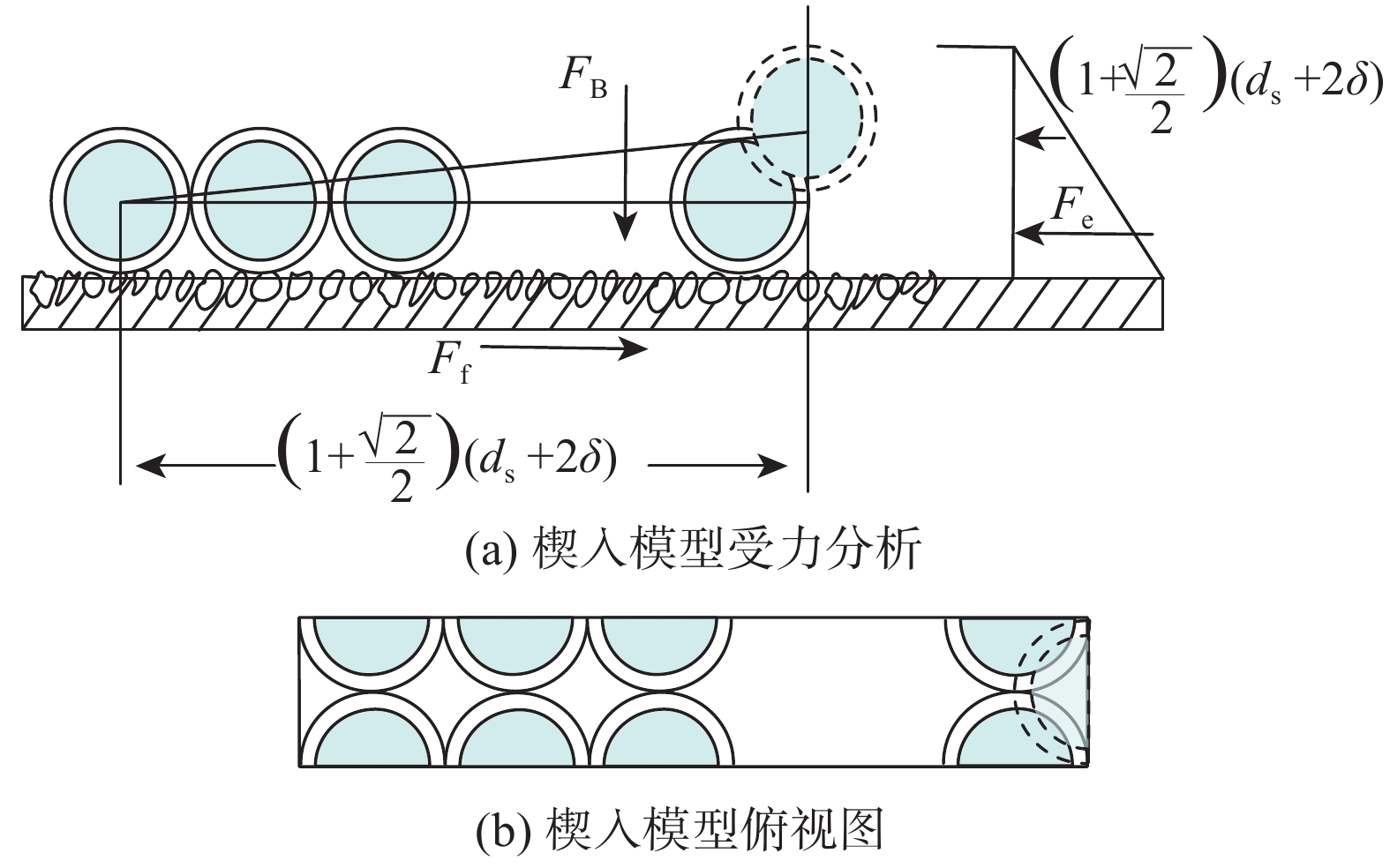
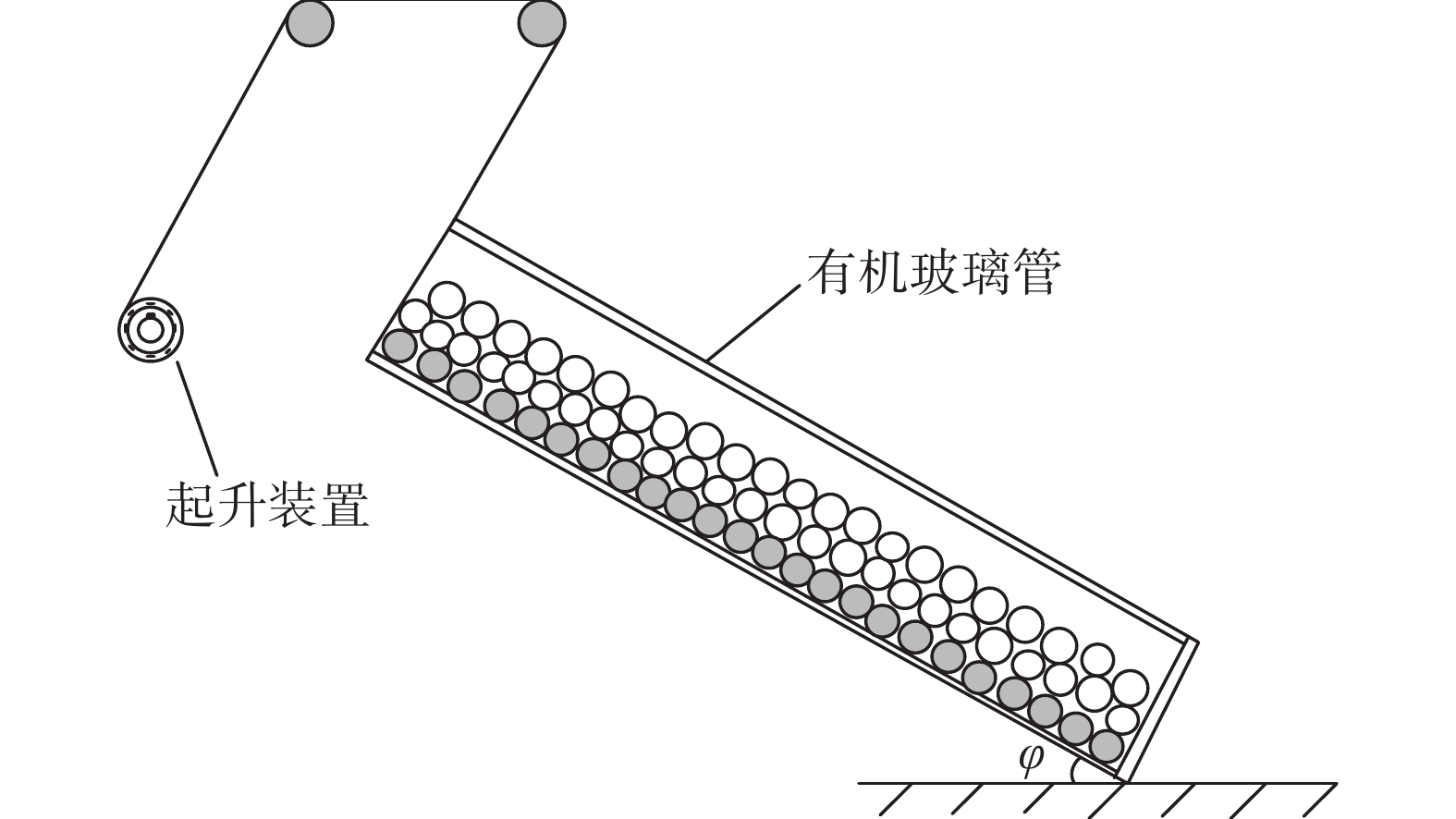
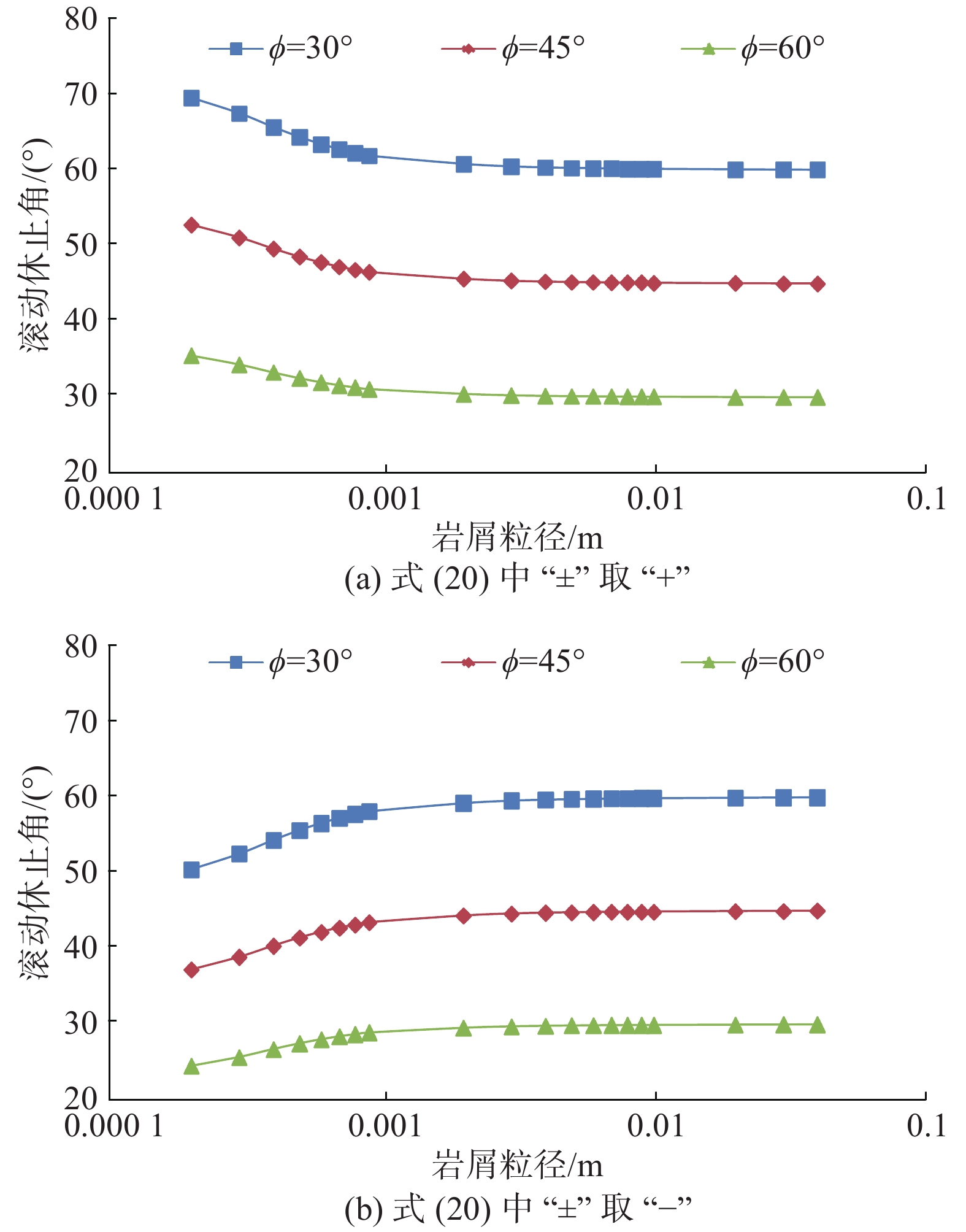
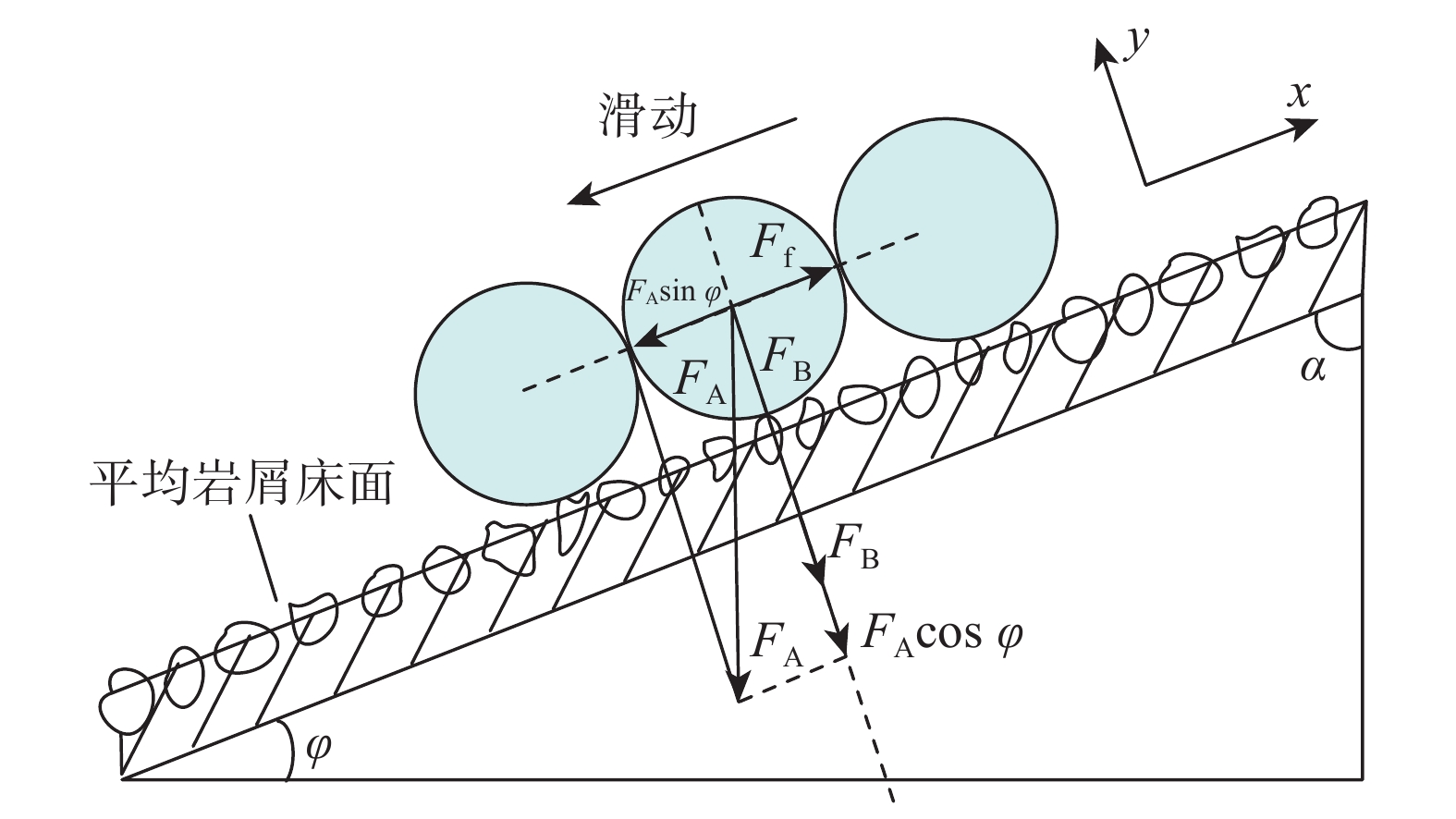
大斜度井段岩屑床容易失稳或整体下滑迅速堆积成砂塞,而岩屑床失稳位置不好预测。为解决该问题,分析了岩屑床在大斜度井段的受力情况,建立了岩屑床休止角预测模型。基于楔入堆积模型,通过分析平均岩屑床面颗粒滚动与滑动时的受力情况,结合泥沙沉积学中的容重概念,建立了岩屑床休止角预测模型;同时,通过岩屑在不同浓度聚丙烯酰胺聚合物(PAM)溶液中的休止角测量试验,对该预测模型进行了修正。不同浓度聚丙烯酰胺聚合物溶液中岩屑床休止角的试验值分别为26.9°、27.5°、29.7°和30.2°,由滑动休止角预测模型得到滑动休止角的理论值分别为24.2°、25.8°、27.1°和28.5°,而滚动休止角理论值也不超过30°,理论值相较于试验值偏于保守,但按理论值可保证钻井作业安全。研究认为,建立和修正后的大斜度井段岩屑床休止角预测模型,其预测结果较为可靠,可在确定井眼清洁工具有效位置、判断井下故障位置时应用和参考。
Abstract:The cuttings bed in the highly-deviated well interval of a horizontal well can easily cause instability or overall sliding and successive rapid sand plug accumulation, while the instability section of cuttings bed is difficult to predict. In order to solve this problem, the force balance of the cuttings bed in a highly-deviated well interval was analyzed, and the prediction method for the repose angle of cuttings bed was studied. Based on the wedging accumulation model in sedimentology, the prediction model for the repose angle of cuttings bed was established by analyzing the force conditions of particle rolling and sliding of the average cuttings bed surface and combining it with the bulk density concept. At the same time, the prediction model was corrected accordingly by measuring the repose angle of cuttings bed in polyacrylamide polymer (PAM) solutions with various concentrations. The test values of the repose angles in those polyacrylamide polymer solutions were 26.9°, 27.5°, 29.7° and 30.2°, respectively, and the theoretical values obtained from the sliding repose angle prediction model were 24.2°, 25.8°, 27.1° and 28.5°, respectively. The theoretical value is more conservative compared with the tested one, whereas the theoretical value can ensure safe drilling. According to this research, the established and corrected prediction model for the repose angle of cuttings bed in a highly-deviated well interval can render reliable prediction results, and it could be applied and provide references in determining the effective section of the wellbore cleaning tools and the location of downhole failures.
-
-
表 1 岩屑床休止角测量结果
Table 1 Results of the cuttings bed repose angle measurement
PAM质量浓度/(mg·L–1) 休止角/(°) 休止井斜角/(°) PAM质量浓度/(mg·L–1) 休止角/(°) 休止井斜角/(°) 320 26.5 63.5 700 27.9 62.1 320 27.7 62.3 700 28.0 62.0 320 25.5 64.5 700 30.2 59.8 320 29.6 60.4 700 30.0 60.0 320 23.9 66.1 700 30.8 59.2 320 28.2 61.8 700 31.5 58.5 550 24.2 65.8 800 31.0 59.0 550 30.2 59.8 800 27.0 63.0 550 26.2 63.8 800 32.0 58.0 550 27.9 62.1 800 28.5 61.5 550 27.6 62.4 800 31.7 58.3 550 28.8 61.2 800 30.8 59.2 -
[1] 孙开畅,刘林锋,明华军,等. 不同粒径及级配对碎石料休止角影响的实验研究[J]. 长江科学学院院报, 2016, 33(08): 91–95. SUN Kaichang, LIU Linfeng, MING Huajun, et al. Experimental research on the influence of particle size and gradation on repose angle of rockfill[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2016, 33(08): 91–95.
[2] 王成华,张小刚,阙云,等. 粒状碎屑溜砂坡的形成和基本特征研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2007, 28(1): 29–35. WANG Chenghua, ZHANG Xiaogang, QUE Yun, et al. Formation and basic characteristics of sand-sliding slope composed of granular clasts[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2007, 28(1): 29–35.
[3] 王成华,阙云,李新坡,等. 粒状碎屑溜砂坡运动特征与动力数值分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2007, 28(2): 219–223. WANG Chenghua, QUE Yun, LI Xinpo, et al. Movement characteristics and dynamical numerical analysis of sand-sliding slope composed by granular[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2007, 28(2): 219–223.
[4] 吴国雄,曾榕彬,王成华,等. 溜砂坡的形成诱发因素及失稳破坏条件[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2006, 27(5): 7–12. WU Guoxiong, ZENG Rongbin, WANG Chenghua, et al. The inducing factors and the collapse conditions of sand-sliding slope[J]. China Railway Science, 2006, 27(5): 7–12.
[5] 孟震,杨文俊. 泥沙颗粒水下休止角与内摩擦角差异化初步探索[J]. 泥沙研究, 2012(4): 76–80. MENG Zhen, YANG Wenjun. Preliminary exploration of difference between submarine angle of repose and internal friction angle of sediment particles[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2012(4): 76–80.
[6] 孟震,杨文俊. 泥沙颗粒休止角与表层沙摩擦角研究进展[J]. 水力发电学报, 2015, 34(10): 117–129. MENG Zhen, YANG Wenjun. Angle of repose and angle of surface friction of sediment particles[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engi-neering, 2015, 34(10): 117–129.
[7] 孟震,王浩,杨文俊. 无黏性泥沙休止角与表层沙摩擦角试验[J]. 天津大学学报(自然科学与工程技术版), 2015, 48(11): 1014–1022. MENG Zhen, WANG Hao, YANG Wenjun. Experiment on angle of repose and angle of surface friction of cohesionless sediment[J]. Journal of Tianjin University (Science and Technology), 2015, 48(11): 1014–1022.
[8] 熊绍隆. 深水孔口前冲刷漏斗形态研究[J]. 西北水电, 1983(4): 10–21. XIONG Shaolong. Study on shape of scouring funnel in front of deep water hole[J]. Northwest Hydropower, 1983(4): 10–21.
[9] 詹义正,谢葆玲. 散体泥沙的水下休止角[J]. 水电能源科学, 1996, 14(1): 56–59. ZHAN Yizheng, XIE Baoling. Under water angle of rest for non-cohesive sediment[J]. Water Resources and Power, 1996, 14(1): 56–59.
[10] 黄长伟,詹义正,卢金友. 黏性~散体均匀沙的动水休止角公式[J]. 广东水利水电, 2008(6): 1–3, 12. HUANG Changwei, ZHAN Yizheng, LU Jinyou. Movable water repose angle formula of uniform sand with viscosity[J]. Guangdong Water Resources and Hydropower, 2008(6): 1–3, 12.
[11] 张红武,汪家寅. 沙石及模型沙水下休止角试验研究[J]. 泥沙研究, 1989(3): 90–96. ZHANG Hongwu, WANG Jiayin. Experimental study on underwater angle of repose of sandstone and model sand[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 1989(3): 90–96.
[12] 金腊华,石秀清. 试论模型沙的水下休止角[J]. 泥沙研究, 1990(3): 87–93. JIN Lahua, SHI Xiuqing. Discussion on underwater repose angle of model sand[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 1990(3): 87–93.
[13] 王延贵,王兆印,曾庆华,等. 模型沙物理特性的试验研究及相似分析[J]. 泥沙研究, 1992(3): 74–83. WANG Yangui, WANG Zhaoyin, ZENG Qinghua, et al. Experi-mental study and similarity analysis of physical characteristics of model sand[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 1992(3): 74–83.
[14] 漆海峰,郭晓镭,陆海峰,等. 煤粉的流动性测试及评价方法[J]. 化工学报, 2012, 63(2): 433–440. QI Haifeng, GUO Xiaolei, LU Haifeng, et al. Measurement of flow-ability of coal powders and research methods[J]. CIESC Journal, 2012, 63(2): 433–440.
[15] 王树传,高文元,屈有元. 含水量和粒度对粉粒状物料流动性的影响[J]. 大连轻工业学院学报, 1996, 15(2): 29–32. WANG Shuchuan, GAO Wenyuan, QU Youyuan. Influence of water content and grain on fluidity of powdery grained material[J]. Journal of Dalian Institute of Light Industry, 1996, 15(2): 29–32.
[16] 陈珊.变化水环境中散体沙休止角的初步研究[D].武汉: 武汉大学, 2014. CHEN Shan. Preliminary research on repose angle of granular sand in changing water environment[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2014.
[17] 唐存本. 泥沙起动规律[J]. 水利学报, 1963(2): 1–12. TANG Cunben. A law for incipient of sediment[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 1963(2): 1–12.
[18] 詹义正, 黄卫东, 陈立, 等.均匀黏性–散体泥沙的统一水下休止角公式[C]// 黄河水利科学研究院.第六届全国泥沙基本理论研究学术讨论会论文集.郑州: 黄河水利出版社, 2005: 191-197. ZHAN Yizheng, HUANG Weidong, CHEN Li, et al. Unified underwater angle of repose formula for uniform viscosity-discrete sediment[C]//Yellow River Institute of Hydraulic Research. Proceedings of the 6th national seminar on sedimentary basic theoretical research. Zhengzhou: The Yellow River Water Conservancy Press, 2005: 191-197.
[19] 韩其为,王玉成,向熙珑. 淤积物的初期干容重[J]. 泥沙研究, 1981(1): 3–15. HAN Qiwei, WANG Yucheng, XIANG Xilong. Initial dry weight of sludge[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 1981(1): 3–15.
[20] 武汉水利电力学院河流泥沙工程学教研室.河流泥沙工程学(上册)[M].北京: 水利电力出版社, 1980: 15. River Sediment Engineering Teaching and Research Section of Wuhan University of Hydraulic and Electric Engineering. River sediment engineering (Volume Ⅰ)[M]. Beijing: Water Resources and Electric Power Press, 1980: 15.
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 董添奇,杨旭辉. 近钻头钻压和扭矩的高精度温度补偿方法. 石油机械. 2024(04): 71-79 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 孙养清,易先中,万继方,易军,吴霁薇,刁斌斌,陈志湘. 机械式复合冲击器的工作特性分析. 石油机械. 2024(06): 29-37+108 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 白彬珍,曾义金,芦鑫,张进双,陶亮. 钻头破岩能量与岩石自适应匹配提速技术. 石油钻探技术. 2023(03): 30-36 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 罗杰,柳军,李强. 深井钻柱纵-扭耦合下的黏滑振动特性分析. 石油机械. 2023(08): 139-147 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 汪伟,陈杰,张鹏翔,柳贡慧,李军,查春青. 旋转配流式扭转冲击钻具设计与分析. 断块油气田. 2023(06): 1047-1052 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 兰永飞,韩玉香,陈明勇,王虎. 扭力冲击器-螺杆复合钻进工艺应用实践. 钻探工程. 2023(S1): 399-404 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)



 下载:
下载: